300-101 Practice Exam Free – 50 Questions to Simulate the Real Exam
Are you getting ready for the 300-101 certification? Take your preparation to the next level with our 300-101 Practice Exam Free – a carefully designed set of 50 realistic exam-style questions to help you evaluate your knowledge and boost your confidence.
Using a 300-101 practice exam free is one of the best ways to:
- Experience the format and difficulty of the real exam
- Identify your strengths and focus on weak areas
- Improve your test-taking speed and accuracy
Below, you will find 50 realistic 300-101 practice exam free questions covering key exam topics. Each question reflects the structure and challenge of the actual exam.
Which value does Frame Relay use to identify a connection between a DTE and DCE?
A. DLCI
B. IP address
C. MAC address
D. VLAN ID
When implementing a 6to4 tunnel, which IPv6 address is the correct translation of the IPv4 address 192.168.99.1?
A. c0a8:6301:2002::/48
B. 2002:c0a8:6301::/48
C. 2002:c0a8:6301::/8
D. 2002::/16
A network engineer wants to monitor hop-by-hop response time on the network. Which IP SLA operation accomplishes this task?
A. ICMP path jitter
B. ICMP-echo
C. ICMP path echo
D. UDP-echo
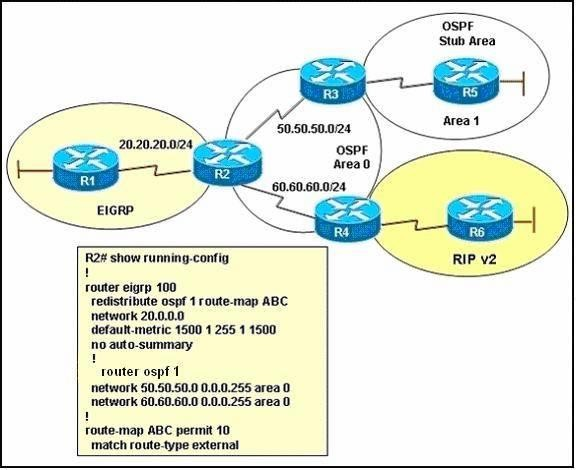
Refer to the exhibit and the partial configuration on router R2. On router R4 all RIP routes are redistributed into the OSPF domain. A second redistribution is configured on router R2 using a route map. Based on the configuration on router R2, which EIGRP external routes will be present in the routing table of R1?
A. the routes originating from the RIP routing domain
B. the routes originating from the OSPF stub area
C. all OSPF inter and intra-area routes
D. all routes originating from RIP and OSPF routing domains
Under which condition does UDP dominance occur?
A. when TCP traffic is in the same class as UDP
B. when UDP flows are assigned a lower priority queue
C. when WRED is enabled
D. when ACLs are in place to block TCP traffic
Refer to the exhibit.When you examine the routing tables of R1 and R4, you are not able to see the R1 Ethernet subnet on the R4 routing table. You are also not able to see the R4 Ethernet subnet on the R1 routing table. Which two configuration changes should be made to resolve this issue? Select the routers where the configuration change will be required, and select the required EIGRP configuration command(s). Choose two answers. (Choose two.)
A. R1 and R4
B. R2 and R3
C. ip summary-address eigrp 1 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 and ip summary-address eigrp 1 10.2.2.0 255.255.255.0
D. variance 2
E. eigrp stub connected
For troubleshooting purposes, which method can you use in combination with the "debug ip packet" command to limit the amount of output data?
A. You can disable the IP route cache globally.
B. You can use the KRON scheduler.
C. You can use an extended access list.
D. You can use an IOS parser.
E. You can use the RITE traffic exporter.
A customer requests policy-based routing. Packets arriving from source 209.165.200.225 should be sent to the next hop at 209.165.200.227, with the precedence bit set to priority. Packets arriving from source 209.165.200.226 should be sent to the next hop at 209.165.200.228, with the precedence bit set to critical. Which configuration completes these requirements?
