212-89 Practice Exam Free – 50 Questions to Simulate the Real Exam
Are you getting ready for the 212-89 certification? Take your preparation to the next level with our 212-89 Practice Exam Free – a carefully designed set of 50 realistic exam-style questions to help you evaluate your knowledge and boost your confidence.
Using a 212-89 practice exam free is one of the best ways to:
- Experience the format and difficulty of the real exam
- Identify your strengths and focus on weak areas
- Improve your test-taking speed and accuracy
Below, you will find 50 realistic 212-89 practice exam free questions covering key exam topics. Each question reflects the structure and challenge of the actual exam.
Contingency planning enables organizations to develop and maintain effective methods to handle emergencies. Every organization will have its own specific requirements that the planning should address. There are five major components of the IT contingency plan, namely supporting information, notification activation, recovery and reconstitution and plan appendices. What is the main purpose of the reconstitution plan?
A. To restore the original site, tests systems to prevent the incident and terminates operations
B. To define the notification procedures, damage assessments and offers the plan activation
C. To provide the introduction and detailed concept of the contingency plan
D. To provide a sequence of recovery activities with the help of recovery procedures
Adam calculated the total cost of a control to protect 10,000 $ worth of data as 20,000 $. What do you advise Adam to do?
A. Apply the control
B. Not to apply the control
C. Use qualitative risk assessment
D. Use semi-qualitative risk assessment instead
Bit stream image copy of the digital evidence must be performed in order to:
A. Prevent alteration to the original disk
B. Copy the FAT table
C. Copy all disk sectors including slack space
D. All the above
An audit trail policy collects all audit trails such as series of records of computer events, about an operating system, application or user activities. Which of the following statements is NOT true for an audit trail policy:
A. It helps calculating intangible losses to the organization due to incident
B. It helps tracking individual actions and allows users to be personally accountable for their actions
C. It helps in compliance to various regulatory laws, rules,and guidelines
D. It helps in reconstructing the events after a problem has occurred
ADAM, an employee from a multinational company, uses his company's accounts to send e-mails to a third party with their spoofed mail address. How can you categorize this type of account?
A. Inappropriate usage incident
B. Unauthorized access incident
C. Network intrusion incident
D. Denial of Service incident
Computer forensics is methodical series of techniques and procedures for gathering evidence from computing equipment, various storage devices and or digital media that can be presented in a course of law in a coherent and meaningful format. Which one of the following is an appropriate flow of steps in the computer forensics process:
A. Examination> Analysis > Preparation > Collection > Reporting
B. Preparation > Analysis > Collection > Examination > Reporting
C. Analysis > Preparation > Collection > Reporting > Examination
D. Preparation > Collection > Examination > Analysis > Reporting
When an employee is terminated from his or her job, what should be the next immediate step taken by an organization?
A. All access rights of the employee to physical locations, networks, systems, applications and data should be disabled
B. The organization should enforce separation of duties
C. The access requests granted to an employee should be documented and vetted by the supervisor
D. The organization should monitor the activities of the system administrators and privileged users who have permissions to access the sensitive information
A computer forensic investigator must perform a proper investigation to protect digital evidence. During the investigation, an investigator needs to process large amounts of data using a combination of automated and manual methods. Identify the computer forensic process involved:
A. Analysis
B. Preparation
C. Examination
D. Collection
Preventing the incident from spreading and limiting the scope of the incident is known as:
A. Incident Eradication
B. Incident Protection
C. Incident Containment
D. Incident Classification
Which of the following is an incident tracking, reporting and handling tool:
A. CRAMM
B. RTIR
C. NETSTAT
D. EAR/ Pilar
Organizations or incident response teams need to protect the evidence for any future legal actions that may be taken against perpetrators that intentionally attacked the computer system. EVIDENCE PROTECTION is also required to meet legal compliance issues. Which of the following documents helps in protecting evidence from physical or logical damage:
A. Network and host log records
B. Chain-of-Custody
C. Forensic analysis report
D. Chain-of-Precedence
The left over risk after implementing a control is called:
A. Residual risk
B. Unaccepted risk
C. Low risk
D. Critical risk
US-CERT and Federal civilian agencies use the reporting timeframe criteria in the federal agency reporting categorization. What is the timeframe required to report an incident under the CAT 4 Federal Agency category?
A. Weekly
B. Within four (4) hours of discovery/detection if the successful attack is still ongoing and agency is unable to successfully mitigate activity
C. Within two (2) hours of discovery/detection
D. Monthly
The Linux command used to make binary copies of computer media and as a disk imaging tool if given a raw disk device as its input is:
A. “dd” command
B. “netstat” command
C. “nslookup” command
D. “find” command
Identify the malicious program that is masked as a genuine harmless program and gives the attacker unrestricted access to the user's information and system. These programs may unleash dangerous programs that may erase the unsuspecting user's disk and send the victim's credit card numbers and passwords to a stranger.
