300-115 Practice Exam Free – 50 Questions to Simulate the Real Exam
Are you getting ready for the 300-115 certification? Take your preparation to the next level with our 300-115 Practice Exam Free – a carefully designed set of 50 realistic exam-style questions to help you evaluate your knowledge and boost your confidence.
Using a 300-115 practice exam free is one of the best ways to:
- Experience the format and difficulty of the real exam
- Identify your strengths and focus on weak areas
- Improve your test-taking speed and accuracy
Below, you will find 50 realistic 300-115 practice exam free questions covering key exam topics. Each question reflects the structure and challenge of the actual exam.
Which virtual router states are defined in the GLBP protocol? (Choose two.)
A. Backup gateway
B. Primary gateway
C. Active virtual gateway
D. Active secondary gateway
E. Active virtual forwarder
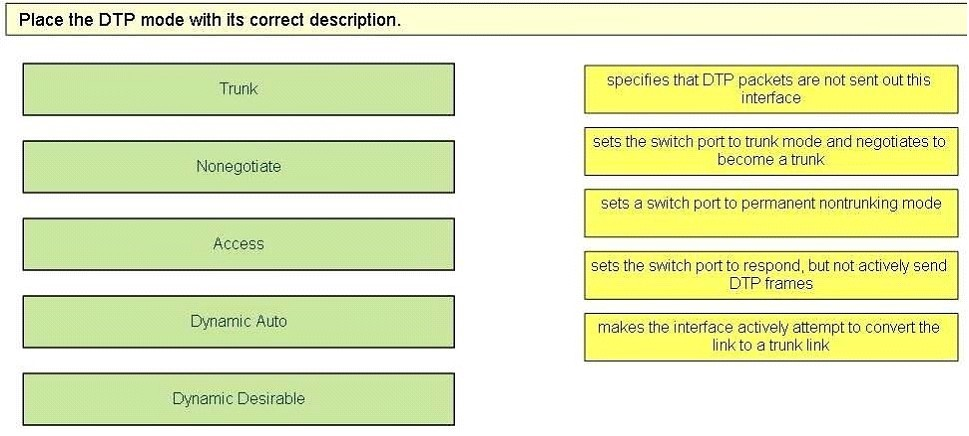
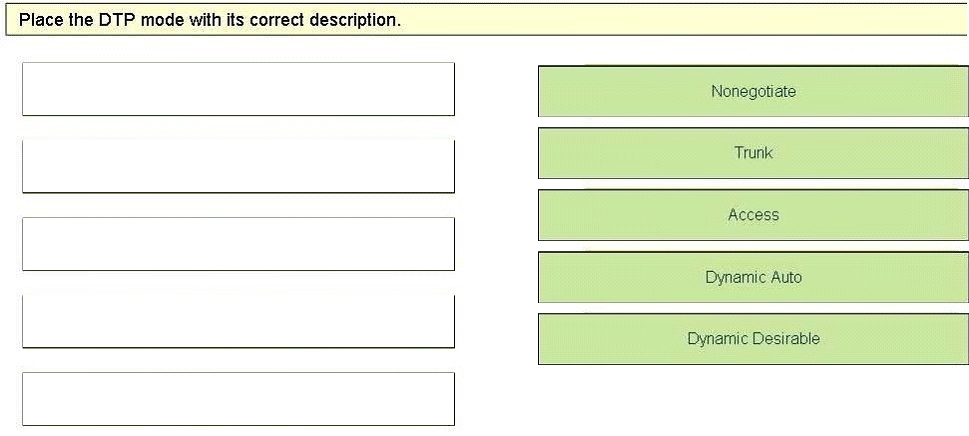
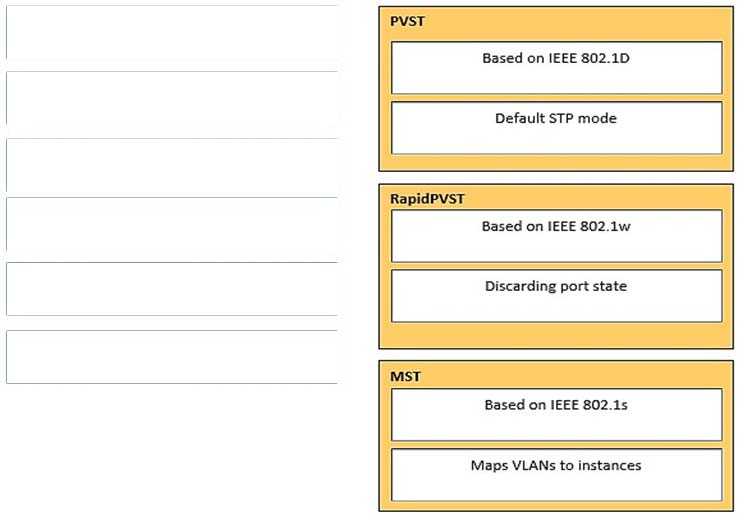
DRAG DROP - Drag and Drop - LLDP-TLV (Concepts Only) ✑ LLDP-MED Capabilities TLV ✑ Network Policy TLV Select and Place: Select and Place:
What protocol allows for centralized management of multiple wireless access points?