A. access-list 1 permit 209.165.200.225 access-list 2 permit 209.165.200.226 ! route-map Texas permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip precedence critical set ip next “”hop 209.165.200.227 ! route-map Texas permit 20 match ip address 2 set ip precedence priority set ip next-hop 209.165.200.228 ! interface ethernet 1 ip policy route-map Texas
B. access-list 1 permit 209.165.200.225 access-list 2 permit 209.165.200.226 ! route-map Texas permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip precedence priority set ip next “”hop 209.165.200.227 ! route-map Texas permit 20 match ip address 2 set ip precedence critical set ip next-hop 209.165.200.228 ! interface ethernet 1 ip policy route-map Texas
C. access-list 1 permit 209.165.200.228 access-list 2 permit 209.165.200.227 ! route-map Texas permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip precedence priority set ip next “”hop 209.165.200.226 ! route-map Texas permit 20 match ip address 2 set ip precedence critical set ip next-hop 209.165.200.225 ! interface ethernet 1 ip policy route-map Texas
D. access-list 1 permit 209.165.200.227 access-list 2 permit 209.165.200.228 ! route-map Texas permit 10 match ip address 1 set ip precedence priority set ip next “”hop 209.165.200.225 !
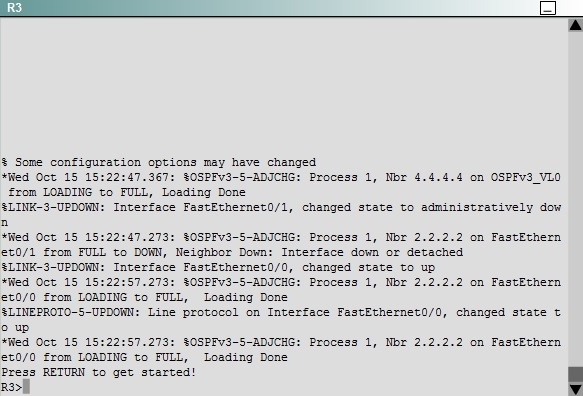
Scenario: You have been asked to evaluate an OSPF network setup in a test lab and to answer questions a customer has about its operation. The customer has disabled your access to the show running-config command.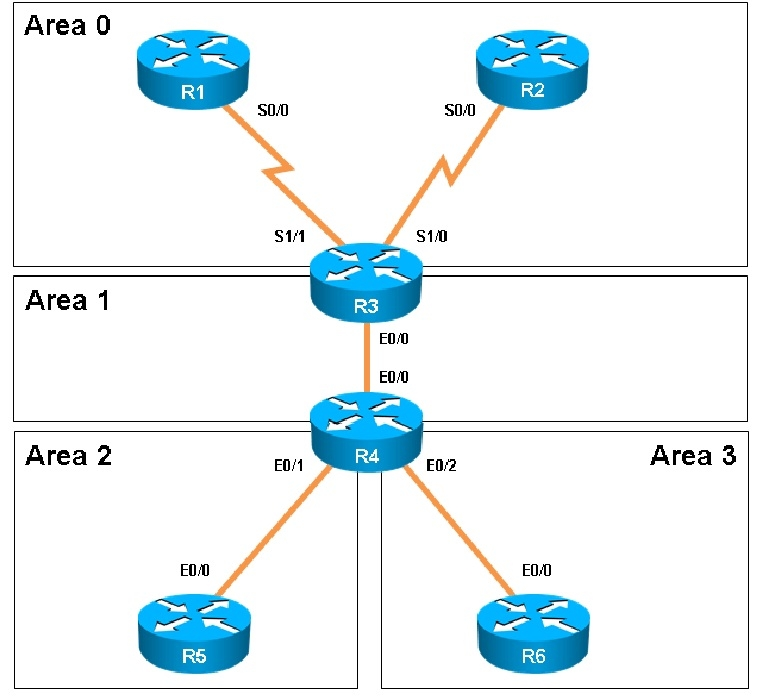
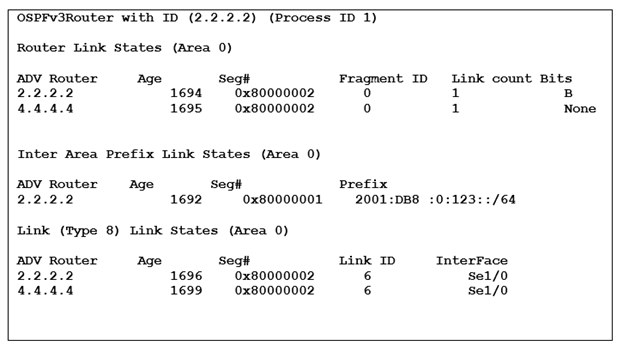
How many times was SPF algorithm executed on R4 for Area 1?
