300-101 Practice Questions Free – 50 Exam-Style Questions to Sharpen Your Skills
Are you preparing for the 300-101 certification exam? Kickstart your success with our 300-101 Practice Questions Free – a carefully selected set of 50 real exam-style questions to help you test your knowledge and identify areas for improvement.
Practicing with 300-101 practice questions free gives you a powerful edge by allowing you to:
- Understand the exam structure and question formats
- Discover your strong and weak areas
- Build the confidence you need for test day success
Below, you will find 50 free 300-101 practice questions designed to match the real exam in both difficulty and topic coverage. They’re ideal for self-assessment or final review. You can click on each Question to explore the details.
Which two reductions are the correct reductions if the IPv6 address 2001:0d02:0000:0000:0014:0000:0000:0095? (Choose two)
A. 2001:0d02:::0014:::0095
B. 2001:d02::14::95
C. 2001:d02:0:0:14::95
D. 2001:d02::14:0:0:95
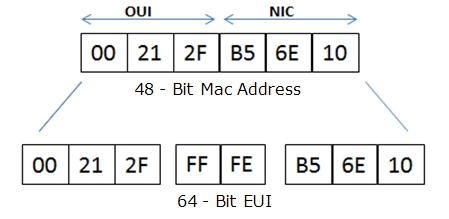
An EUl-64 bit address is formed by adding a reserved 16-bit value, in which position of the Mac address?
A. between the vendor OID and the NIC-specific part of the MAC address.
B. after the NIC-specific part of the MAC address.
C. before the vendor OID part of the MAC address.
D. anywhere in the Mac address, because the value that is added is reserved. A
Considering the IPv6 address independence requirement, which process do you avoid when you use NPTv6 for translation?
A. IPv6 duplication and conservation
B. IPsec AH header modification
C. checksum verification
D. rewriting of higher layer information
Which protocol can you use to remotely install an IOS on a Cisco switch?
A. SFTP
B. NetFlow
C. FTP
D. SNMP
Which two statements about route redistribution when implementing OSPF are true? (Choose two.)
A. Routes learned using any IP routing protocol can only be redistributed into non IP routing protocols.
B. OSPF can import routes learned using EIGRP, RIP, and IS-IS.
C. OSPF routes cannot be exported into EIGRP, RIP, and IS-IS.
D. At the interdomain level, OSPF cannot import routes learned using BGP.
Which option is the best for protecting CPU utilization on a device?
A. fragmentation
B. COPP
C. ICMP redirects
D. ICMP unreachable messages
What is the hop count ...RIP?
A. 15
B. 255
C. 0
D. 16
498 DRAG DROP Select and Place:
A network engineer wants an NTP client to be able to update the local system without updating or synchronizing with the remote system. Which option for the ntp command is needed to accomplish this? access-group
A. peer
B. query-only
C. serve-only
D. serve
When a tunnel interface is configured in the default mode, which statement about routers and the tunnel destination address is true?
A. The router must have WCCP redirects enabled inbound from the tunnel destination.
B. The router must have redirects enabled outbound toward the tunnel destination.
C. The router must have a route installed toward the tunneldestination.
D. The router must have Cisco Discovery Protocol enabled on the tunnel to form a CDP neighborship with the tunnel destination.
What is the default OSPF hello interval on a Frame Relay point-to-point network?
A. 10
B. 20
C. 30
D. 40
Which command creates a manual summary on an interface when using EIGRP?
A. summary-address eigrp 100 172.32.0.0 255.255.254.0
B. ip summary-address eigrp 100 172.32.0.0 255.255.254.0
C. area 100 range 172.32.0.0 255.255.254.0
D. ip summary-address 100.172.32.0.0 255.255.254.0
A network administrator executes the command clear ip route. Which two tables does this "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 4 command clear and rebuild? (Choose two.)
A. IP routing
B. FIB
C. ARP cache
D. MAC address table
E. Cisco Express Forwarding table
F. topology table
What does stateful NAT64 do that stateless NAT64 does not do?
A. Stateful NAT64 maintains bindings or session state while performing translation
B. Stateful NAT64 maintains bindings of IPv4 to IPv6 link-local addresses
C. Stateful NAT64 translates IPv4 to IPv6
D. Stateful NAT64 translates IPv6 to IPv4
PPPoE requires certain signals and information to establish, accept, control and terminate the session. The basic signalling is shown below.
