vCenter Server Roles and Permissions
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Define the term permission in the context of vCenter Server
- Describe the rules for applying permissions
- Create a custom role
- Create a permission
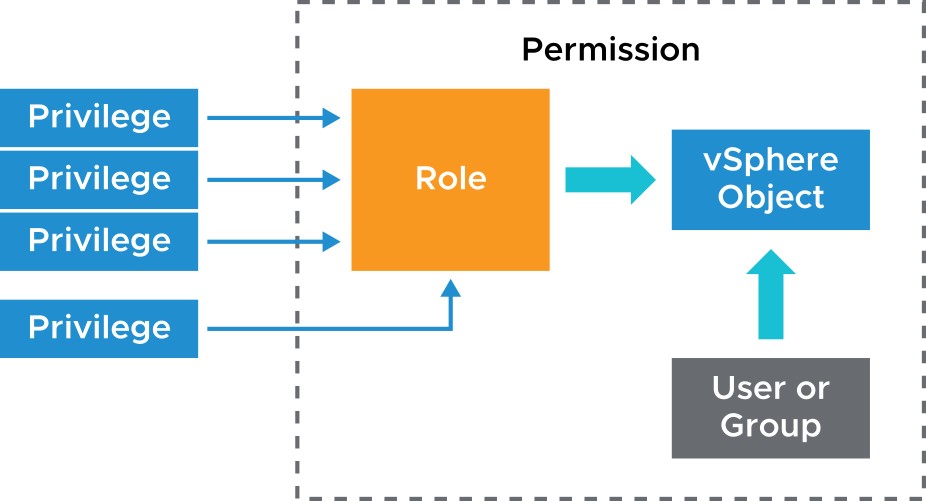
About vCenter Server Permissions

Using the access control system, the vCenter Server administrator can define user privileges to access objects in the inventory. The following concepts are important:
- Privilege: An action that can be performed
- Object: The target of the action
- User or group: Indication of who can perform the action
- Role: A set of privileges
- Permission: Gives one user or group a role (set of privileges) for the selected object
About Roles

Privileges are grouped into roles:
- A privilege allows access to a specific task and is grouped with other privileges related to it.
- Roles allow users to perform tasks.
vCenter Server provides a few system roles, which you cannot modify.
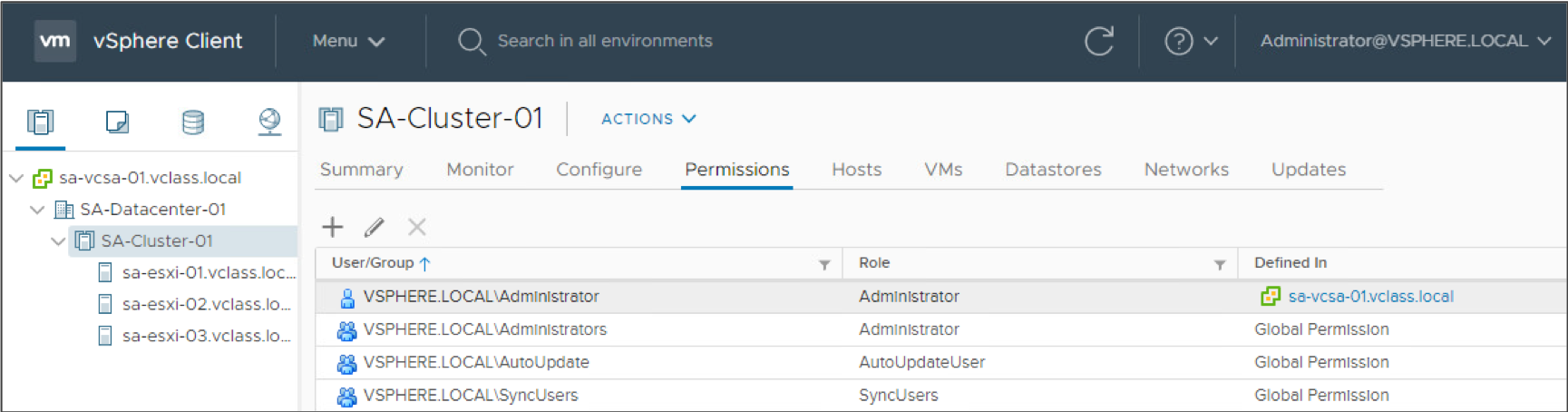
About Objects
- Objects are entities on which actions are performed. Objects include data centers, folders, clusters, hosts, datastores, networks, and virtual machines.