A. 1
B. 5
C. 9
D. 20
E. 54
F. 224
ROUTE.com is a small IT corporation that has an existing enterprise network that is running IPv6 0SPFv3. Currently OSPF is configured on all routers. However, R4's loopback address (FEC0:4:4) cannot be seen in R1's IPv6 routing table. You are tasked with identifying the cause of this fault and implementing the needed corrective actions that uses OPSF features and does not change the current area assignments. You will know that you have corrected the fault when R4's loopback address (FEC0:4:4) can be seen in RTs IPv6 routing table. Special Note: To gain the maximum number of points you must remove all incorrect or unneeded configuration statements related to this issue.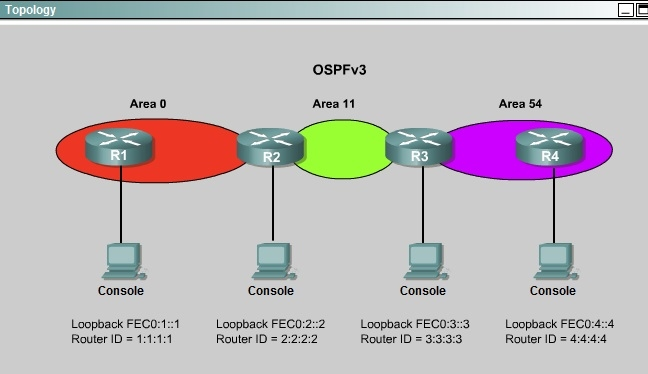
A. B. C. D.
When an EIGRP topology change is detected, what is the correct order of events when there is a FS?
A. The neighbor adjacency is deleted. The feasible route is used. DUAL is notified. Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
B. DUAL is notified. Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor. The neighbor adjacency is deleted. Routes enter the Active state and the feasible route is used.
C. The neighbor adjacency is deleted. Routes enter the Active state and the feasible route is used. DUAL is notified. Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
D. DUAL is notified. The neighbor adjacency is deleted. Remove all topology entries learned from that neighbor.
You have completed an OSPF implementation, and you are verifying OSPF operation. During this verification, you notice that the OSPF route of 172.16.10.0 is repeatedly appearing and disappearing from the routing table. Further investigation finds that the OSPF CPU utilization is very high and the routers are constantly performing SPF calculations. You determine that 172.16.20.2 is the source of the 172.16.10.0 route. Using the show ip ospf database router 172.16.20.1 command, you notice that when this show command is performed repeatedly, the contents of the LSA change every few seconds. What could be the cause of this problem?
A. OSPF authentication errors between some of the routers.
B. Two routers have the same OSPF router ID.
C. Issues with mistuned OSPF timers.
D. OSPF LSA pacing issues between some of the routers.
Refer to the exhibit.Which command only announces the 1.2.3.0/24 network out of FastEthernet 0/0?
A. distribute list 1 out
B. distribute list 1 out FastEthernet0/0
C. distribute list 2 out
D. distribute list 2 out FastEthernet0/0
Refer to exhibit.The exhibit shows R1 topology table to reach 192.168.1.0/24 network. Which route(s) will be installed in routing table of R1 to reach network 192.168.1.0/24 after configuring R1 with the following command? Router(config-router)# variance 2
A. R2 only
B. R2 and R3
C. R2 and R4
What does the default value of the EIGRP variance command of 1 mean?
