vSphere Virtualization of Resources
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objective:
• Explain how vSphere interacts with CPUs, memory, networks, and storage
Virtual Machine: Guest and Consumer of ESXi Host
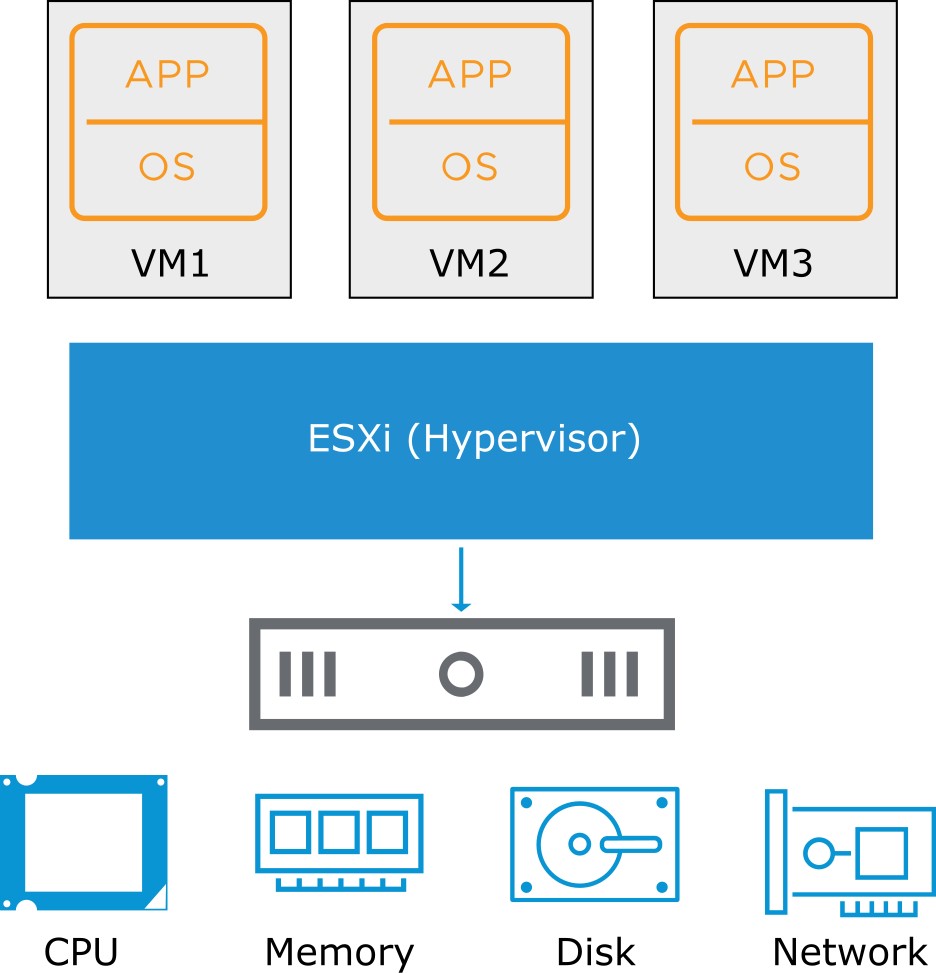
Any application in any supported OS can run in a VM (guest) and consume CPU, memory, disk, and network from host-based resources.
Physical and Virtual Architecture
Virtualization technology abstracts physical components into software components and provides solutions for many IT problems. 
