vSphere Replication and Backup
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Identify the components in the vSphere Replication architecture
- Deploy and configure vSphere Replication
- Recover replicated virtual machines
- Explain the backup and restore solution for VMs
- Describe the benefits of vSphere Storage APIs – Data Protection
About vSphere Replication

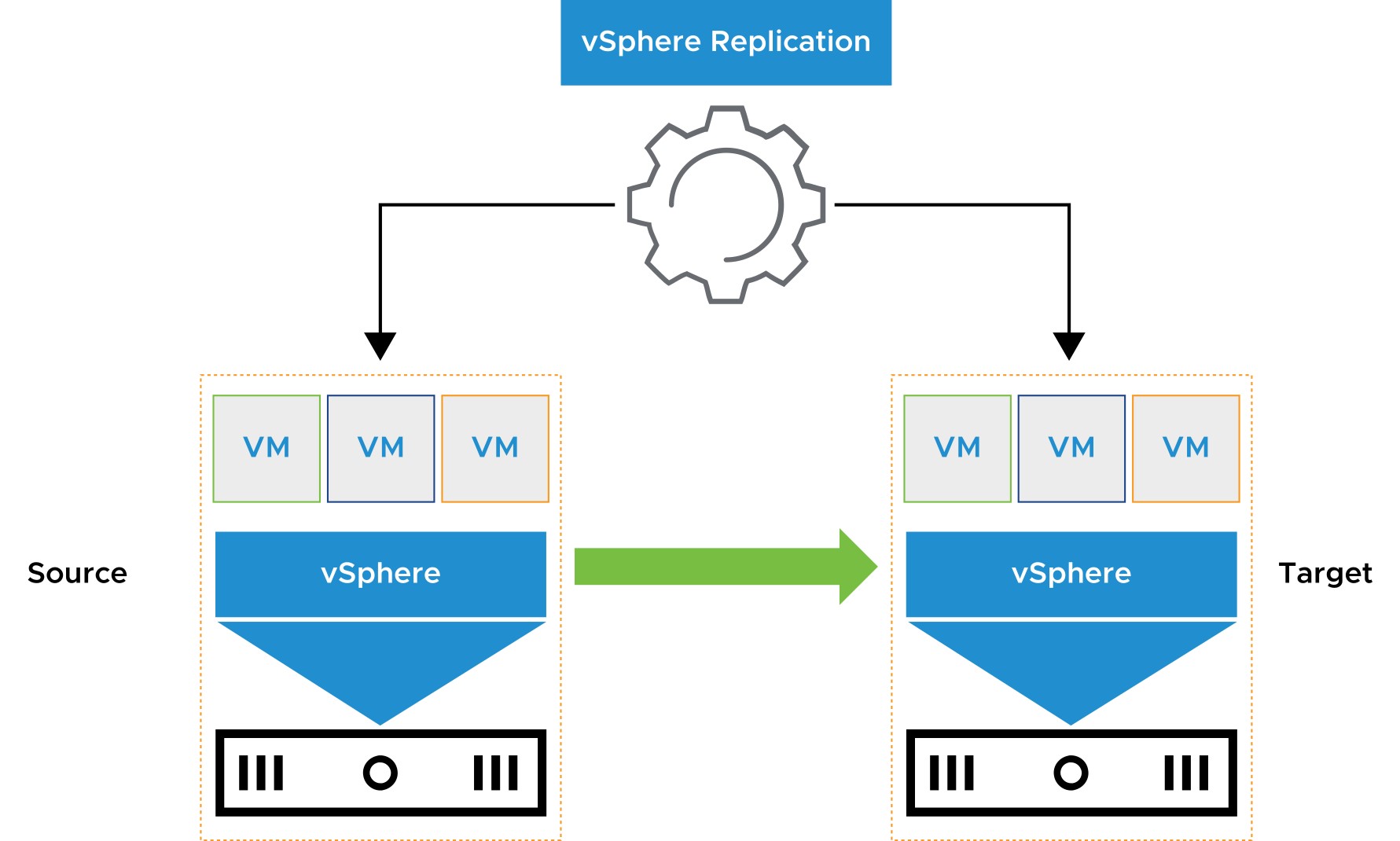
- vSphere Replication is an extension for vCenter Server.
- It provides hypervisor-based VM replication and recovery.