A. Load balancing is disabled on this router.
B. The router performs equal-cost load balancing.
C. Only the path that is the feasible successor should be used.
D. The router only performs equal-cost load balancing on all paths that have a metric greater than 1.
You have been asked to evaluate how EIGRP is functioning in a customer network.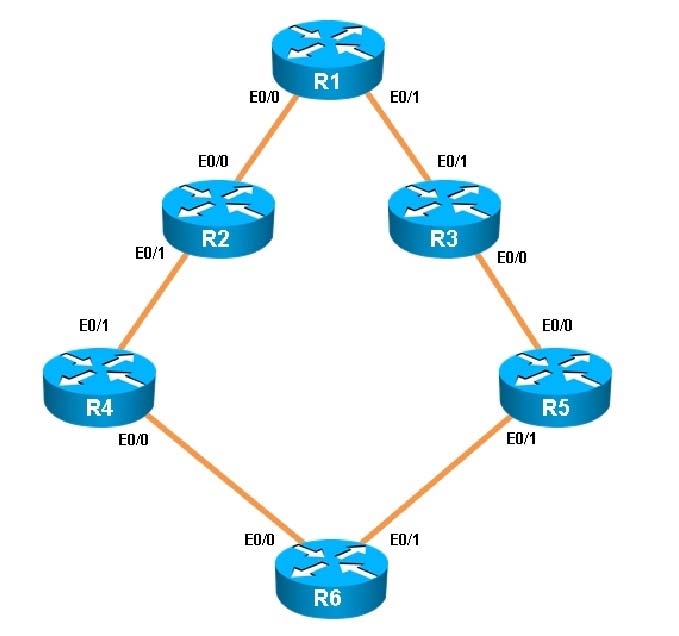
Which key chain is being used for authentication of EIGRP adjacency between R4 and R2?
A. CISCO
B. EIGRP
C. key
D. MD5
Scenario: You have been asked to evaluate an OSPF network setup in a test lab and to answer questions a customer has about its operation. The customer has disabled your access to the show running-config command. Which of the following statements is true about the serial links that terminate in R3
A. The R1-R3 link needs the neighbor command for the adjacency to stay up
B. The R2-R3 link OSPF timer values are 30, 120, 120
C. The R1-R3 link OSPF timer values should be 10,40,40
D. R3 is responsible for flooding LSUs to all the routers on the network.
A network administrator executes the command clear ip route. Which two tables does this "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 4 command clear and rebuild? (Choose two.)
A. IP routing
B. FIB
C. ARP cache
D. MAC address table
E. Cisco Express Forwarding table
F. topology table
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer has configured GRE between two IOS routers. The state of the tunnel interface is continuously oscillating between up and down. What is the solution to this problem?
A. Create a more specific ARP entry to define how to reach the remote router.
B. Save the configuration and reload the router.
C. Create a more specific static route to define how to reach the remote router.
D. Check whether the Internet service provider link is stable,
Drag and drop the Cisco Express Forwarding adjacency types from the left to the correct type of processing on the right.A. B. C. D.
By default, which statement is correct regarding the redistribution of routes from other routing protocols into OSPF? Select the best response.
A. They will appear in the OSPF routing table as type E1 routes.
B. They will appear in the OSPF routing table as type E2 routes
C. Summarized routes are not accepted.
D. All imported routes will be automatically summarized when possible.
E. Only routes with lower administrative distances will be imported. B
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer executes the show ipv6 ospf database command and is presented with the output that is shown. Which flooding scope is referenced in the link-state type?