Physical Resource Sharing
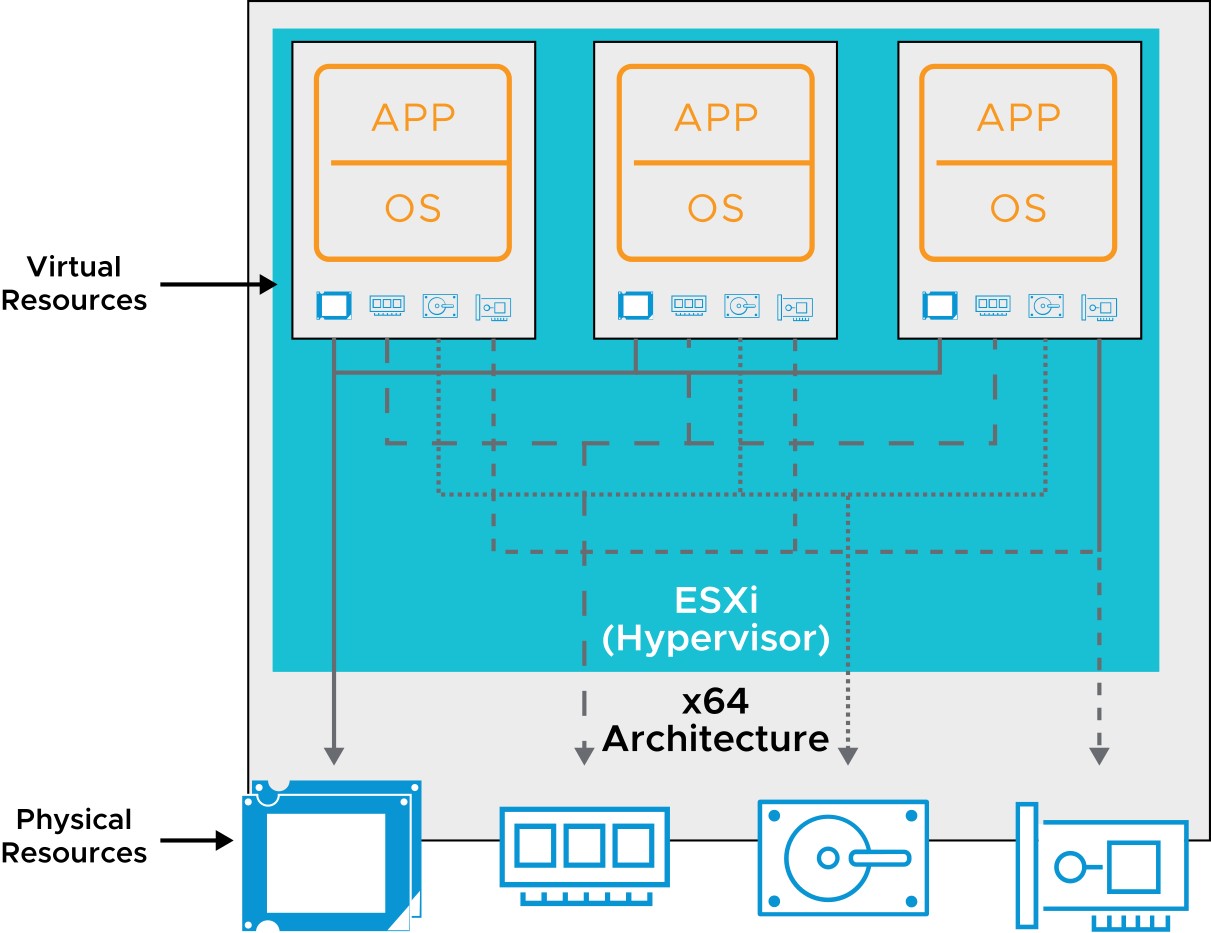
Multiple VMs, running on a physical host, share the compute, memory, network, and storage resources of the host.
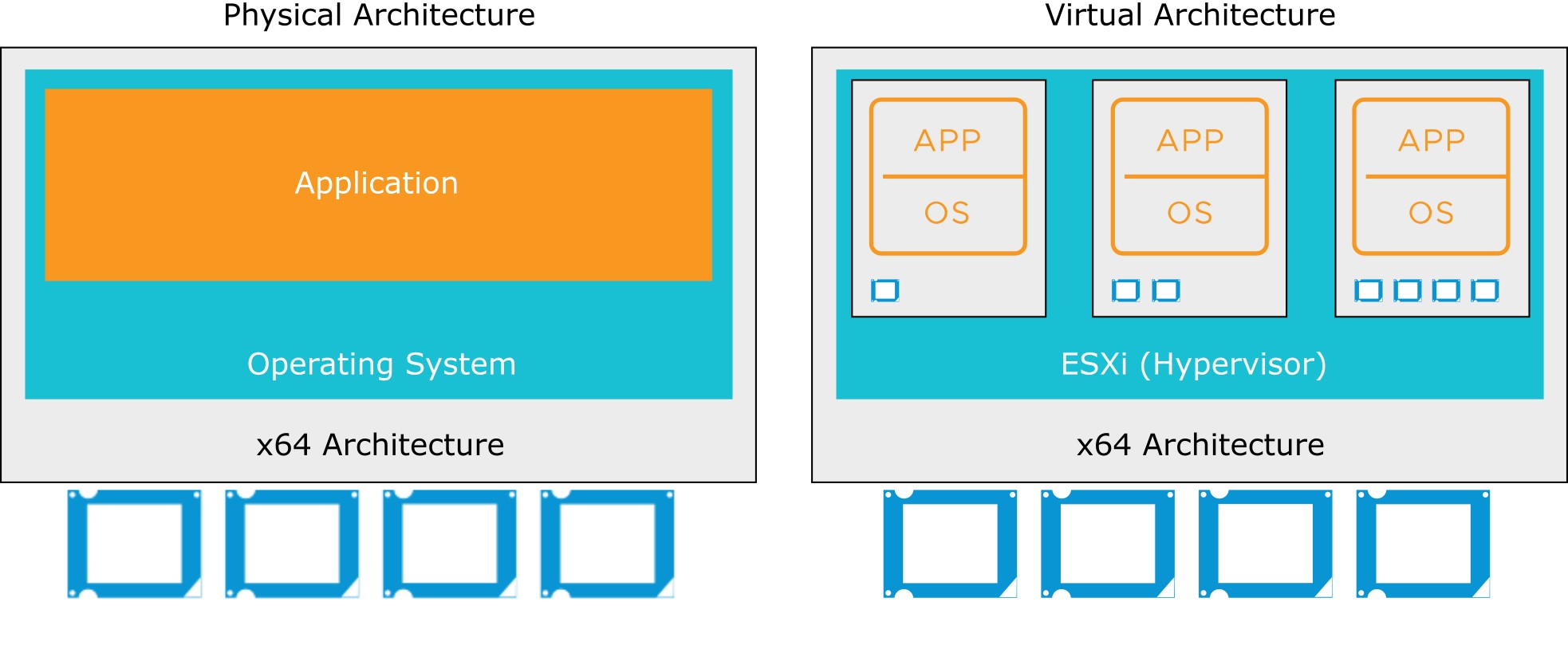
CPU Virtualization
- In a physical environment, the operating system assumes the ownership of all the physical CPUs in the system.