About the vSphere Replication Appliance
The vSphere Replication appliance provides all the components that are required to perform VM replication. 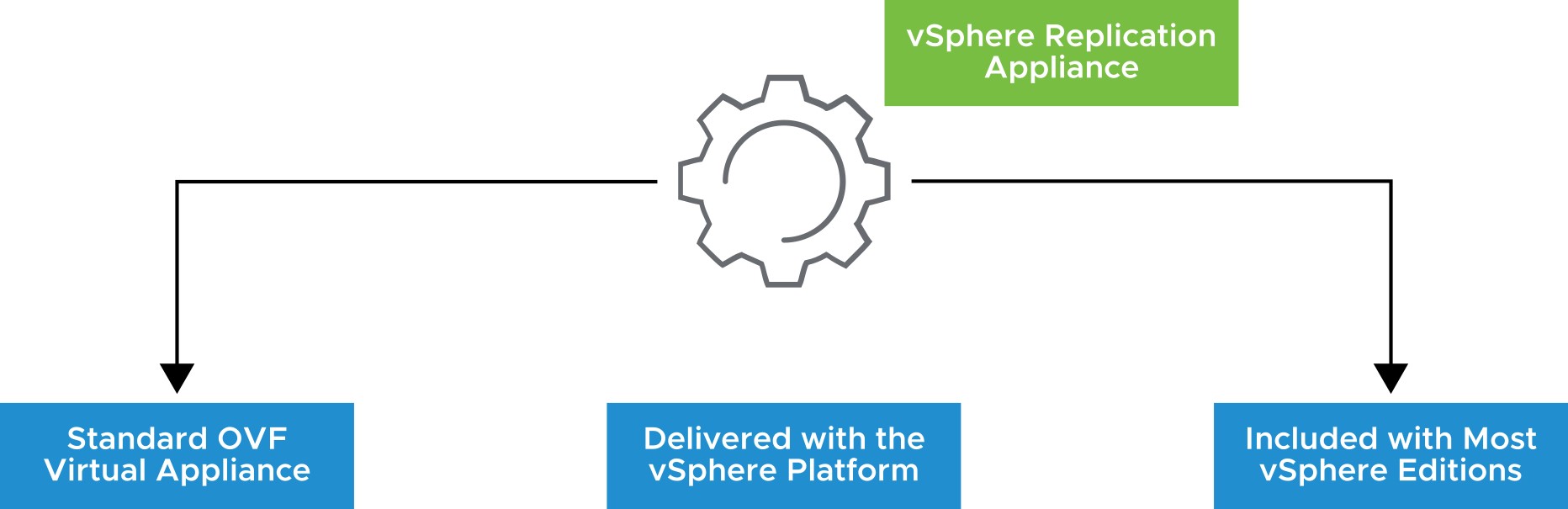
Replication Functions
With vSphere Replication, you can replicate a VM from a source site to a target site, monitor and manage the replication status, and recover the VM at the target site. 