A. (PPPoE Active Discovery Request), PADI (PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation)
B. (PPPoR Active Discovery Request), PARP (PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation)
C. (PPPoE Active Discovery Reaching), PADI (PPPoE Active Discovery Initiating)
D. (PPP Active Discovery Request), PADI (PPP Active Discovery Initiation)
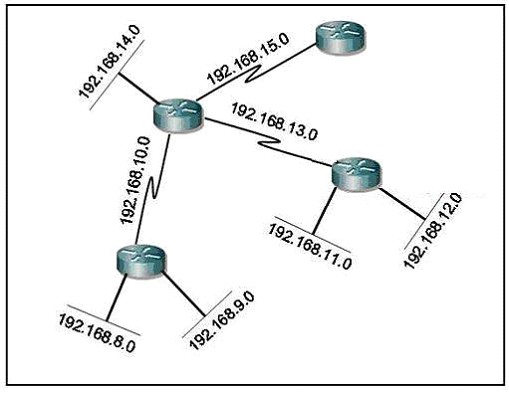
Refer to the exhibit.On all routers in the network, EIGRP has been configured for load balancing across the three links. However, traffic destined for Network B from R1 is only load balanced over paths R1- R2-R5 and R1-R3-R5. What is the cause of the problem?
A. EIGRP will not select more than two links for unequal cost path load balancing.
B. Because the path has a different link type, EIGRP will not select path R1-R4-R5 for load balancing.
C. Because Router R4 is not a feasible successor, EIGRP will not select path R1-R4-R5 for load balancing.
D. EIGRP will not select path R1-R4-R5 for load balancing unless the value of the variance parameter is increased.
Which of the following is a GRE Tunnel characteristic?
A. GRE impose more CPU overhead than IPSec on VPN gateways
B. GRE tunnels can run through IPsec tunnels.
C. GRE Tunnel doesn’t have support for IPv6
D. GRE consists of two sub-protocols: Encapsulated Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH).
Refer to the exhibit.What happens when the router stops receiving advertisements for the 10.1.2.0/24 network?
A. The summary route will be removed from the table.
B. The summary route will remain in the table.
C. The more specific routes will be advertised from the table.
D. 10.1.2.0/24 will still be advertised but packets destined for it will be dropped when they reach this router.
Your network consists of a large hub-and-spoke Frame Relay network with a CIR of 56 kb/s for each spoke. Which statement about the selection of a dynamic protocol is true? Choose the best response.
A. EIGRP would be appropriate if LMI type ANSI is NOT used.
B. EIGRP would be appropriate, because the Frame Relay spokes could be segmented into their own areas.
C. EIGRP would be appropriate, because by default, queries are not propagated across the slow speed Frame Relay links.
D. EIGRP would be appropriate, because you can manage how much bandwidth is consumed over the Frame Relay interface.
Which PPP authentication method sends authentication information in clear text?
A. MS CHAP
B. CDPCP
C. CHAP
D. PAP
What does the default value of the EIGRP variance command of 1 mean?
A. Load balancing is disabled on this router.
B. The router performs equal-cost load balancing.
C. Only the path that is the feasible successor should be used.
D. The router only performs equal-cost load balancing on all paths that have a metric greater than 1.
Refer to the exhibit.In a redundant hub-and-spoke deployment using EIGRP, what feature can be used to ensure that routers C through F are not used as transit routers for data traveling from router B to network 10.1.1.0? Select the best response
A. Use address summarization at routers C, D, E, and F.
B. Use the EIGRP Stub feature on routers C, D, E, and F.
C. Use passive-interface on the spoke links in routers A and B.
D. Change the administrative distance in routers A and B for routes learned from routers C, D, E, and F.
Which feature can automatically assign IP addresses in a PPPoE environment?
A. DHCP
B. BOOTP
C. PPP
D. APIPA
An EUI-64-bit address is formed by adding a reserved 16-bit value in which position of the Mac address?
A. Between the vendor OID and the NIC-specific part of the MAC address.
B. After the NIC-specific part of the MAC address.
C. Before the vendor OID part of the MAC address.
D. Anywhere in the Mac address, because the value that is added is reserved.
Refer to the exhibit.You are the network administrator responsible for the NProuter, the 10.1.1.1 router, and the 10.1.1.2 router. What can you determine about the OSPF operations from the debug output?
A. The NProuter has two OSPF neighbors in the “Full” adjacency state.
B. The NProuter serial0/0 interface has the OSPF dead timer set to 10 seconds.
C. The NProuter serial0/0 interface has been configured with an OSPF network type of “pointto-point”.
D. The 10.1.1.1 and 10.1.1.2 routers are not using the default OSPF dead and hello timers setting.
Refer to exhibit. If the IGP in AS65000 is RIPv2, which networks are displayed when you enter show ip route on router R2?