- CPU virtualization emphasizes performance and runs directly on the available CPUs.
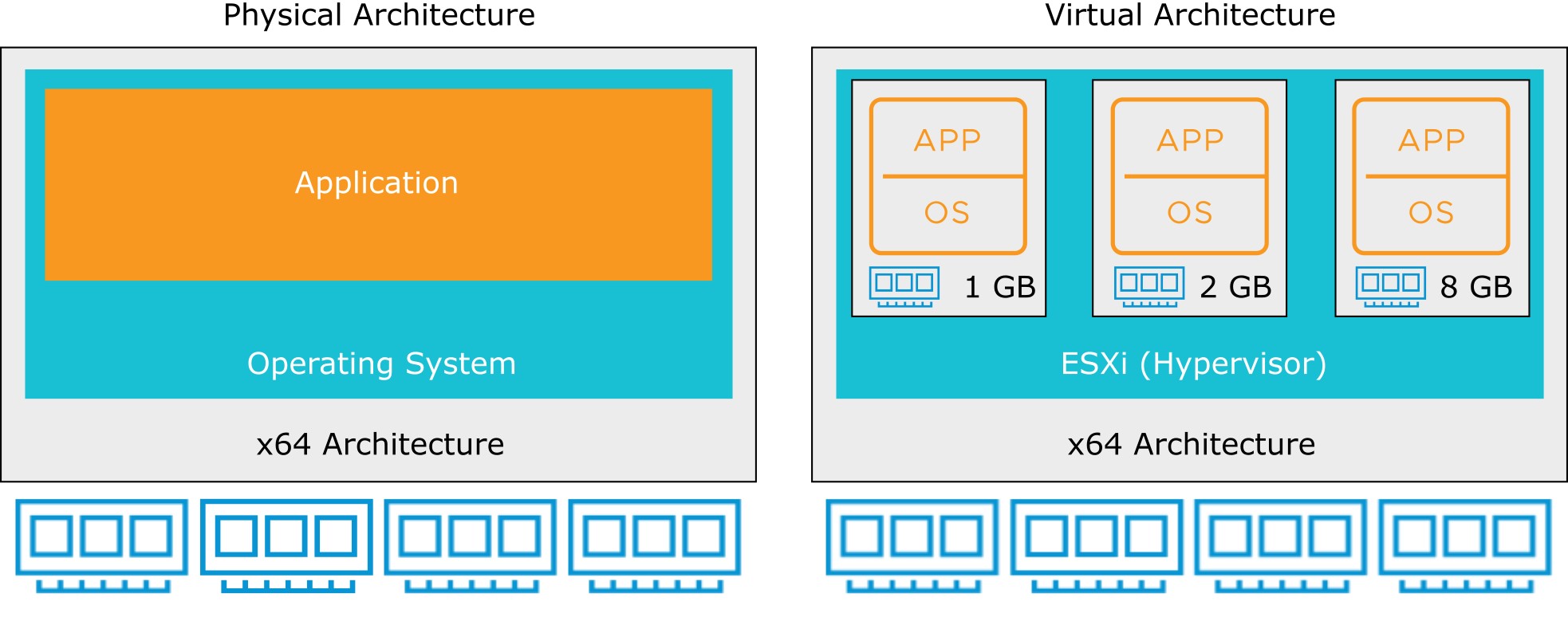
Physical and Virtualized Host Memory Usage
- In a physical environment, the operating system assumes the ownership of all physical memory in the system.