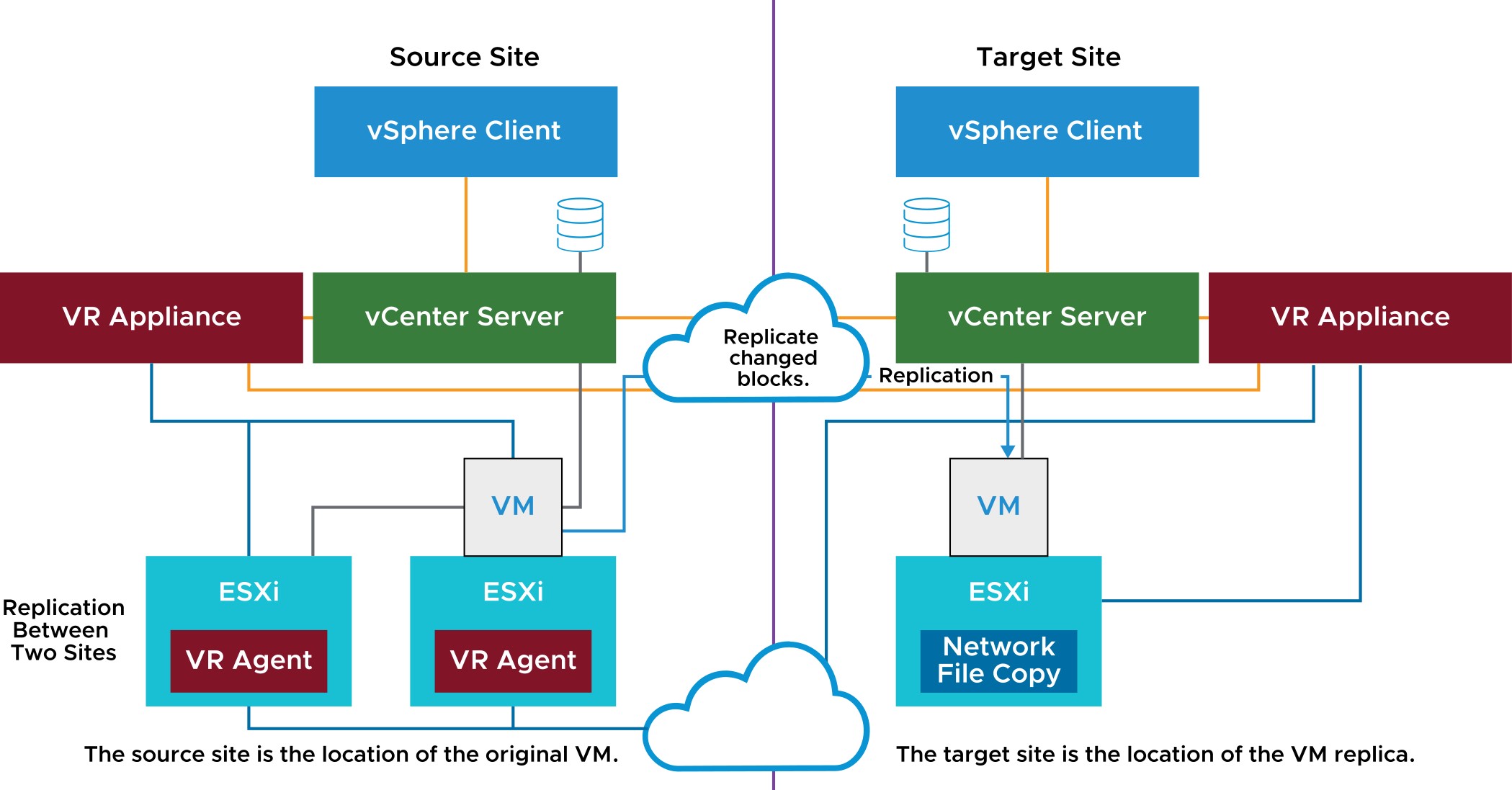
Deploying the vSphere Replication Appliance
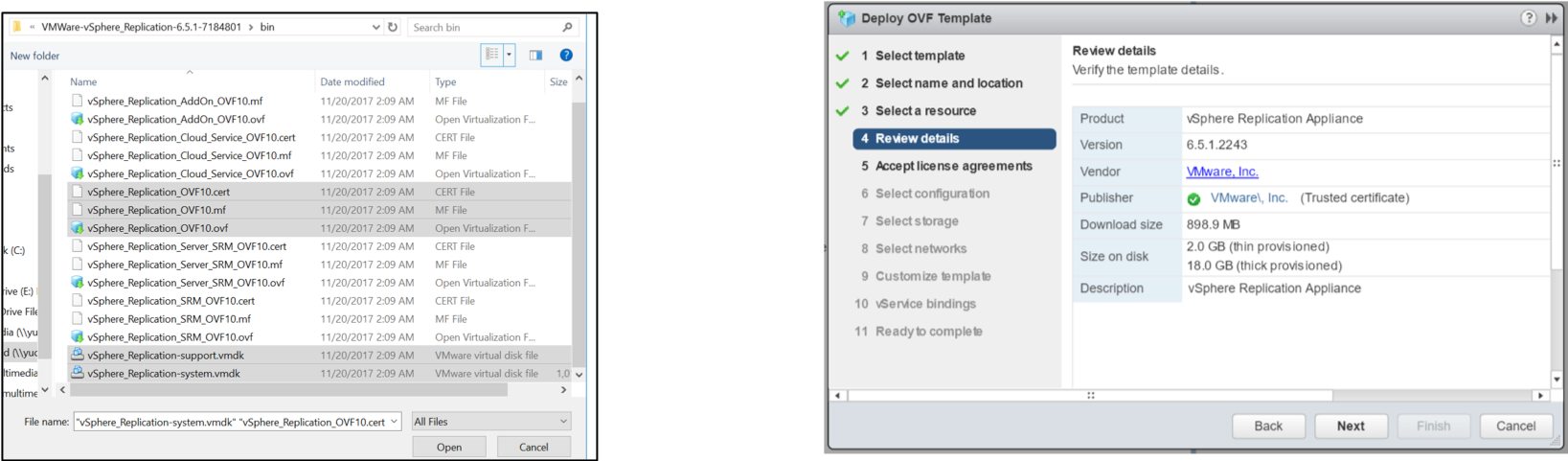
You use the vSphere Client to deploy the vSphere Replication appliance on an ESXi host:
- Download the installation package to a local directory or obtain its URL.