A. WPA
B. WEP
C. ad hoc
D. LWAPP D
Which two restrictions of the port security feature are true? (Choose two.)
A. Static port MAC address assignments are not supported.
B. It is not supported on PVLAN ports.
C. It is not supported on EtherChannel port-channel interfaces.
D. A single device can learn a maximum of three sticky MAC addresses.
E. It is supported on destination SPAN ports.
You have been assigned to create a plan to implement HSRP on the router connecting your company's network to the Internet. The router should be the active router in the HSRP group. On the active router, the following conditions should be met: Enable preemption with no delay - Set Hello timer to 10 seconds and hold time to 25 seconds Set the priority to 150 - Which of the following commands should be included in the plan to meet the given requirements? (Choose all that apply.)
A. standby 1 preempt delay minimum 10
B. standby 1 preempt
C. standby 1 priority 150
D. standby 1 timers 10 25
E. standby 1 timers 25 10
F. standby track interface S0/1
What is the value of the TPID/tag protocol identifier in dot1q?
A. 0x8100
B. 0x8a88
C. 0x8b45
D. 0x8200
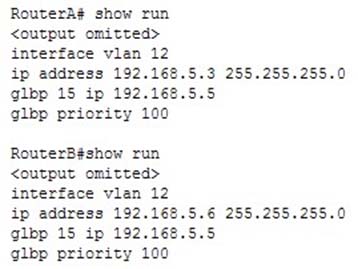
Which three authentication methods does GLBP use? (Choose three.)
A. Single Sign On authentication
B. MD5 authentication
C. No authentication
D. Plain text authentication
E. DCSP authentication
F. 6-to-4 authentication
Which two of the following procedures can be performed on a VTP server to reset the VTP configuration revision number to 0? (Choose two.)
A. Disable VTP pruning, then enable VTP pruning.
B. Change the VTP mode to client, and then back to server mode.
C. Change the VTP mode to transparent, then back to server mode.
D. Change the VTP domain name to a non-existent domain name, and then back to the correct domain name.
Refer to the exhibit.What is the result of the configuration?
A. The EtherChannels would not form because the load-balancing method must match on the devices.
B. The EtherChannels would form and function properly even though the load-balancing and EtherChannel modes do not match.
C. The EtherChannels would form, but network loops would occur because the load-balancing methods do not match.
D. The EtherChannels would form and both devices would use the dst-ip load-balancing method because Switch1 is configured with EtherChannel mode active.
A network is running VTPv2. After verifying all VTP settings, the network engineer notices that the new switch is not receiving the list of VLANs from the server. Which action resolves this problem?
A. Reload the new switch.
B. Restart the VTP process on the new switch.
C. Reload the VTP server.
D. Verify connected trunk ports.
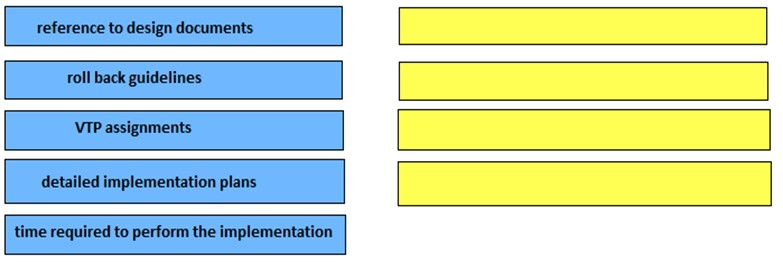
DRAG DROP - Select and Place: Drag the choices on the left to the boxes on the right that should be included when creating an implementation plan. Not all choices will be used. Select and Place:
Which option lists the information that is contained in a Cisco Discovery Protocol advertisement?