A. Link-local
B. Area
C. As (OSPF domain)
D. Reserved
Scenario: You have been asked to evaluate an OSPF network setup in a test lab and to answer questions a customer has about its operation. The customer has disabled your access to the show running-config command.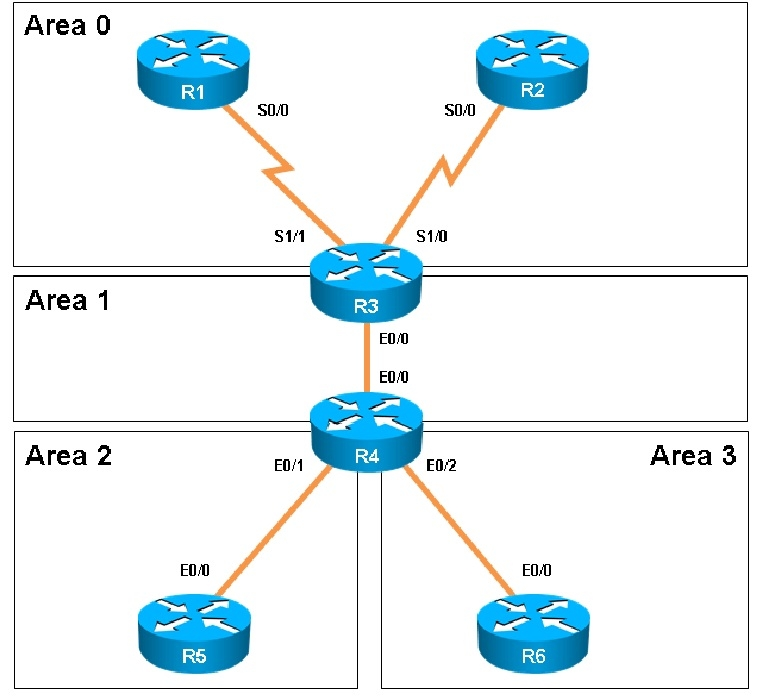
Which of the following statements is true about the serial links that terminate in R3
A. The R1-R3 link needs the neighbor command for the adjacency to stay up
B. The R2-R3 link OSPF timer values are 30, 120, 120
C. The R1-R3 link OSPF timer values should be 10,40,40
D. R3 is responsible for flooding LSUs to all the routers on the network.
How is network layer addressing accomplished in the OSI protocol suite?
A. Internet Protocol address
B. Media Access Control address
C. Packet Layer Protocol address
D. Network Service Access Point address
E. Authority and Format Identifier address
Which Cisco Express Forwarding component(s) contain forwarding information?
A. FIB, adjacency table
B. adjacency table
C. FIB, RIB, Adjanceny table
D. FIB
E. RIB
Which command can be entered on router R5 to configure 80 percent of the bandwidth of a link for EIGRP Autonomous System 55?
A. R5(config-if#)#ip bandwidth percent eigrp bandwidth 55 80
B. R5(config-pmap-c)#priority percent 80
C. R5(config-if)#ipv6 bandwidth-percent eigrp 55 80
D. R5(config-if)#ipv6 bandwidth-percent eigrp 80 55
E. R5(config-if)#ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 80 55
Which two statements are true about EIGRP manual summarization? (Choose two.)
A. Manual summarization is configured on a per interface basis.
B. Manual summaries can be configured with the classful mask only.
C. When manual summarization is configured, autosummarization is automatically disabled by default.
D. The summary address is assigned an administrative distance of 10 by default.
E. The summary address is entered into the routing table and is shown to be sourced from the Null0 interface.
Which TCP port for BGP?
A. port 161
B. port 123
C. port 179
D. port 47
After implementing EIGRP on your network, you issue the show ip eigrp traffic command on router C. The following output is shown: RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic - IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1 Hellos sent/received: 2112/2076 - Updates sent/received: 47/38 - Queries sent/received: 5/3 - Replies sent/received: 3/4 - Acks sent/received: 29/33 - Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0 - SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0 - Moments later, you issue the same command a second time and the following output is shown: RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic - IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1 Hellos sent/received: 2139/2104 - Updates sent/received: 50/39 - Queries sent/received: 5/4 - Replies sent/received: 4/4 - Acks sent/received: 31/37 - Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0 - SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0 - Moments later, you issue the same command a third time and the following output is shown: RouterC#show ip eigrp traffic - IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 1 Hellos sent/received: 2162/2126 - Updates sent/received: 53/42 - Queries sent/received: 5/5 - Replies sent/received: 5/4 - Acks sent/received: 35/41 - Input queue high water mark 2, 0 drops SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0 - SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0 - What information can you determine about this network?