- Use the standard vSphere OVF deployment wizard to deploy the appliance.
- Select Menu > Hosts and Clusters.
- Right-click an ESXi host and select Deploy OVF template.
Configuring vSphere Replication for a Single VM
To configure vSphere Replication for a VM in the vSphere Client, right-click the VM in the inventory and select All vSphere Replication Actions > Configure.

Configuring Recovery Point Objective and Point in Time Instances
During replication configuration, you can set an RPO and enable retention of instances from multiple points in time.

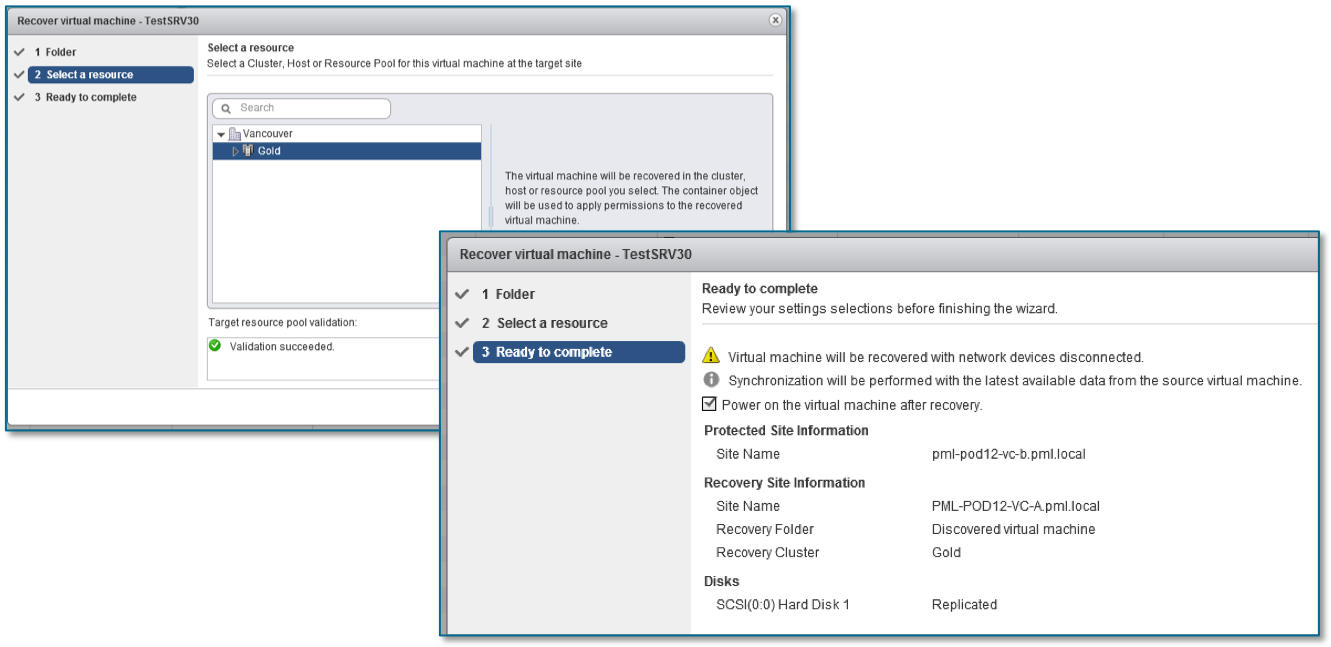
Recovering Replicated VMs
With vSphere Replication, you can recover VMs that were successfully replicated at the target site. You can recover one VM at a time on the Incoming Replications tab.