A. native VLAN IDs, port-duplex, hardware platform
B. native VLAN IDs, port-duplex, memory errors
C. native VLAN IDs, memory errors, hardware platform
D. port-duplex, hardware platform, memory errors
Which two settings are the parts of a Default LLDP configuration? (Choose two.)
A. The LLDP hold time is 60 seconds.
B. The LLDP global state is Disabled.
C. The LLDP reinitialisation delay is 5 seconds.
D. The LLDP interface state is Enabled.
E. The LLDP timer is 60 seconds.
What command would be used to verify trusted DHCP ports?
A. show mls qos
B. show ip dhcp snooping
C. show ip trust
D. show ip arp trust
Your customer has asked you to come in and verify the operation of routers R1 and R2 which are configured to use HSRP. They have questions about how these two devices will perform in the event of a device failure.What percentage of the outgoing traffic from the 172.16.10.0/24 subnet is being forwarded through R1?
A. R1-0%
B. R1-50 %, R2-50%
C. R2-100%
D. R1-100%
Which two statements about SPAN source and destination ports during an active session are true? (Choose two.)
A. The source port can be only an Ethernet physical port.
B. The source port can be monitored in multiple SPAN sessions.
C. The destination port can be destination in multiple SPAN sessions.
D. The destination port does not participate in STP.
E. You can mix individual source ports and source VLANs within a single session.
Your customer has asked you to come in and verify the operation of routers R1 and R2 which are configured to use HSRP. They have questions about how these two devices will perform in the event of a device failure.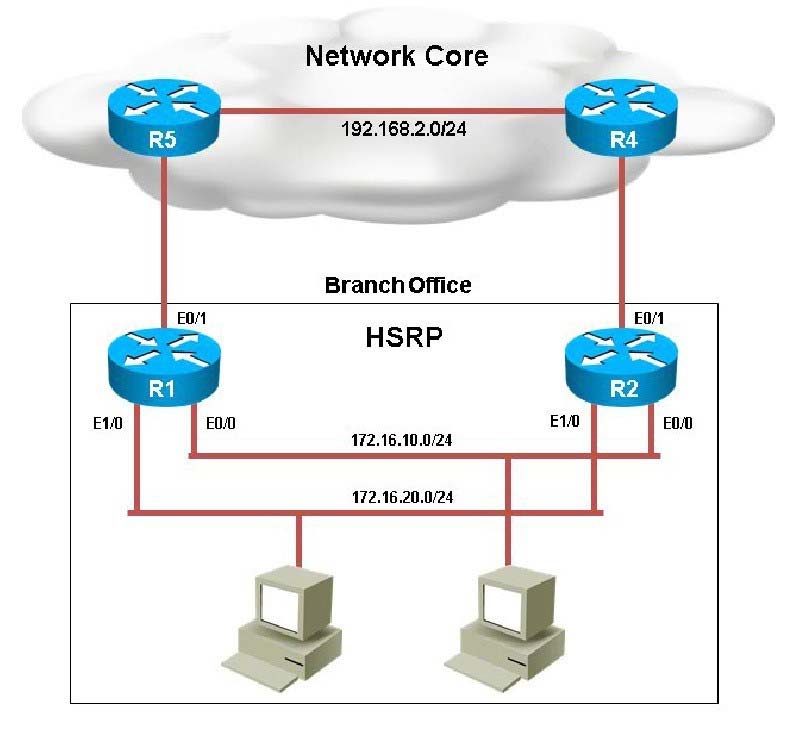

What is the virtual mac-address of HSRP group 1?
A. 0000.0c07.ac02
B. 4000.0000.0010
C. 0000.0c07.ac01
D. 4000.0000.ac01
E. 4000.0000.ac02
F. 0000.0c07.0010
Drag and Drop Question - Select and Place:
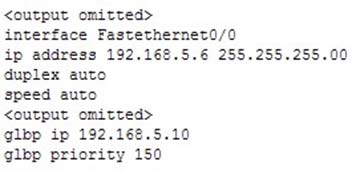
How many Active Virtual Gateways (AVG) can be used in a GLBP protocol?
A. Only one AVG can be elected on a switch
B. Two AVG could be elected on a switch
C. Two AVG just could be elected in GLBP v2
D. GLBP supports 8 AVGs per group
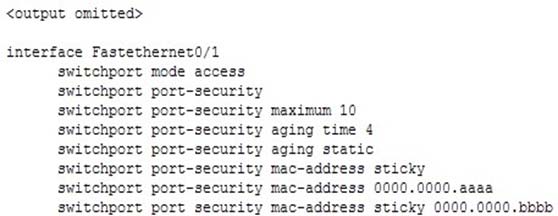
In the following partial output of the show run command, which MAC address or addresses will be removed from the list of secure addresses after 240 seconds?