- All objects have a Permissions tab. The Permissions tab shows which user or group and role are associated with the selected object.
Adding Permissions to the vCenter Server Inventory
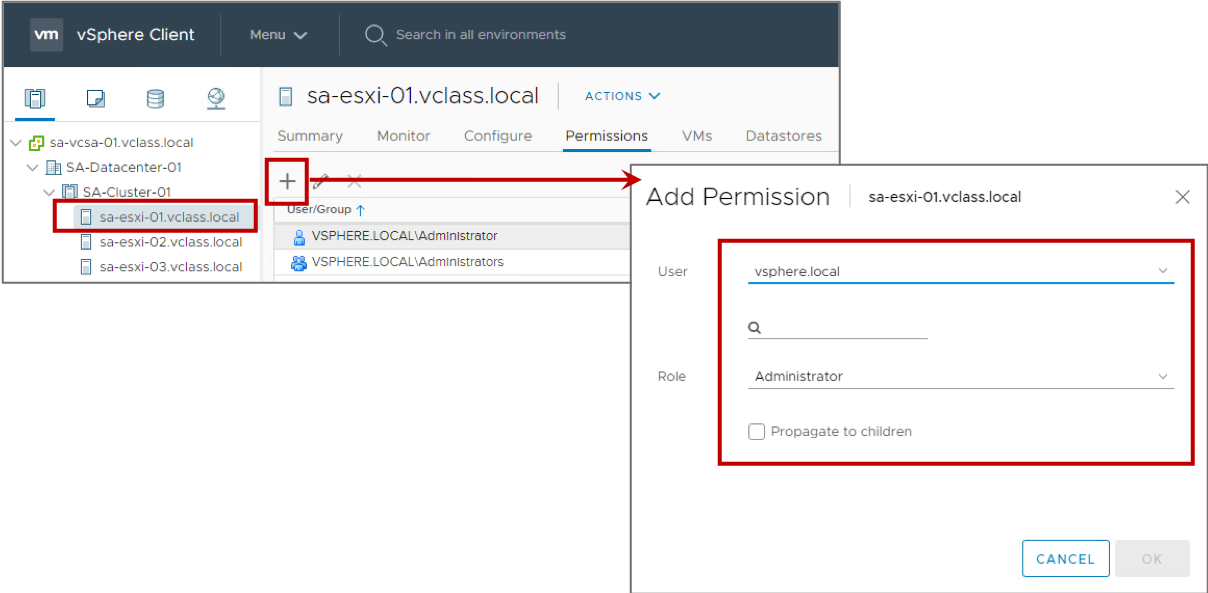
To add a permission:
- Select an object.
- Select a user or group from a domain.
- Select a role.
- Propagate the permission to the child objects.
Viewing Roles and User Assignments
The Roles pane shows which users are assigned the selected role on a particular object.