A. The network is stable.
B. There is a flapping link or interface, and router C knows an alternate path to the network.
C. There is a flapping link or interface, and router C does not know an alternate path to the network.
D. EIGRP is not working correctly on router C.
E. There is not enough information to make a determination.
Which three items can you track when you use two time stamps with IP SLAs? (Choose three.)
A. delay
B. jitter
C. packet loss
D. load
E. throughput
F. path
Refer to the exhibit.After configuring the routes, the network engineer executes the show ip route command. What is the expected results?
A. Gateway of last resort is 10.0.2.1 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets C 10.0.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 10.0.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 S*0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.0.2.1(1/0] via 10.0.1.1
B. Gateway of last resort is 10 0.2 1 to network 0.0.0.0 10 0.0 0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnet C 10.0.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 S* 0.0.0 0/0 [1/0] via 10.0.2.1
C. Gateway of last report is not set
D. Gateway of test resort is 10.0.1.1 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted 1 subnet C 10.0.1.0 is directly connected FastEthernet0/1 S*0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.0.1.1
Which two statements about EVN are true? (Choose two.)
A. Virtual network tags are assigned per-VRF.
B. It is supported only on access ports.
C. Virtual network tags are assigned globally.
D. Routing metrics can be manipulated only from directly within the routing-context configuration.
E. The VLAN ID in the 802.1q frame carries the virtual network tag.
F. The VLAN ID is the ISL frame carries the virtual network tag. AE
The following configuration is applied to a router at a branch site: ipv6 dhcp pool dhcp-pool dns-server 2001:DB8:1:B::1 dns-server 2001:DB8:3:307C::42 domain-name example.com ! If IPv6 is configured with default settings on all interfaces on the router, which two dynamic IPv6 addressing mechanisms could you use on end hosts to provide end-to-end connectivity? (Choose two.)
A. EUI-64
B. SLAAC
C. DHCPv6
D. BOOTP
What two situations could require the use of multiple routing protocols? (Choose two)
A. when using UNIX host-based routers
B. when smaller broadcast domains are desired
C. because having multiple routing protocols confuses hackers
D. when migrating from an older Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) to a new IGP
E. when all equipment is manufactured by Cisco
F. when there are multiple paths to destination networks AD
Refer to the exhibit.Network administrators have set up a hub and spoke topology with redundant connections using EIGRP. However, they are concerned that a network outage between Router R1 and Router R2 will cause traffic from the 10.1.1.x network to the 10.1.2.x network to traverse the remote office links and overwhelm them. What command should be used to configure the spoke routers as EIGRP stub routers that will not advertise connected networks, static routes, or summary addresses?
A. eigrp stub
B. eigrp stub receive-only
C. eigrp stub connected static
D. no eigrp stub connected static
E. No additional command is needed beyond a default EIGRP configuration.
Which routing protocol will continue to receive and process routing updates from neighbors after the passive interface router configuration command is entered?
A. EIGRP
B. RIP
C. OSPF
D. IS-IS
A network administrator is troubleshooting a DMVPN setup between the hub and the spoke. Which action should the administrator take before troubleshooting the IPsec configuration?
A. Verify the GRE tunnels.
B. Verify ISAKMP.
C. Verify NHRP.
D. Verify crypto maps.
Based on the exhibited output, which three statements are true? (Choose three.)
A. R1 is configured with the variance command.
B. The route to 10.2.0.0/16 was redistributed into EIGRP.
C. A default route has been redistributed into the EIGRP autonomous system.
D. R1 is configured with the ip summary-address command.
E. The router at 10.1.1.2 is configured with the ip default-network 0.0.0.0 command.
Which STP feature can reduce TCNs on ports that are connected to end devices?