A. Cookie tracker
B. Worm
C. Trojan
D. Virus
The correct sequence of Incident Response and Handling is:
A. Incident Identification, recording, initial response, communication and containment
B. Incident Identification, initial response, communication, recording and containment
C. Incident Identification, communication, recording, initial response and containment
D. Incident Identification, recording, initial response, containment and communication
Ensuring the integrity, confidentiality and availability of electronic protected health information of a patient is known as:
A. Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act
B. Health Insurance Portability and Privacy Act
C. Social Security Act
D. Sarbanes-Oxley Act
Which of the following is NOT one of the common techniques used to detect Insider threats:
A. Spotting an increase in their performance
B. Observing employee tardiness and unexplained absenteeism
C. Observing employee sick leaves
D. Spotting conflicts with supervisors and coworkers
An access control policy authorized a group of users to perform a set of actions on a set of resources. Access to resources is based on necessity and if a particular job role requires the use of those resources. Which of the following is NOT a fundamental element of access control policy
A. Action group: group of actions performed by the users on resources
B. Development group: group of persons who develop the policy
C. Resource group: resources controlled by the policy
D. Access group: group of users to which the policy applies
A distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is a more common type of DoS Attack, where a single system is targeted by a large number of infected machines over the Internet. In a DDoS attack, attackers first infect multiple systems which are known as:
A. Trojans
B. Zombies
C. Spyware
D. Worms
A Host is infected by worms that propagates through a vulnerable service; the sign(s) of the presence of the worm include:
A. Decrease in network usage
B. Established connection attempts targeted at the vulnerable services
C. System becomes instable or crashes
D. All the above
Which policy recommends controls for securing and tracking organizational resources:
A. Access control policy
B. Administrative security policy
C. Acceptable use policy
D. Asset control policy
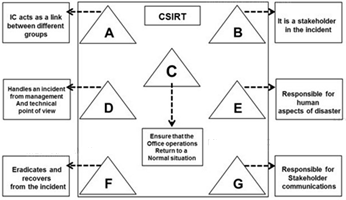
The flow chart gives a view of different roles played by the different personnel of CSIRT. Identify the incident response personnel denoted by A, B, C, D, E, F and G.
A. A-Incident Analyst, B- Incident Coordinator, C- Public Relations, D-Administrator, E- Human Resource, F-Constituency, G-Incident Manager
B. A- Incident Coordinator, B-Incident Analyst, C- Public Relations, D-Administrator, E- Human Resource, F-Constituency, G-Incident Manager
C. A- Incident Coordinator, B- Constituency, C-Administrator, D-Incident Manager, E- Human Resource, F-Incident Analyst, G-Public relations
D. A- Incident Manager, B-Incident Analyst, C- Public Relations, D-Administrator, E- Human Resource, F-Constituency, G-Incident Coordinator
Which of the following is a correct statement about incident management, handling and response:
A. Incident response is on the functions provided by incident handling
B. Incident handling is on the functions provided by incident response
C. Triage is one of the services provided by incident response
D. Incident response is one of the services provided by triage
What is correct about Quantitative Risk Analysis:
A. It is Subjective but faster than Qualitative Risk Analysis
B. Easily automated
C. Better than Qualitative Risk Analysis
D. Uses levels and descriptive expressions
Absorbing minor risks while preparing to respond to major ones is called:
A. Risk Mitigation
B. Risk Transfer
C. Risk Assumption
D. Risk Avoidance
Insider threats can be detected by observing concerning behaviors exhibited by insiders, such as conflicts with supervisors and coworkers, decline in performance, tardiness or unexplained absenteeism. Select the technique that helps in detecting insider threats:
A. Correlating known patterns of suspicious and malicious behavior
B. Protecting computer systems by implementing proper controls
C. Making is compulsory for employees to sign a none disclosure agreement
D. Categorizing information according to its sensitivity and access rights
In which of the steps of NIST's risk assessment methodology are the boundary of the IT system, along with the resources and the information that constitute the system identified?
A. Likelihood Determination
B. Control recommendation
C. System characterization
D. Control analysis
An estimation of the expected losses after an incident helps organization in prioritizing and formulating their incident response. The cost of an incident can be categorized as a tangible and intangible cost. Identify the tangible cost associated with virus outbreak?
A. Loss of goodwill
B. Damage to corporate reputation
C. Psychological damage
D. Lost productivity damage
Computer viruses are malicious software programs that infect computers and corrupt or delete the data on them. Identify the virus type that specifically infects Microsoft Word files?
A. Micro Virus
B. File Infector
C. Macro Virus
D. Boot Sector virus
One of the goals of CSIRT is to manage security problems by taking a certain approach towards the customers' security vulnerabilities and by responding effectively to potential information security incidents. Identify the incident response approach that focuses on developing the infrastructure and security processes before the occurrence or detection of an event or any incident:
A. Interactive approach
B. Introductive approach
C. Proactive approach
D. Qualitative approach
Which of the following terms may be defined as "a measure of possible inability to achieve a goal, objective, or target within a defined security, cost plan and technical limitations that adversely affects the organization's operation and revenues?
