CSSLP Exam Prep Free – 50 Practice Questions to Get You Ready for Exam Day
Getting ready for the CSSLP certification? Our CSSLP Exam Prep Free resource includes 50 exam-style questions designed to help you practice effectively and feel confident on test day
Effective CSSLP exam prep free is the key to success. With our free practice questions, you can:
- Get familiar with exam format and question style
- Identify which topics you’ve mastered—and which need more review
- Boost your confidence and reduce exam anxiety
Below, you will find 50 realistic CSSLP Exam Prep Free questions that cover key exam topics. These questions are designed to reflect the structure and challenge level of the actual exam, making them perfect for your study routine.
Which of the following software review processes increases the software security by removing the common vulnerabilities, such as format string exploits, race conditions, memory leaks, and buffer overflows?
A. Management review
B. Code review
C. Peer review
D. Software audit review
Which of the following are included in Technical Controls? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
A. Identification and authentication methods
B. Configuration of the infrastructure
C. Password and resource management
D. Implementing and maintaining access control mechanisms
E. Security devices
F. Conducting security-awareness training
Which of the following methods offers a number of modeling practices and disciplines that contribute to a successful service-oriented life cycle management and modeling?
A. Service-oriented modeling framework (SOMF)
B. Service-oriented architecture (SOA)
C. Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture (SABSA)
D. Service-oriented modeling and architecture (SOMA)
Which of the following is an example of over-the-air (OTA) provisioning in digital rights management?
A. Use of shared secrets to initiate or rebuild trust.
B. Use of software to meet the deployment goals.
C. Use of concealment to avoid tampering attacks.
D. Use of device properties for unique identification.
Which of the following methods determines the principle name of the current user and returns the jav a.security.Principal object in the HttpServletRequest interface?
A. getUserPrincipal()
B. isUserInRole()
C. getRemoteUser()
D. getCallerPrincipal()
Which of the following security controls works as the totality of protection mechanisms within a computer system, including hardware, firmware, and software, the combination of which is responsible for enforcing a security policy?
A. Common data security architecture (CDSA)
B. Application program interface (API)
C. Trusted computing base (TCB)
D. Internet Protocol Security (IPSec)
Which of the following terms ensures that no intentional or unintentional unauthorized modification is made to data?
A. Non-repudiation
B. Integrity
C. Authentication
D. Confidentiality
Companies use some special marks to distinguish their products from those of other companies. These marks can include words, letters, numbers, drawings, etc. Which of the following terms describes these special marks?
A. Business mark
B. Trademark
C. Sales mark
D. Product mark
You are the project manager for GHY Project and are working to create a risk response for a negative risk. You and the project team have identified the risk that the project may not complete on time, as required by the management, due to the creation of the user guide for the software you're creating. You have elected to hire an external writer in order to satisfy the requirements and to alleviate the risk event. What type of risk response have you elected to use in this instance?
A. Transference
B. Exploiting
C. Avoidance
D. Sharing
Which of the following testing methods tests the system efficiency by systematically selecting the suitable and minimum set of tests that are required to effectively cover the affected changes?
A. Unit testing
B. Integration testing
C. Acceptance testing
D. Regression testing
Which of the following is a standard that sets basic requirements for assessing the effectiveness of computer security controls built into a computer system?
A. FITSAF
B. FIPS
C. TCSEC
D. SSAA
What are the various phases of the Software Assurance Acquisition process according to the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) and Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Acquisition and Outsourcing Working Group?
A. Implementing, contracting, auditing, monitoring
B. Requirements, planning, monitoring, auditing
C. Planning, contracting, monitoring and acceptance, follow-on
D. Designing, implementing, contracting, monitoring
Which of the following types of redundancy prevents attacks in which an attacker can get physical control of a machine, insert unauthorized software, and alter data?
A. Data redundancy
B. Hardware redundancy
C. Process redundancy
D. Application redundancy
Which of the following sections come under the ISO/IEC 27002 standard?
A. Security policy
B. Asset management
C. Financial assessment
D. Risk assessment
Which of the following statements is true about residual risks?
A. It is the probabilistic risk after implementing all security measures.
B. It can be considered as an indicator of threats coupled with vulnerability.
C. It is a weakness or lack of safeguard that can be exploited by a threat.
D. It is the probabilistic risk before implementing all security measures.
Della works as a security engineer for BlueWell Inc. She wants to establish configuration management and control procedures that will document proposed or actual changes to the information system. Which of the following phases of NIST SP 800-37 C&A methodology will define the above task?