A. BPDU guard
B. Root guard
C. PortFast
D. BackboneFast
A network engineer is migrating an IPv4 point-to multipoint Frame Relay network to IPv6. Which IPv6 address type must be used in a Frame Relay map configuration command to ensure that the OSPF protocol still works after migration?
A. unique-local
B. link-local
C. global
D. site-local
E. multicast
Refer to the following. Router # sh ip route eigrp - 13.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks D 13.0.0.0/8 is a summary, 00:00:32, Null0 What happens to packets that are forwarded from the 13.0.0.0/8 network to the Null0 interface?
A. Flagged
B. Accepted
C. Summarized
D. Dropped
Refer to the exhibit.What happens when the router stops receiving advertisements for the 10.1.2.0/24 network?
A. The summary route will be removed from the table.
B. The summary route will remain in the table.
C. The more specific routes will be advertised from the table.
D. 10.1.2.0/24 will still be advertised but packets destined for it will be dropped when they reach this router.
When using SNMPv3 with NoAuthNoPriv, which string is matched for authentication?
A. username
B. password
C. community-string
D. encryption-key
What are two important differences between OSPFv2 and OSPFv3? (Choose two.)
A. Only OSPFv3 provides support for IPv6.
B. Only OSPFv3 automatically chooses a router ID for the local device.
C. Only OSPFv3 automatically enable interfaces when you create them in device configuration mode.
D. Only OSPFv3 supports multiple OSPF instances on a single link.
E. Only OSPFv3 automatically detects OSPF neighbors on an NBMA interface.
Refer to the Exhibit.Routers in the Diagram are configured with EIGRP. If RTB and RTC fail, which action will RTA take with respect to the HQ network?
A. RTA will automatically route packets via RTD to the HQ network.
B. RTA will place the route via RTD into the hold down state.
C. RTA will go into the active state for all routers.
Identify three characteristics of EIGRP feasible successors? (Choose three.)
A. A feasible successor is selected by comparing the advertised distance of a non-successor route to the feasible distance of the best route.
B. If the advertised distance of the non-successor route is less than the feasible distance of best route, then that route is identified as a feasible successor.
C. If the successor becomes unavailable, then the feasible successor can be used immediately without recalculating for a lost route.
D. The feasible successor can be found in the routing table.
E. Traffic will be load balanced between feasible successors with the same advertised distance.
Which two statements are true about EIGRP manual summarization? (Choose two.)
A. Manual summarization is configured on a per interface basis.
B. Manual summaries can be configured with the classful mask only.
C. When manual summarization is configured, autosummarization is automatically disabled by default.
D. The summary address is assigned an administrative distance of 10 by default.
E. The summary address is entered into the routing table and is shown to be sourced from the Null0 interface.
IP CEF load-sharing options (Choose three.)
A. Tunnel
B. Universal
C. Include-ports
D. Source
E. Destination ABC
What is the administrative distance for EBGP?
A. 200
B. 20
C. 30
D. 70
Refer to the exhibit.A company would prefer all Internet-bound OSPF routed traffic to use ISP ABC with ISP DEF as a backup. As the network consultant, what three configuration changes should you make? (Choose three.)
A. The default-information originate command should be configured on router B1 and B4.
B. The default-information originate command should be configured on router B2 and B3.
C. If the metric value for ISP ABC is set at the default, the ISP DEF metric value should be set to 1.
D. If the metric value for ISP ABC is set at the default, the ISP DEF metric value should be set to 25.
E. The metric type value should be set to type 1.
F. The metric type value should be set to type 2.
Free Access Full 300-101 Practice Exam Free
Looking for additional practice? Click here to access a full set of 300-101 practice exam free questions and continue building your skills across all exam domains.
Our question sets are updated regularly to ensure they stay aligned with the latest exam objectives—so be sure to visit often!
Good luck with your 300-101 certification journey!