A. 0000.0000.aaaa
B. 0000.0000.bbbb
C. 0000.0000.aaaa and 0000.0000.bbbbb
D. none of the MAC addresses will be removed after 240 seconds A
Which option is a benefit of configuring UDLD on a link between two switches?
A. UDLD determines the best switching path
B. UDLD helps prevent switching loops
C. UDLD provides a backup mechanism for fiber
D. UDLD removes switching loops
What is the default HSRP priority?
A. 50
B. 100
C. 120
D. 1024
Which two control protocols use the native VLAN 1 by default? (Choose two.)
A. STP
B. CDP
C. LACP
D. NTP
E. VTP
Which two protocols can be automatically negotiated between switches for trunking? (Choose two.)
A. PPP
B. DTP
C. ISL
D. HDLC
E. DLCI
F. DOT1Q
In a Virtual Switching System, DSW1 and DSW2 need to communicate with each other to determine the role. Which technology is it using?
A. STP
B. NA
C. VSL Protocol (Virtual Switch Link)
D. LACP
Where does the VLAN information get saved to?
A. The information is saved to the vlan.dat file.
B. The information is saved to the running configuration file.
C. The information is saved to the vlan.txt file.
D. The information is saved to the vlan.conf file.
Which two command sequences must you enter on a pair of switches so that they negotiate an EtherChannel using the Cisco proprietary port-aggregation protocol? (Choose two.) A.B.
C.
D.
E.
What is the maximum number of virtual MAC addresses that GLBP allows per group?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 6
D. 8
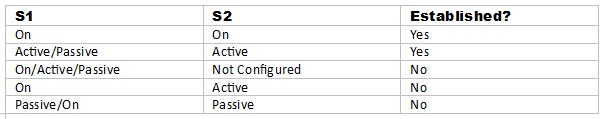
After reviewing UDLD status on switch ports, an engineer notices that the current bidirectional state for an access port is "Unknown". Which statement describes what this indicates about the status of the port?
A. UDLD moved into aggressive mode after inconsistent acknowledgements were detected.
B. The UDLD port is placed in the “unknown” state for 5 seconds until the next UDLD packet is received on the interface.
C. The port is fully operational and no known issues are detected.
D. The bidirectional status of “unknown” indicates that the port will go into the disabled state because it stopped receiving UDLD packets from its neighbor.
What are possible Etherchannel load balancing mechanism based on layer 3? (Choose 2)
A. Mac source
B. Mac source-destination
C. IP Source
D. IP Source-destination
E. Mac destination
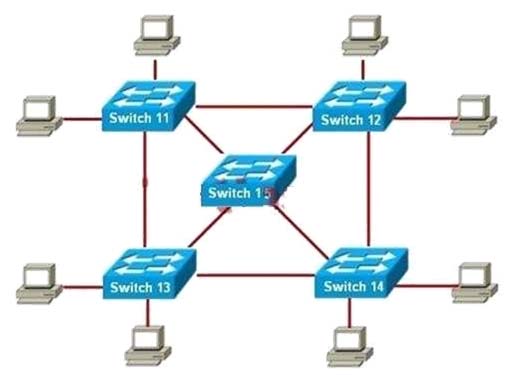
Refer to the exhibit. Switch 15 is configured as the root switch for VLAN 10 but not for VLAN 20. If the STP configuration is correct, what will be true about Switch 15?
A. All ports will be in forwarding mode.
B. All ports in VLAN 10 will be in forwarding mode.
C. All ports in VLAN 10 will be in forwarding mode and all ports in VLAN 20 will be in blocking mode.
D. All ports in VLAN 10 will be in forwarding mode and all ports in VLAN 20 will be in standby mode.
DRAG DROP - Select and Place: Select and Place:
Which feature is automatically enabled when a voice VLAN is configured, but not automatically disabled when a voice VLAN is removed?
A. portfast
B. port-security
C. spanning tree
D. storm control
A network engineer configured an Ethernet switch using these commands. Switchone(config) # Spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default Which statement about the spanning-tree portfast feature on the switch is true?
A. If an interface is enabled for portfast receives BDPU, the port goes through the spanning-tree listening, learning, and forwarding states.
B. If an interface is enabled for portfast receives BDPU, the port does not go through the spanning-tree listening, learning, and forwarding states.