A. VLSM subnets in 10.0.0.0/16 and the major network 10.2.0.0/16 only
B. VLSM subnets in 10.0.0.0/16 and the major network 10.2.0.0/16 only
C. VLSM subnets in 10.0.0.0/16 only
D. major networks 10.1.0.0/16 and 10.2.0.0/16 only
E. VLSM subnets in 10.0.0.0/16 and the major networks 10.1.0.0/16 10.2.0.0/16 D
Refer to the exhibit.A Boston company bought the assets of a New York company and is trying to route traffic between the two data networks using EIGRP. The show command output shows that traffic will not flow between the networks. As a network consultant, you were asked to modify the configuration and certify the interoperability of the two networks. For traffic to flow from subnet 172.16.8.0/24 to the 172.16.16.0/24 subnet. Which configuration change do you recommend?
A. Turn off autosummarization on routers N1 and B1.
B. Add IP summary addresses to the Internet-pointing interfaces of routers N1 and B1.
C. Turn off auto summarization on routers N2 and B2.
D. Add wildcard masks to the network commands on routers N2 and B2.
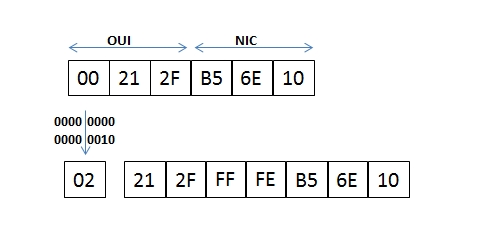
After you review the output of the command show ipv6 interface brief, you see that several IPv6 addresses have the 16-bit hexadecimal value of "fFFE" inserted into the address. Based on this information, what do you conclude about these IPv6 addresses?
A. IEEE EUI-64 was implemented when assigning IPv6 addresses on the device.
B. The addresses were misconfigured and will not function as intended.
C. IPv6 addresses containing “FFFE” indicate that the address is reserved for multicast.
D. The IPv6 universal/local flag (bit 7) was flipped.
E. IPv6 unicast forwarding was enabled, but IPv6 Cisco Express Forwarding was disabled.
A network engineer wants to notify a manager in the event that the IP SLA connection loss threshold is reached. Which two features are needed to implement this functionality? (Choose two.)
A. Cisco IOS EEM
B. SNMP traps
C. threshold action
D. MOS
E. logging local
Which two statements about GRE tunnel keys are true? (Choose two.)
A. The key ID must be the same on each device.
B. They prevent the injection of unwanted frames.
C. They prevent the injection of unwanted packets.
D. They must be stored to a keychain.
E. They provide the highe level of security that is available. AC
Choose correct statement about Dynamic NAT. (Choose two.)
A. inside local
B. outside local
C. this list will be translated to this subnet (which is pool)
D. outside global
A network engineer is configuring two dedicated Internet connections within the Internet module. One connection is the primary connection to all wired business communications, while the other is the primary connection for all customer wireless traffic. If one of the links goes down, the affected traffic needs to be redirected to the redundant link. Which current technology should be deployed to monitor the scenario?
A. PBR
B. IP QoS
C. MMC
D. IP SLA
E. IP SAA
Which technology was originally developed for routers to handle fragmentation in the path between end points?
A. PMTUD
B. MSS
C. windowing
D. TCP
E. global synchronization
In which state do DR and BDR establish adjacency with each OSPF router in the network?
A. Init State
B. Exstart State
C. Exchange State
Into which two types of areas would an area border router (ABR) inject a default route? (Choose two)
A. stub
B. the autonomous system of an exterior gateway protocol (EGP)
C. NSSA
D. totally stubby
E. the autonomous system of a different interior gateway protocol (IGP)
F. area 0
Which IP SLA operation requires Cisco endpoints?
A. UDP Jitter for VoIP
B. ICMP Path Echo
C. ICMP Echo
D. UDP Jitter
Which two tasks must you perform to configure a BGP peer group? (Choose two.)
A. Activate each neighbor.
B. Activate the default route.
C. Configure the soft-update value.
D. Assign neighbor to the peer-group.
E. Set the advertisement interval.
Which logical operator do you use to ensure that the status of an object track list is up only when all configured objects are up?