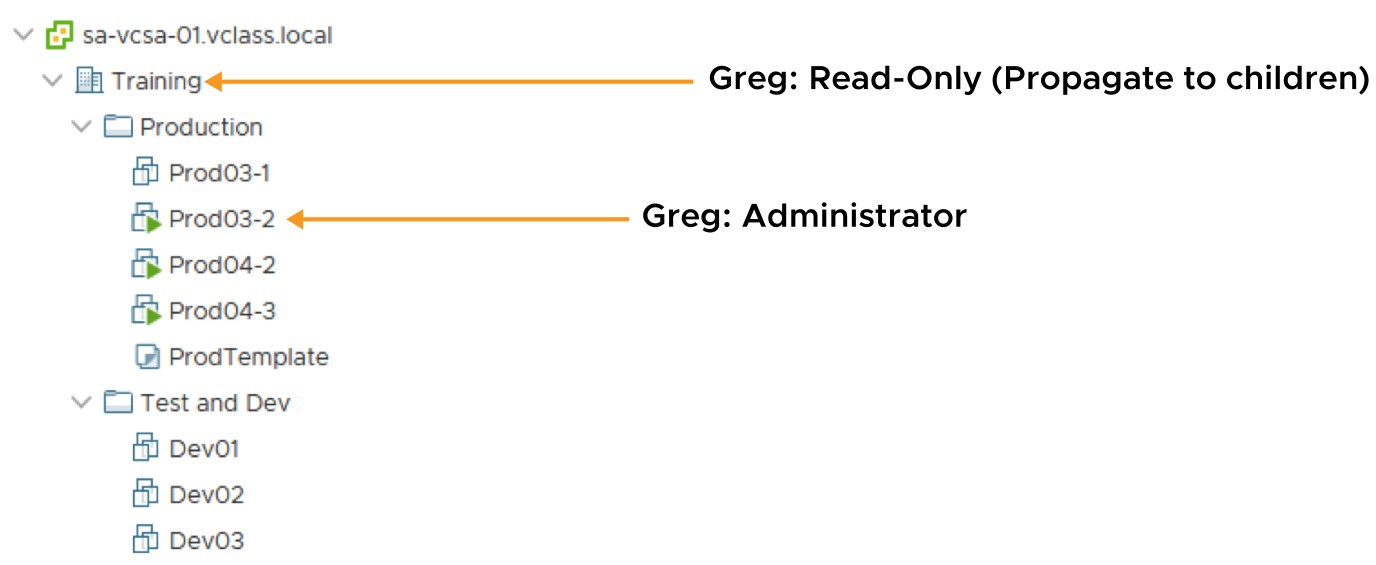
Applying Permissions: Scenario 1
A permission can propagate down the object hierarchy to all subobjects, or it can apply only to an immediate object.
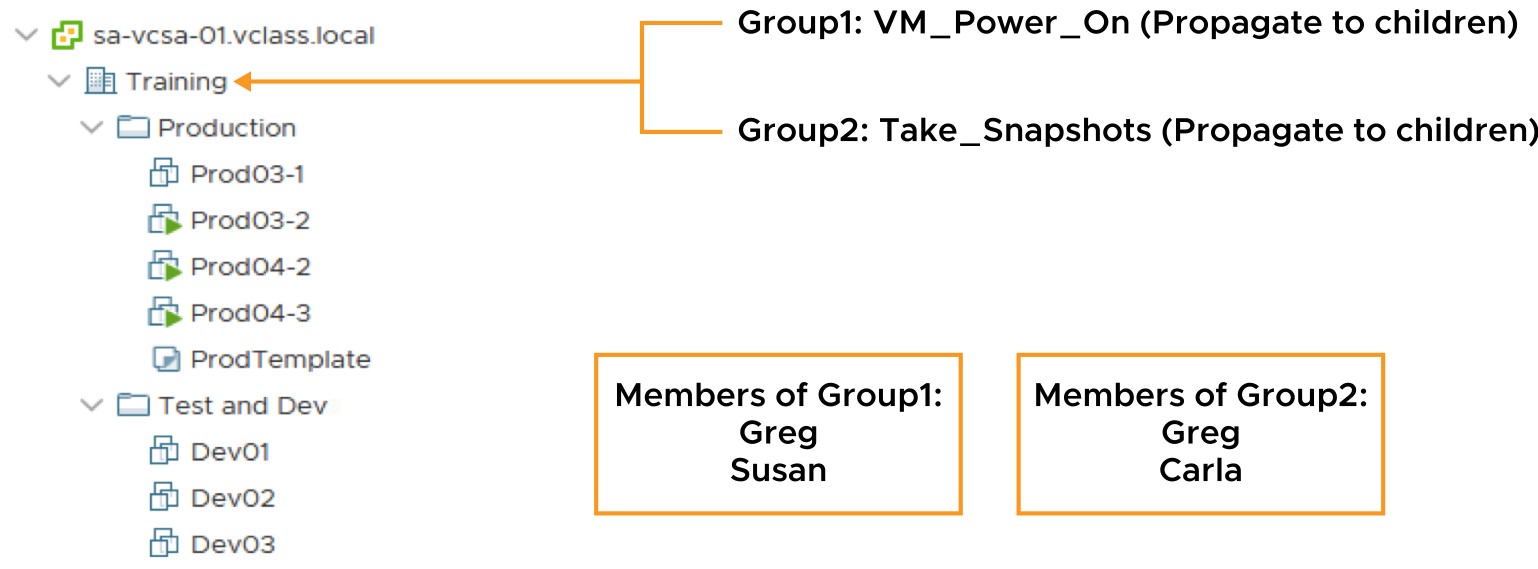
Applying Permissions: Scenario 2
When a user is a member of multiple groups with permissions on the same object, the user is assigned the union of privileges assigned to the groups for that object.