Backup and Restore Solution for VMs
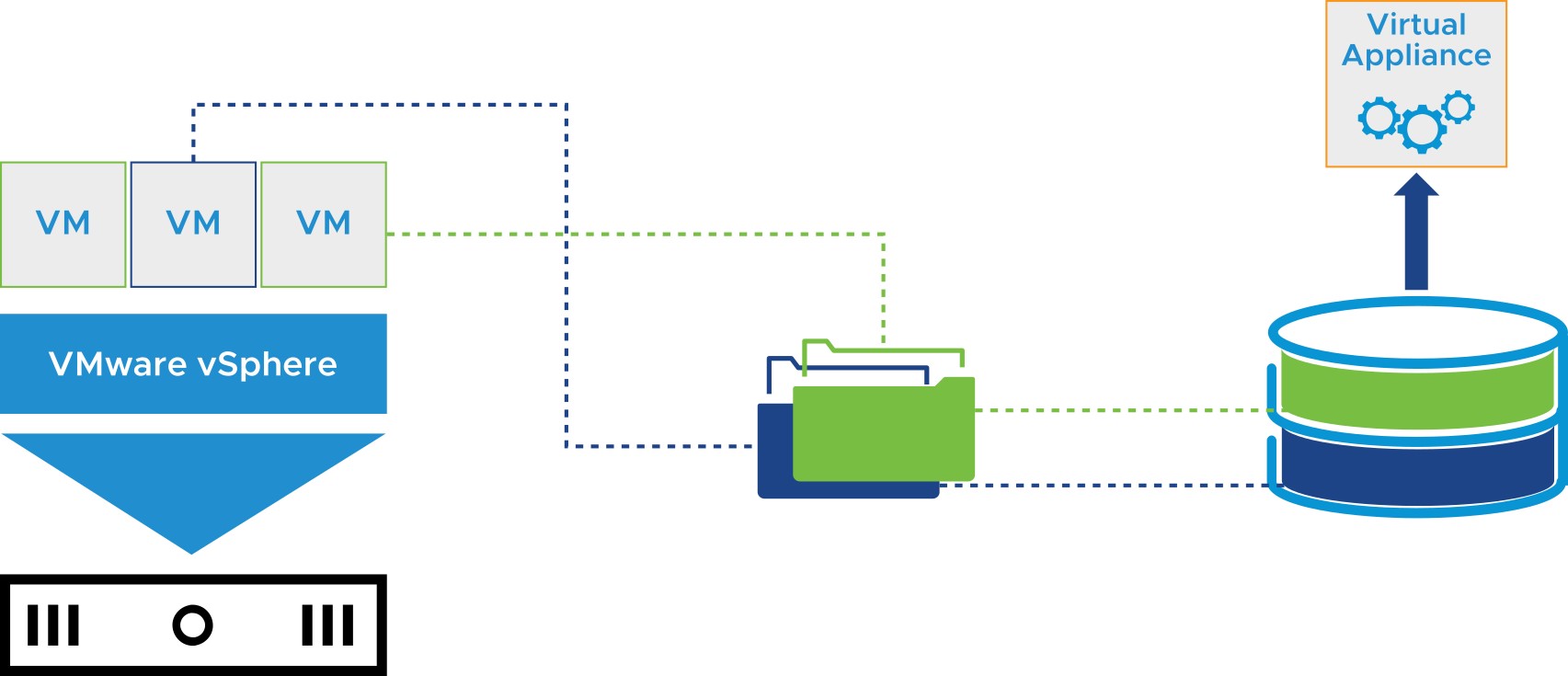
- To protect your VM’s data, you can use a backup solution based on vSphere Storage APIs – Data Protection.
- With vSphere Storage APIs – Data Protection, backup products can perform centralized, efficient, off-host, LAN-free backups of vSphere VMs.