A. and
B. true
C. xor
D. or
To configure 6to4 on a dual-stack edge router. Which three of the following are valid in 6to4 Tunneling configuration? (Choose three)
A. IPv4 Tunnel IP address
B. Tunnel mode (6to4)
C. Tunnel Keepalives
D. IPv4 Tunnel Destination
E. IPv4 Tunnel Source.
F. 6to4 IPv6 address (within 2002::/16)
Refer to the exhibit.After configuring the rotes, the network engineer executes the show ip route command. What is the expected result?
A. Gateway of last resort is 10.0.2.1 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnetsC 10.0.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0C 10.0.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1S” 0.0.0.0/0[1/0] via 10.0.2.1 [1/0] via 10.0.1.1Router #
B. Gateway of last resort is 10.0.1.1 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnet C 10.0.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 S” 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.0.1.1 Router #
C. Gateway of last resort is not set Router #
D. Gateway of last resort is 10.0.2.1 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnet C 10.0.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 S”0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.0.2.1 Router #
What is VRF-Lite?
A. VRF without MPLS
B. VRF without VPN
C. VRF without Cisco Express Forwarding switching
D. VRF without independent routing tables
When policy-based routing (PBR) is being configured, which three criteria can the set command specify? (Choose three.)
A. All interfaces through which the packets can be routed
B. All interfaces in the path toward the destination
C. Adjacent next hop router in the path toward the destination
D. All routers in the path toward the destination
E. All networks in the path toward the destination
F. Type of service and precedence in the IP packets
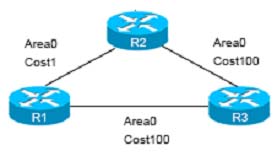
Refer to the exhibit. You notice that traffic from R1 to the 192.168.10.0/24 network prefers the path through R3 instead of the least-cost path through R2. What is the most likely reason for this router selection?
A. OSPF prefers external routers over interarea router.
B. OSPF prefers interarea routers over intra-area routers.
C. OSPF prefers external routers over intra-area routers.
D. OSPF prefers intra-area routers over interarea routers.
An engineer is asked to monitor the availability of the next-hop IP address of 172.16.201.25 every 3 seconds using an ICMP echo packet via an ICMP echo probe. Which two commands accomplish this task? (Choose two.)
A. router(config-ip-sla)#icmp-echo 172.16.201.25 source-interface FastEthernet 0/0
B. router(config-ip-sla-echo)#timeout 3
C. router(config-ip-sla)#icmp-jitter 172.16.201.25 interval 100 D. router(config-ip-sla-echo)#frequency 3
D. router(config-ip-sla)#udp-echo 172.16.201.25 source-port 23 F. router(config-ip-sla-echo)#threshold 3
Fill in the Blank. How to minimize Unicast flooding? _________________________________ By decreasing the ARP time compared to CAM table time
What are the three modes of Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding?
A. strict mode, loose mode, and VRF mode
B. strict mode, loose mode, and broadcast mode
C. strict mode, broadcast mode, and VRF mode
D. broadcast mode, loose mode, and VRF mode
Which two statements about PAP and CHAP authentication are true? (Choose two)
A. PAP uses a challenge string from the server to the client.
B. PAP can query a TACACS+ server to verify access credentials.
C. CHAP requires the client to supply a username and optional password.
D. PAP requires the client to supply a username and optional password.
E. CHAP uses a challenge string from the server to the client.
Given the accompanying output, which additional command is needed to redistribute IGRP into EIGRP? Router eigrp 123 - Network 10.10.10.0 - No auto-summary - Router igrp 123 - Network 172.16.0.0 - Network 172.17.0.0 -
A. Under the router igrp mode add redistribute eigrp 123
B. Under the router eigrp mode add redistribute igrp 123
C. Under the router eigrp mode add redistribute igrp 123 subnets
D. None, EIGRP and IGRP are automatically redistributed in this instance.
Congestion in the network. What is the effect on UDP?
A. Sender will have to buffer more data.
B. Receiver will have to buffer more data before sending packets to higher layers
C. There will be latency.
Company has migrated to IPv6 in their network. Which three IPv6 notations represent the same address? (Select three.)
A. 2031::130F::9C0:876A:130B
B. 2031:0000:130F:0000:0000:09C0:876A:130B
C. 2031:0:130F:::9C0:876A:130B
D. 2031::130F:0::9C0:876A:130B
E. 2031:0:130F:0:0:09C0:876A:130B
F. 2031:0:130F::9C0:876A:130B
Free Access Full 300-101 Practice Questions Free
Want more hands-on practice? Click here to access the full bank of 300-101 practice questions free and reinforce your understanding of all exam objectives.
We update our question sets regularly, so check back often for new and relevant content.
Good luck with your 300-101 certification journey!