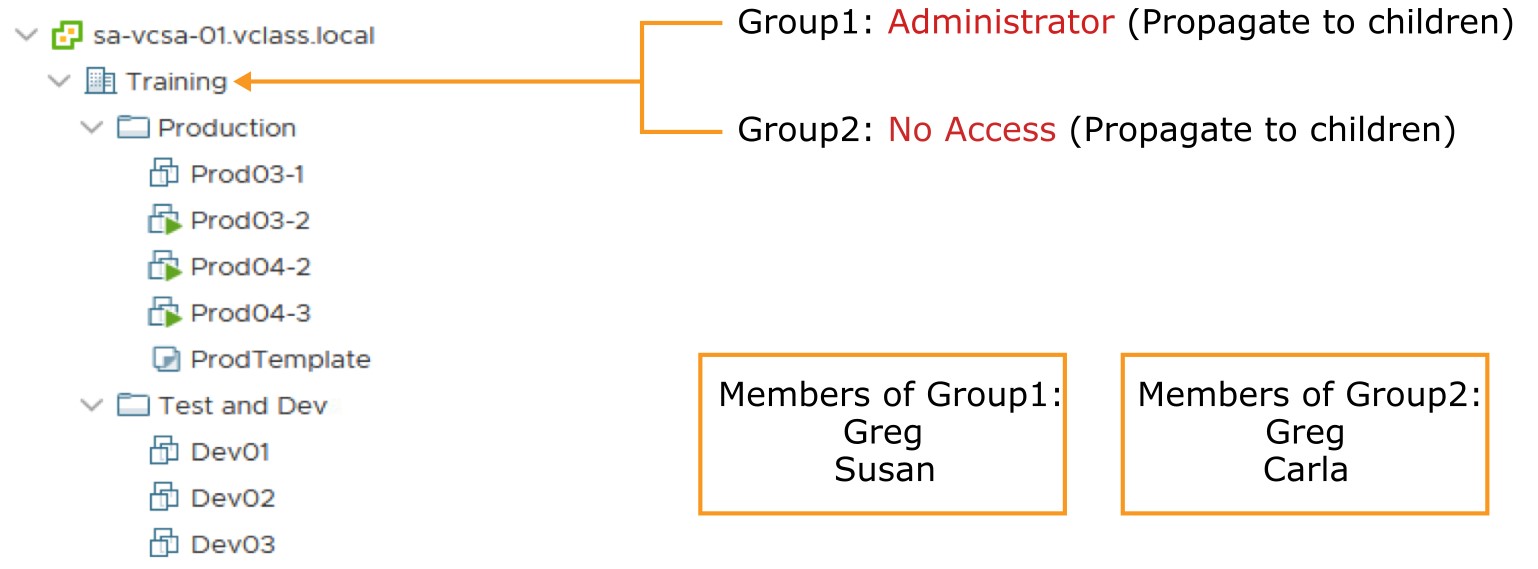
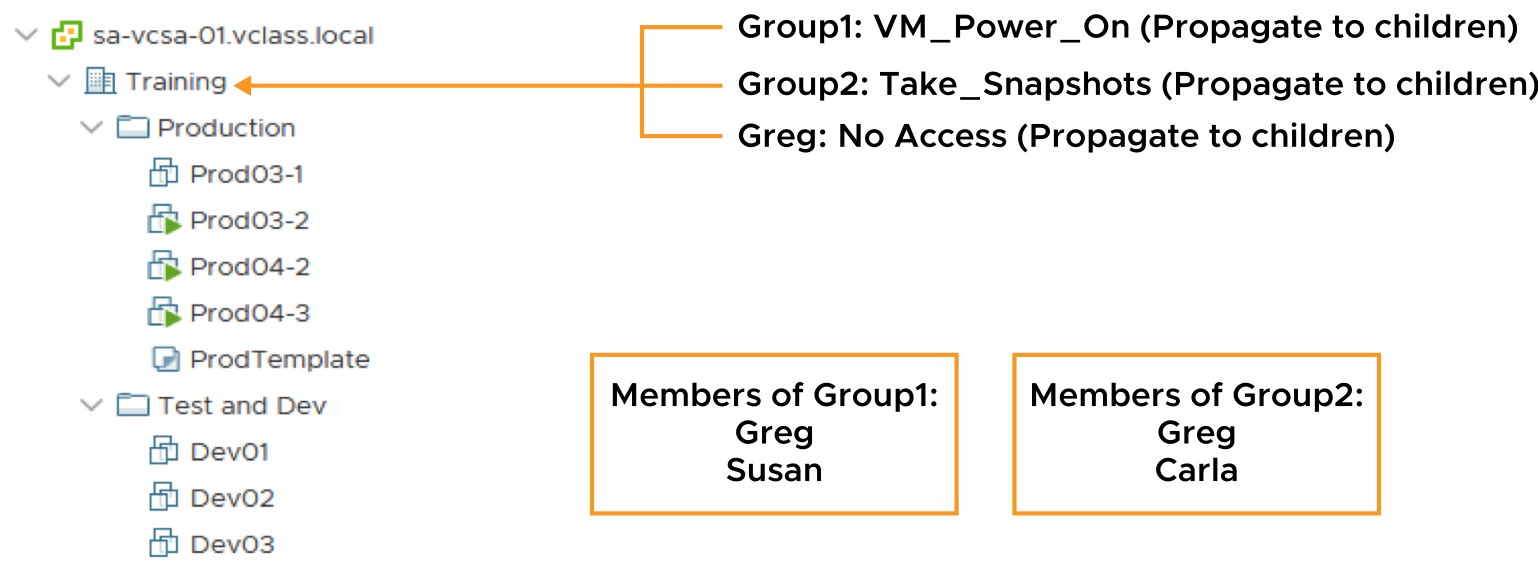
Activity: Applying Group Permissions (1)
If Group1 has the Administrator role and Group2 has the No Access role, what permissions does Greg have?

Activity: Applying Group Permissions (2)
- Greg has Administrator privileges.
- Greg is assigned the union of privileges assigned to Group1 and Group2.