vSphere Storage APIs – Data Protection: Offloaded Backup Processing
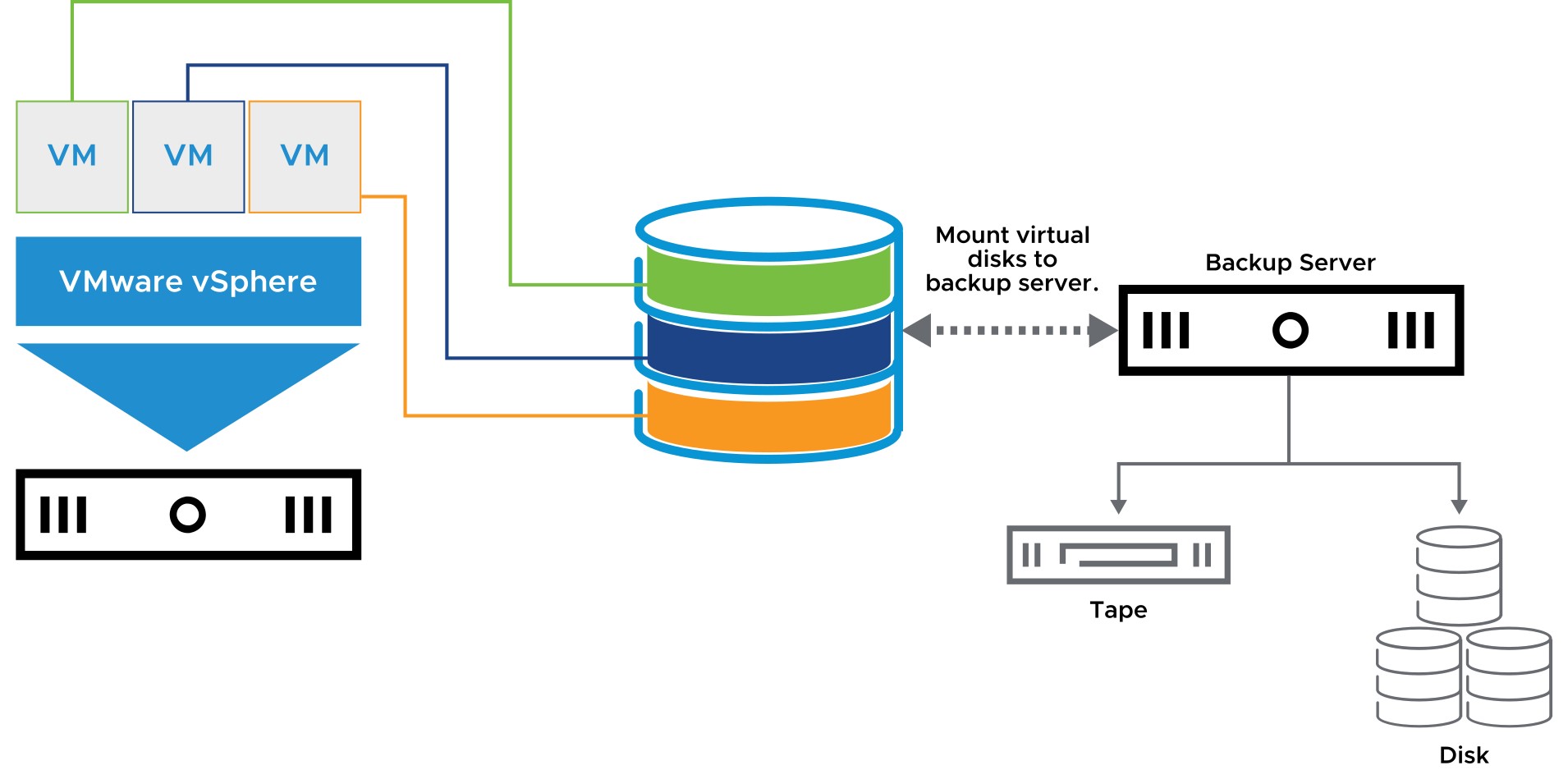
- Configure the storage environment so that the backup server can access the storage volumes that are managed by the ESXi hosts.
- Backup processing is offloaded from the ESXi host to the backup server, which prevents local ESXi resources from becoming overloaded.