C. If an interface is enabled for portfast receives BDPU, the port is shut down immediately.
D. If an interface is enabled for portfast receives BDPU, the port goes into the spanning-tree inconsistent state.
Which two statements about dynamic MAC address learning are true? (Choose two.)
A. Dynamically-learned MAC addresses can be cleared on a per-interface basis only.
B. It must be enabled on ports with port security enabled.
C. It can be disabled on a per-VLAN basis only.
D. Switch interfaces learn MAC addresses dynamically by default.
E. Dynamically-learned MAC addresses supersede static MAC addresses
Which of the following is required to allow load balancing between three HSRP routers connected to the same LAN?
A. A single HSRP group with all three routers as active routers for the group
B. A single HSRP group with one active router for the group
C. Two HSRP groups, each with an active router
D. Two HSRP groups with one active router for both the groups
E. Three HSRP groups, each with an active router
F. Three HSRP groups with one active router for all groups
Which three VLANs are part of the extended range of available VLANs? (Choose three.)
A. 1006
B. 4095
C. 4195
D. 3000
E. 4094
F. 1001
A network engineer deployed a switch that operates the LAN base feature set and decides to use the SDM VLAN template. The SDM template is causing the CPU of the switch to spike during peak working hours. What is the root cause of this issue?
A. The VLAN receives additional frames from neighboring switches.
B. The SDM VLAN template causes the MAC address-table to overflow.
C. The VLAN template disables routing in hardware.
D. The switch needs to be rebooted before the SDM template takes effect.
Which two pieces of information are carried in a Cisco Discovery Protocol advertisement? (Choose two.)
A. Processor Type
B. VTP domain name
C. Routing protocol
D. Memory usage
E. Spanning-Tree mode
F. Native VLAN-ID
Which parameters are found in VTP advertisements? (Choose three.)
A. Password
B. VTP mode
C. IP address
D. Switch name
E. Revision number
F. Management domain name
Refer to the exhibit.Which EtherChannel negotiation protocol is configured on the interface f0/13 f0/15?
A. Link Combination Control Protocol
B. Port Aggregation Protocol
C. Port Combination Protocol
D. Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Which command enables GLBP on an interface?
A. glbp
B. glbp 10 ip 192.168.1.1
C. standby mode glbp
D. switchport mode glbp
Which two commands prune VLAN 10 from a switch interface? (Choose two.)
A. switchport trunk native vlan 10
B. switchport trunk allowed remove vlan 10
C. switchport trunk allowed vlan add 10
D. no vlan 10
E. switchport trunk allowed except vlan 10
Which two new features are included in VTPv3? (Choose two.)
A. VTP now supports MD5 passwords
B. VLANs in the extended range are now eligible to participate in VTP
C. VTPs can now be configured in off mode
D. It can be configured to prevent the override of the VLAN database
E. VLANs configured for token ring are now eligible to participate in VTP
Which command correctly configures standby tracking for group 1 using the default decrement priority value?
A. standby 1 track 100
B. standby 1 track 100 decrement 1
C. standby 1 track 100 decrement 5
D. standby 1 track 100 decrement 20
What is the link called between a VSS?
A. VSL (Virtual Switch Link)
B. SVI
C. DCSP
D. VLAN
Which feature describes MAC addresses that are dynamically learned or manually configured, stored in the address table, and added to the running configuration?
A. sticky
B. dynamic
C. static
D. secure
Which statement is true when UDLD is configured on a link and the link is determined to be unidirectional?
A. The port remains up for a configured time interval and then error disables if the link remains unidirectional.
B. LLDP is enabled on the port.
C. The port sends a log message to the console.
D. The port is disabled immediately.
What is the multicast address for HSRPv2?
A. 224.0.0.102
B. 127.0.0.1
C. 224.1.1.2
D. 224.1.1.102
An administrator recently configured all ports for rapid transition using PortFast. After testing, it has been determined that several ports are not transitioning as they should. What is the reason for this?
A. RSTP has been enabled per interface and not globally.
B. The STP root bridge selection is forcing key ports to remain in non-rapid transitioning mode.
C. STP is unable to achieve rapid transition for trunk links.
D. The switch does not have the processing power to ensure rapid transition for all ports.
Free Access Full 300-115 Practice Exam Free
Looking for additional practice? Click here to access a full set of 300-115 practice exam free questions and continue building your skills across all exam domains.
Our question sets are updated regularly to ensure they stay aligned with the latest exam objectives—so be sure to visit often!
Good luck with your 300-115 certification journey!