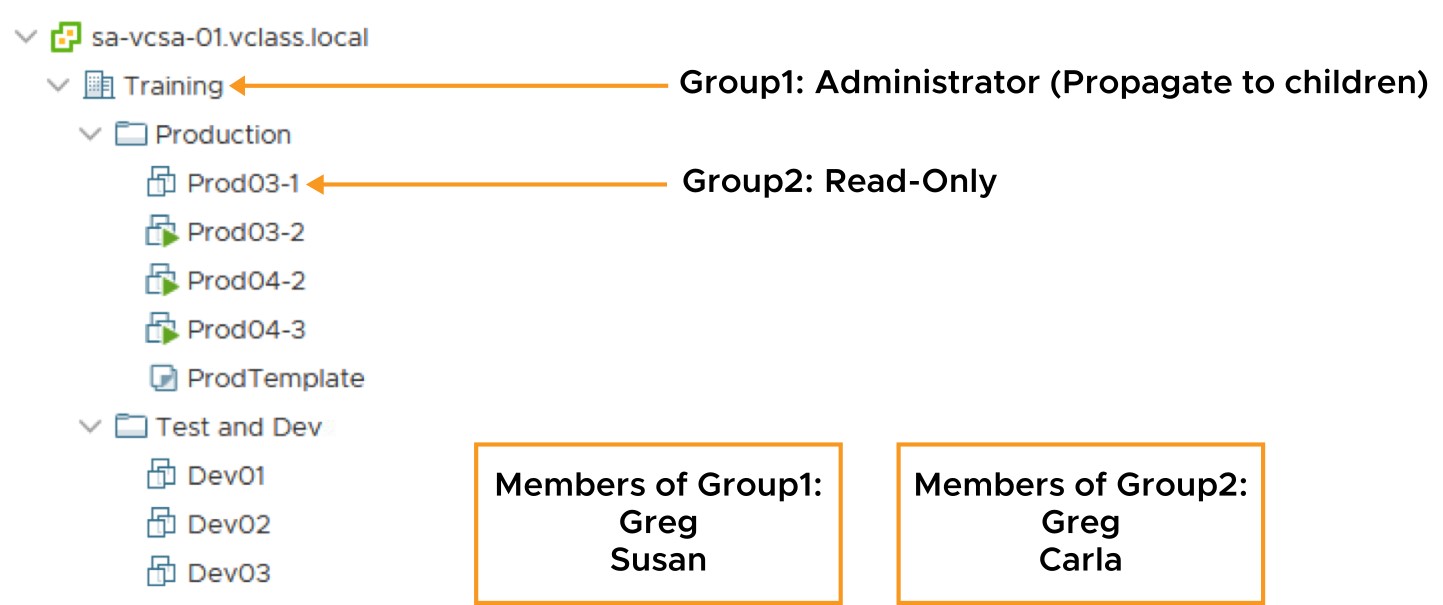
Applying Permissions: Scenario 3
- A user can be a member of multiple groups with permissions on different objects. In this case, the same permissions apply for each object on which the group has permissions, as though the permissions were granted directly to the user.
Applying Permissions: Scenario 4