A. Initiation
B. Security Certification
C. Continuous Monitoring
D. Security Accreditation
Which of the following requires all general support systems and major applications to be fully certified and accredited before these systems and applications are put into production? Each correct answer represents a part of the solution. Choose all that apply.
A. NIST
B. Office of Management and Budget (OMB)
C. FIPS
D. FISMA
Which of the following NIST Special Publication documents provides a guideline on network security testing?
A. NIST SP 800-42
B. NIST SP 800-53A
C. NIST SP 800-60
D. NIST SP 800-53
E. NIST SP 800-37
F. NIST SP 800-59
Which of the following areas of information system, as separated by Information Assurance Framework, is a collection of local computing devices, regardless of physical location, that are interconnected via local area networks (LANs) and governed by a single security policy?
A. Local Computing Environments
B. Networks and Infrastructures
C. Supporting Infrastructures
D. Enclave Boundaries
Which of the following types of attacks occurs when an attacker successfully inserts an intermediary software or program between two communicating hosts?
A. Denial-of-service attack
B. Dictionary attack
C. Man-in-the-middle attack
D. Password guessing attack
Which of the following technologies is used by hardware manufacturers, publishers, copyright holders and individuals to impose limitations on the usage of digital content and devices?
A. Hypervisor
B. Grid computing
C. Code signing
D. Digital rights management
Which of the following elements of BCP process includes the areas of plan implementation, plan testing, and ongoing plan maintenance, and also involves defining and documenting the continuity strategy?
A. Business continuity plan development
B. Business impact assessment
C. Scope and plan initiation
D. Plan approval and implementation
Which of the following coding practices are helpful in simplifying code? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
A. Programmers should use multiple small and simple functions rather than a single complex function.
B. Software should avoid ambiguities and hidden assumptions, recursions, and GoTo statements.
C. Programmers should implement high-consequence functions in minimum required lines of code and follow proper coding standards.
D. Processes should have multiple entry and exit points.
Which of the following is a name, symbol, or slogan with which a product is identified?
A. Trademark
B. Copyright
C. Trade secret
D. Patent
Which of the following attacks causes software to fail and prevents the intended users from accessing software?
A. Enabling attack
B. Reconnaissance attack
C. Sabotage attack
D. Disclosure attack
Which of the following is a set of exclusive rights granted by a state to an inventor or his assignee for a fixed period of time in exchange for the disclosure of an invention?
A. Copyright
B. Snooping
C. Utility model
D. Patent
FIPS 199 defines the three levels of potential impact on organizations. Which of the following potential impact levels shows limited adverse effects on organizational operations, organizational assets, or individuals?
A. Moderate
B. Low
C. Medium
D. High
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a logical process used by programmers to develop software. Which of the following SDLC phases meets the audit objectives defined below: System and data are validated. System meets all user requirements. System meets all control requirements.
A. Evaluation and acceptance
B. Programming and training
C. Definition
D. Initiation
You work as a systems engineer for BlueWell Inc. Which of the following tools will you use to look outside your own organization to examine how others achieve their performance levels, and what processes they use to reach those levels?
A. Benchmarking
B. Six Sigma
C. ISO 9001:2000
D. SEI-CMM
Which of the following access control models uses a predefined set of access privileges for an object of a system?
A. Role-Based Access Control
B. Discretionary Access Control
C. Policy Access Control
D. Mandatory Access Control
Martha registers a domain named Microsoft.in. She tries to sell it to Microsoft Corporation. The infringement of which of the following has she made?
A. Copyright
B. Trademark
C. Patent
D. Intellectual property
In which of the following phases of the DITSCAP process does Security Test and Evaluation (ST&E) occur?
A. Phase 2
B. Phase 4
C. Phase 3
D. Phase 1
Which of the following federal agencies has the objective to develop and promote measurement, standards, and technology to enhance productivity, facilitate trade, and improve the quality of life?
A. National Security Agency (NSA)
B. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
C. United States Congress
D. Committee on National Security Systems (CNSS)
Which of the following access control models are used in the commercial sector? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose two.
A. Biba model
B. Clark-Biba model
C. Clark-Wilson model
D. Bell-LaPadula model
Bill is the project manager of the JKH Project. He and the project team have identified a risk event in the project with a high probability of occurrence and the risk event has a high cost impact on the project. Bill discusses the risk event with Virginia, the primary project customer, and she decides that the requirements surrounding the risk event should be removed from the project. The removal of the requirements does affect the project scope, but it can release the project from the high risk exposure. What risk response has been enacted in this project?
A. Mitigation
B. Transference
C. Acceptance
D. Avoidance
You are advising a school district on disaster recovery plans. In case a disaster affects the main IT centers for the district they will need to be able to work from an alternate location. However, budget is an issue. Which of the following is most appropriate for this client?