- Memory virtualization emphasizes performance and runs directly on the available RAM.
Physical and Virtual Networking
- Virtual Ethernet adapters and virtual switches are key virtual networking components.
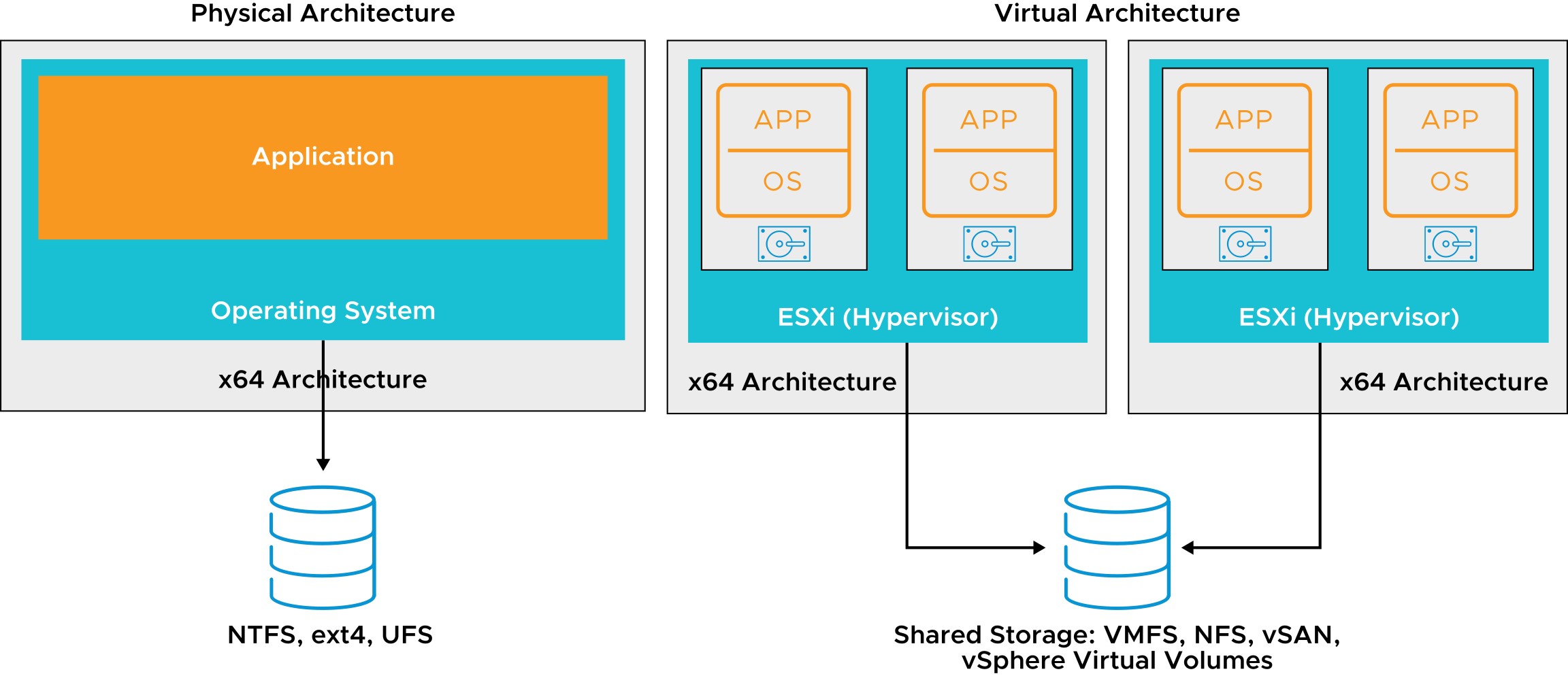
Physical File Systems and Datastores
- vSphere VMFS provides a distributed storage architecture, where multiple ESXi hosts can read or write to the shared storage concurrently.