- A user (or group) is given only one role for any given object.
- Permissions defined explicitly for the user on an object take precedence over all group permissions on that same object.
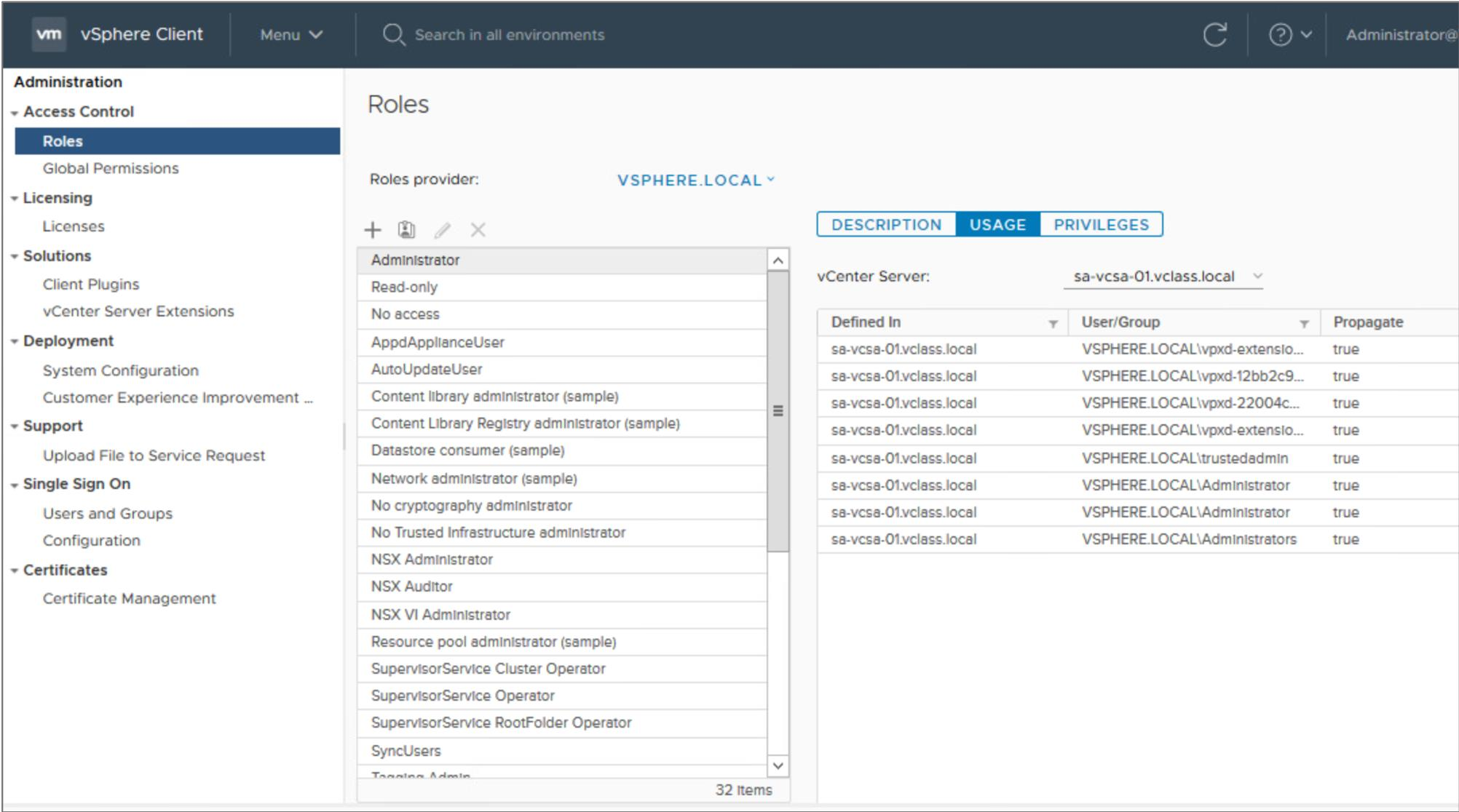
Creating a Role
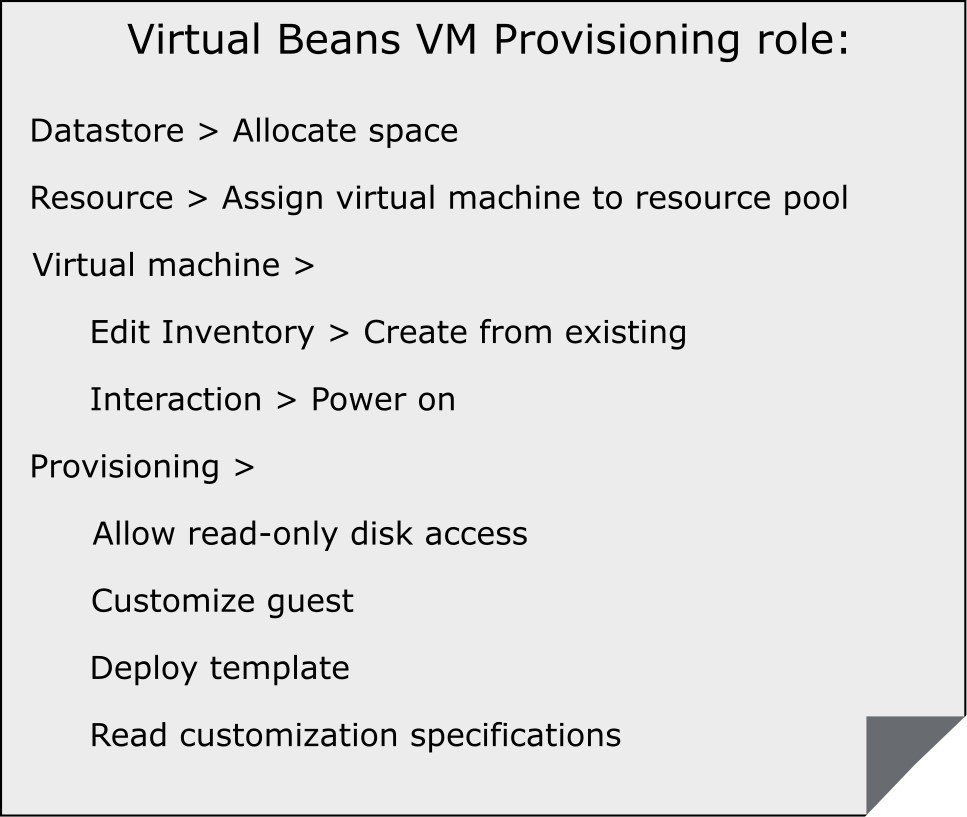
- Create roles for only necessary tasks.