A. Risk
B. Vulnerability
C. Threat
D. Incident Response
Which of the following service(s) is provided by the CSIRT:
A. Vulnerability handling
B. Technology watch
C. Development of security tools
D. All the above
Incidents such as DDoS that should be handled immediately may be considered as:
A. Level One incident
B. Level Two incident
C. Level Three incident
D. Level Four incident
An assault on system security that is derived from an intelligent threat is called:
A. Threat Agent
B. Vulnerability
C. Attack
D. Risk
A computer Risk Policy is a set of ideas to be implemented to overcome the risk associated with computer security incidents. Identify the procedure that is NOT part of the computer risk policy?
A. Procedure to identify security funds to hedge risk
B. Procedure to monitor the efficiency of security controls
C. Procedure for the ongoing training of employees authorized to access the system
D. Provisions for continuing support if there is an interruption in the system or if the system crashes
The free, open source, TCP/IP protocol analyzer, sniffer and packet capturing utility standard across many industries and educational institutions is known as:
A. Snort
B. Wireshark
C. Cain & Able
D. nmap
A US Federal agency network was the target of a DoS attack that prevented and impaired the normal authorized functionality of the networks. According to agency's reporting timeframe guidelines, this incident should be reported within two (2) HOURS of discovery/detection if the successful attack is still ongoing and the agency is unable to successfully mitigate the activity. Which incident category of the US Federal Agency does this incident belong to?
A. CAT 5
B. CAT 1
C. CAT 2
D. CAT 6
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of flow of the stages in an incident response:
A. Containment – Identification – Preparation – Recovery – Follow-up – Eradication
B. Preparation – Identification – Containment – Eradication – Recovery – Follow-up
C. Eradication – Containment – Identification – Preparation – Recovery – Follow-up
D. Identification – Preparation – Containment – Recovery – Follow-up – Eradication
A threat source does not present a risk if NO vulnerability that can be exercised for a particular threat source. Identify the step in which different threat sources are defined:
A. Identification Vulnerabilities
B. Control analysis
C. Threat identification
D. System characterization
Which of the following incidents are reported under CAT -5 federal agency category?
A. Exercise/ Network Defense Testing
B. Malicious code
C. Scans/ probes/ Attempted Access
D. Denial of Service DoS
An information security incident is
A. Any real or suspected adverse event in relation to the security of computer systems or networks
B. Any event that disrupts normal today’s business functions
C. Any event that breaches the availability of information assets
D. All of the above
If the loss anticipated is greater than the agreed upon threshold; the organization will:
A. Accept the risk
B. Mitigate the risk
C. Accept the risk but after management approval
D. Do nothing
Risk management consists of three processes, risk assessment, mitigation and evaluation. Risk assessment determines the extent of the potential threat and the risk associated with an IT system through its SDLC. How many primary steps does NIST's risk assessment methodology involve?
A. Twelve
B. Four
C. Six
D. Nine
Based on the some statistics; what is the typical number one top incident?
A. Phishing
B. Policy violation
C. Un-authorized access
D. Malware
A payroll system has a vulnerability that cannot be exploited by current technology. Which of the following is correct about this scenario:
A. The risk must be urgently mitigated
B. The risk must be transferred immediately
C. The risk is not present at this time
D. The risk is accepted
The service organization that provides 24x7 computer security incident response services to any user, company, government agency, or organization is known as:
A. Computer Security Incident Response Team CSIRT
B. Security Operations Center SOC
C. Digital Forensics Examiner
D. Vulnerability Assessor
An incident recovery plan is a statement of actions that should be taken before, during or after an incident. Identify which of the following is NOT an objective of the incident recovery plan?
A. Creating new business processes to maintain profitability after incident
B. Providing a standard for testing the recovery plan
C. Avoiding the legal liabilities arising due to incident
D. Providing assurance that systems are reliable
One of the main objectives of incident management is to prevent incidents and attacks by tightening the physical security of the system or infrastructure. According to CERT's incident management process, which stage focuses on implementing infrastructure improvements resulting from postmortem reviews or other process improvement mechanisms?
A. Protection
B. Preparation
C. Detection
D. Triage
Incident management team provides support to all users in the organization that are affected by the threat or attack. The organization's internal auditor is part of the incident response team. Identify one of the responsibilities of the internal auditor as part of the incident response team:
A. Configure information security controls
B. Perform necessary action to block the network traffic from suspected intruder
C. Identify and report security loopholes to the management for necessary actions
D. Coordinate incident containment activities with the information security officer
Free Access Full 212-89 Practice Exam Free
Looking for additional practice? Click here to access a full set of 212-89 practice exam free questions and continue building your skills across all exam domains.
Our question sets are updated regularly to ensure they stay aligned with the latest exam objectives—so be sure to visit often!
Good luck with your 212-89 certification journey!