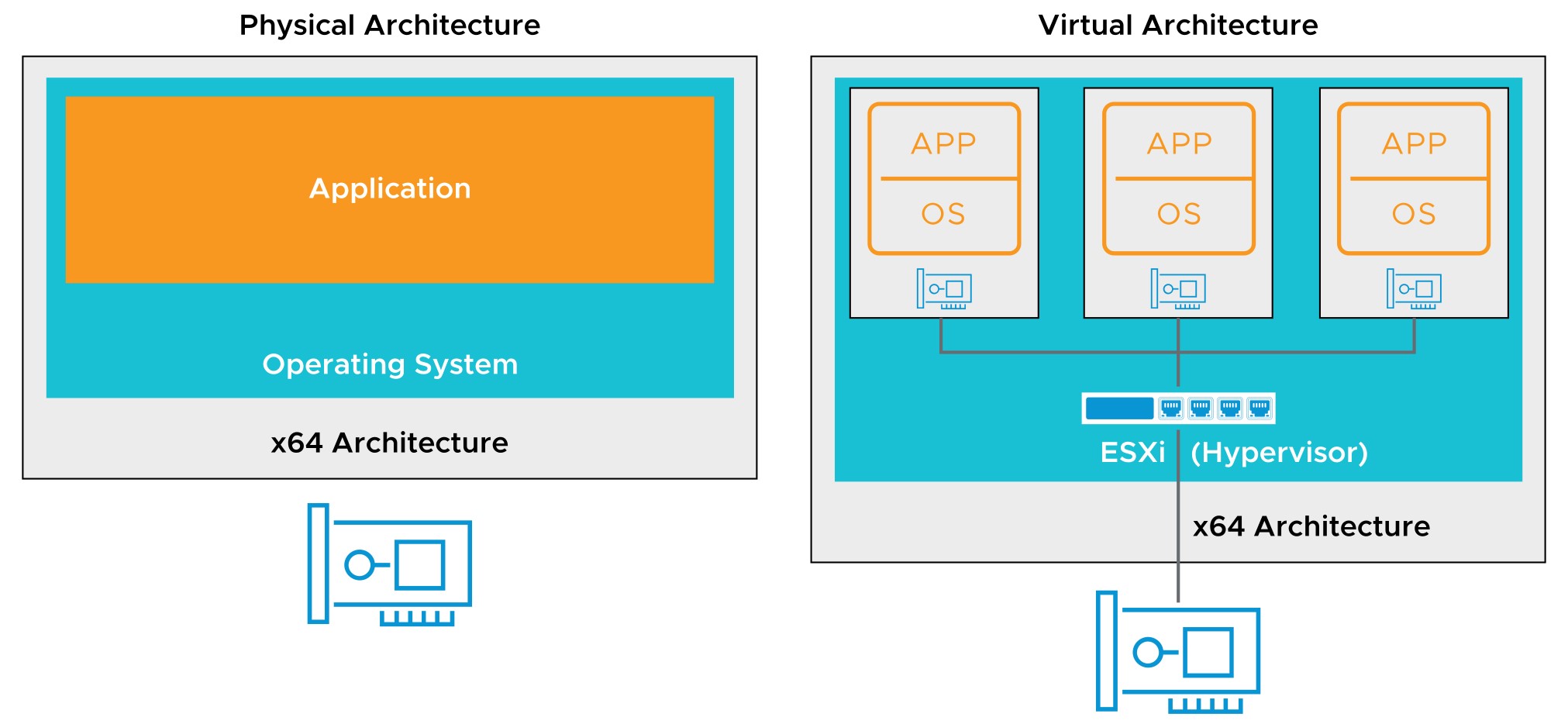
GPU Virtualization
GPU graphics devices optimize complex graphics operations. These operations can run at high performance without overloading the CPU. Virtual GPUs can be added to VMs for the following use cases:
- Rich 2D and 3D graphics
- VMware Horizon virtual desktops
- Graphics-intensive applications, such as those used by architects and engineers
- Server applications for massively parallel tasks, such as scientific computation applications You can configure VMs with up to four vGPU devices to cover use cases requiring multiple GPU accelerators.
VMware supports AMD and NVIDIA graphics cards.
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, vSphere Virtualization of Resources, you should be able to meet the following objective:
• Explain how vSphere interacts with CPUs, memory, networks, and storage