A. Cold site
B. Off site
C. Warm site
D. Hot site
Which of the following DoD directives is referred to as the Defense Automation Resources Management Manual?
A. DoD 8910.1
B. DoD 7950.1-M
C. DoDD 8000.1
D. DoD 5200.22-M
E. DoD 5200.1-R
The Phase 4 of DITSCAP C&A is known as Post Accreditation. This phase starts after the system has been accredited in Phase 3. What are the process activities of this phase? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
A. Security operations
B. Maintenance of the SSAA
C. Compliance validation
D. Change management
E. System operations
F. Continue to review and refine the SSAA
You work as the senior project manager in SoftTech Inc. You are working on a software project using configuration management. Through configuration management you are decomposing the verification system into identifiable, understandable, manageable, traceable units that are known as Configuration Items (CIs). According to you, which of the following processes is known as the decomposition process of a verification system into Configuration Items?
A. Configuration status accounting
B. Configuration identification
C. Configuration auditing
D. Configuration control
You are responsible for network and information security at a large hospital. It is a significant concern that any change to any patient record can be easily traced back to the person who made that change. What is this called?
A. Availability
B. Confidentiality
C. Non repudiation
D. Data Protection
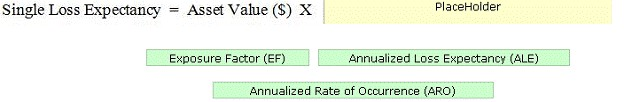
DRAG DROP - Drop the appropriate value to complete the formula. Select and Place:
You work as a project manager for BlueWell Inc. You with your team are using a method or a (technical) process that conceives the risks even if all theoretically possible safety measures would be applied. One of your team member wants to know that what is a residual risk. What will you reply to your team member?
A. It is a risk that remains because no risk response is taken.
B. It is a risk that can not be addressed by a risk response.
C. It is a risk that will remain no matter what type of risk response is offered.
D. It is a risk that remains after planned risk responses are taken.
Certification and Accreditation (C&A or CnA) is a process for implementing information security. It is a systematic procedure for evaluating, describing, testing, and authorizing systems prior to or after a system is in operation. Which of the following statements are true about Certification and Accreditation? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose two.
A. Certification is a comprehensive assessment of the management, operational, and technical security controls in an information system.
B. Accreditation is a comprehensive assessment of the management, operational, and technical security controls in an information system.
C. Accreditation is the official management decision given by a senior agency official to authorize operation of an information system.
D. Certification is the official management decision given by a senior agency official to authorize operation of an information system.
Which of the following processes culminates in an agreement between key players that a system in its current configuration and operation provides adequate protection controls?
A. Information Assurance (IA)
B. Information systems security engineering (ISSE)
C. Certification and accreditation (C&A)
D. Risk Management
The organization level is the Tier 1 and it addresses risks from an organizational perspective. What are the various Tier 1 activities? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
A. The organization plans to use the degree and type of oversight, to ensure that the risk management strategy is being effectively carried out.
B. The level of risk tolerance.
C. The techniques and methodologies an organization plans to employ, to evaluate information system-related security risks.
D. The RMF primarily operates at Tier 1.
The Web resource collection is a security constraint element summarized in the Java Servlet Specification v2.4. Which of the following elements does it include? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose two.
A. HTTP methods
B. Role names
C. Transport guarantees
D. URL patterns
In which of the following deployment models of cloud is the cloud infrastructure operated exclusively for an organization?
A. Public cloud
B. Community cloud
C. Private cloud
D. Hybrid cloud
Which of the following persons in an organization is responsible for rejecting or accepting the residual risk for a system?
A. Information Systems Security Officer (ISSO)
B. Designated Approving Authority (DAA)
C. System Owner
D. Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
In which of the following cryptographic attacking techniques does an attacker obtain encrypted messages that have been encrypted using the same encryption algorithm?
A. Chosen plaintext attack
B. Chosen ciphertext attack
C. Ciphertext only attack
D. Known plaintext attack
Which of the following statements about the availability concept of Information security management is true?
A. It ensures that modifications are not made to data by unauthorized personnel or processes.
B. It determines actions and behaviors of a single individual within a system.
C. It ensures reliable and timely access to resources.
D. It ensures that unauthorized modifications are not made to data by authorized personnel or processes.
Access Full CSSLP Exam Prep Free
Want to go beyond these 50 questions? Click here to unlock a full set of CSSLP exam prep free questions covering every domain tested on the exam.
We continuously update our content to ensure you have the most current and effective prep materials.
Good luck with your CSSLP certification journey!