- For example, you can create a Virtual Beans VM Provisioning role that allows a user to deploy VMs from a template.
- Use folders to contain the scope of permissions. For instance, assign the Virtual Beans VM Provisioning role to user nancy@vmbeans.com and apply it to the Production VMs folder.
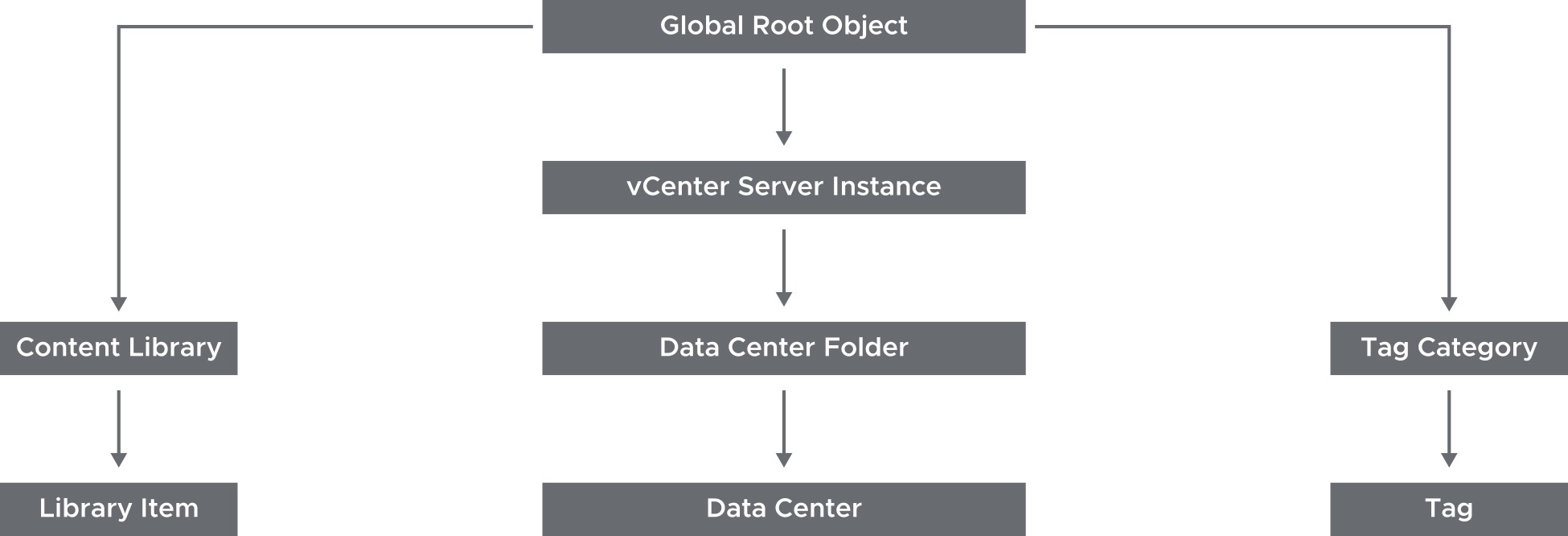
About Global Permissions
Global permissions support assigning privileges across solutions from a global root object:
- Span solutions such as vCenter Server and vRealize Orchestrator
- Give a user or group privileges for all objects in all object hierarchies
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this vCenter Server Roles and Permissions lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Define the term permission in the context of vCenter Server
- Describe the rules for applying permissions
- Create a custom role
- Create a permission