vSphere Storage APIs – Data Protection: Changed-Block Tracking
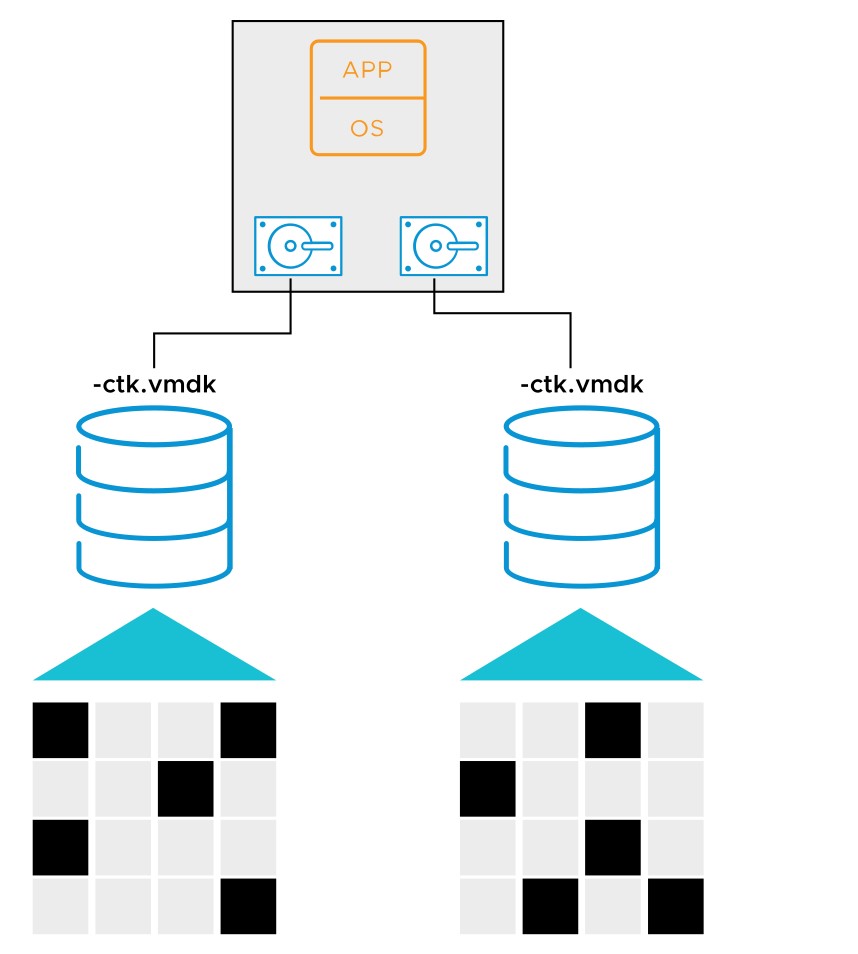
- With changed-block tracking, the backup solution copies only file blocks that changed since the last backup.
- Changed-block tracking supports faster incremental backups.
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this vSphere Replication and Backup lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Identify the components in the vSphere Replication architecture
- Deploy and configure vSphere Replication
- Recover replicated virtual machines
- Explain the backup and restore solution for VMs
- Describe the benefits of vSphere Storage APIs – Data Protection
Activity: Virtual Beans VM Management (1)
use for key VM management processes. Provide one or more suggestions for each process.
| Virtual Beans Process | vSphere Suggestions |
| Provisioning and deploying VMs | |
| Maintaining VMs (patching and upgrading operating systems and applications) | |
| Backing up VMs | |
| Disaster recovery and business continuity |
Activity: Virtual Beans VM Management (2)
use for key VM management processes. Provide one or more suggestions for each process.
| Virtual Beans Process | vSphere Suggestions | |||
| Provisioning and deploying VMs |
|
|||
| Maintaining VMs (patching and upgrading operating systems and applications) | Take a snapshot of the VM before applying any patches or updates. Manage all templates with the content library. Using the content library, you can update templates while VMs are deployed from the template. | |||
Activity: Virtual Beans VM Management (3)
use for key VM management processes. Provide one or more suggestions for each process.
Backing up VMs• Use a vSphere Storage APIs – Data Protection solution. Check knowledge base article 1021175 for backup solutions that are currently available.
Disaster recovery and business • Use vSphere Replication, which protects VMs from partial or continuity complete site failure. • For planned downtime, use the various types of vSphere vMotion migrations to move VMs between hosts, between vCenter Server instances, and even between data centers.
Key Points
- vCenter Server provides features for provisioning virtual machines, such as templates, cloning, and content libraries.
- By deploying VMs from a template, you can create many VMs easily and quickly.
- You can dynamically manage a VM’s configuration by adding hot-pluggable devices and increasing the size of a VM’s virtual disk.
- Hot migrations use vSphere vMotion, vSphere Storage vMotion, or both.
- You can use VM snapshots to preserve the state of the VM so that you can return repeatedly to the same state.
- You can use vSphere Replication to protect VMs as part of a disaster recovery strategy.
- Backup products that use vSphere Storage APIs – Data Protection can be used to back up VM data.