Overview of vSphere and Virtual Machines
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Explain basic virtualization concepts
- Describe how vSphere fits into the software-defined data center and the cloud infrastructure
- Describe how to proactively manage your vSphere environment
Terminology
Virtualization is associated with several key concepts, products, and features.
| Term | Definition | Examples |
| Operating system | Software designed to allocate physical resources to applications | Microsoft Windows, Linux |
Application Software that runs on an operating system, Microsoft Office, Chrome consuming physical resources
| Virtual machine | Specialized application that abstracts hardware resources into software | |
| Guest | The operating system that runs in a VM (also called the guest operating system) | Microsoft Windows, Linux |
| Hypervisor | Specialized operating system designed to run VMs | ESXi, Workstation, Fusion |
| Host | Physical computer that provides resources to the ESXi hypervisor |
| Term | Definition |
| vSphere | Server virtualization product of VMware that combines the ESXi hypervisor and the vCenter Server management platform |
| Cluster | Group of ESXi hosts whose resources are shared by VMs |
| vSphere vMotion | Feature that supports the migration of powered-on VMs from host to host without service interruption |
| vSphere HA | Cluster feature that protects against host hardware failures by restarting VMs on hosts that are running normally |
| vSphere DRS | Cluster feature that uses vSphere vMotion to place VMs on hosts and ensure that each VM receives the resources that it needs |
About Virtual Machines
A virtual machine (VM) is a software representation of a physical computer and its components. The virtualization software converts the physical machine and its components into files.
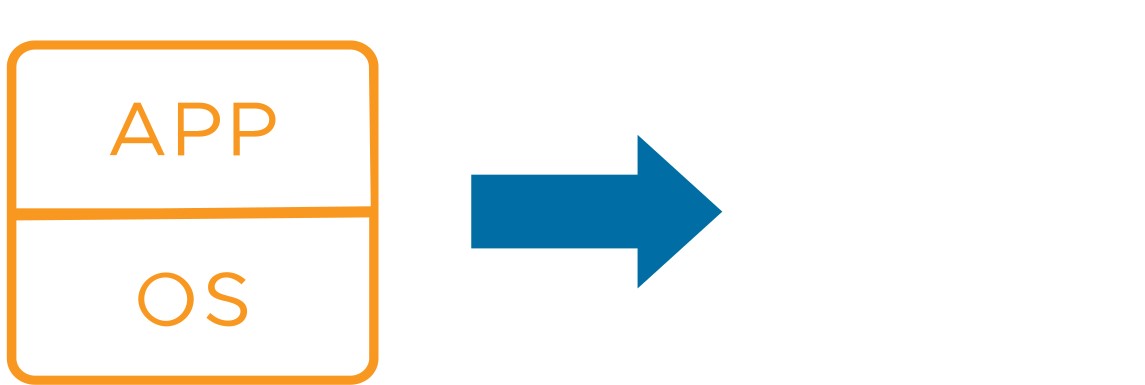
Virtual Machine Components
- Guest operating system
- VMware Tools
- Virtual resources, such as:
- CPU and memory
- Network adapters
- Disks and controllers
- Parallel and serial ports
Benefits of Using Virtual Machines
Physical machines:
- Difficult to move or copy
- Bound to a specific set of hardware components
- Often have a short life cycle
- Require personal contact to upgrade hardware

Virtual machines:
- Easy to move or copy
- Independent of physical hardware because VMs are encapsulated into files
- Isolated from other VMs running on same physical hardware
- Insulated from physical hardware changes

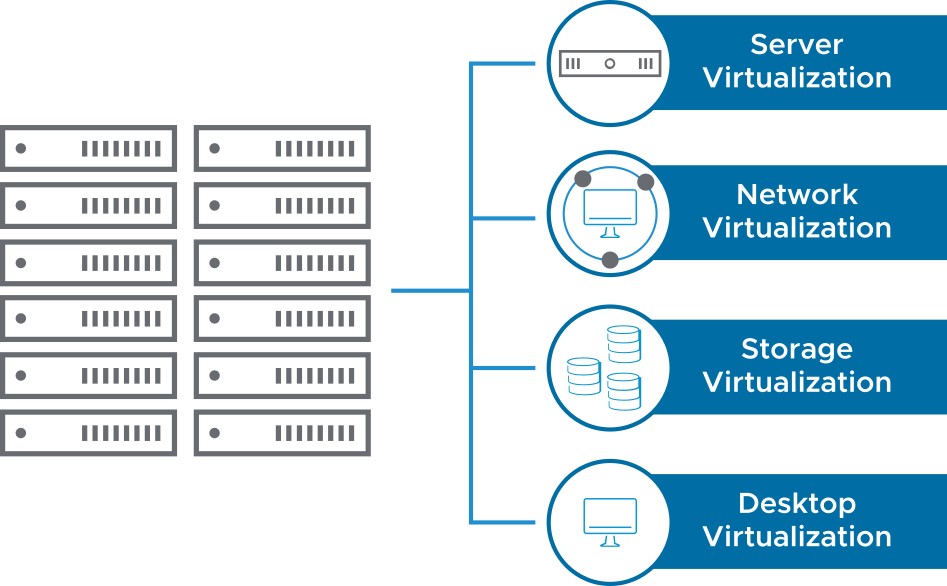
Types of Virtualization

- Virtualization is the process of creating a software-based representation of something physical, such as a server, desktop, network, or storage device.
- Virtualization is the single most effective way to reduce IT expenses while boosting efficiency and agility for all business sizes.
About the Software-Defined Data Center
In a software-defined data center (SDDC), all infrastructure is virtualized, and the control of the data center is automated by software. vSphere is the foundation of the SDDC.
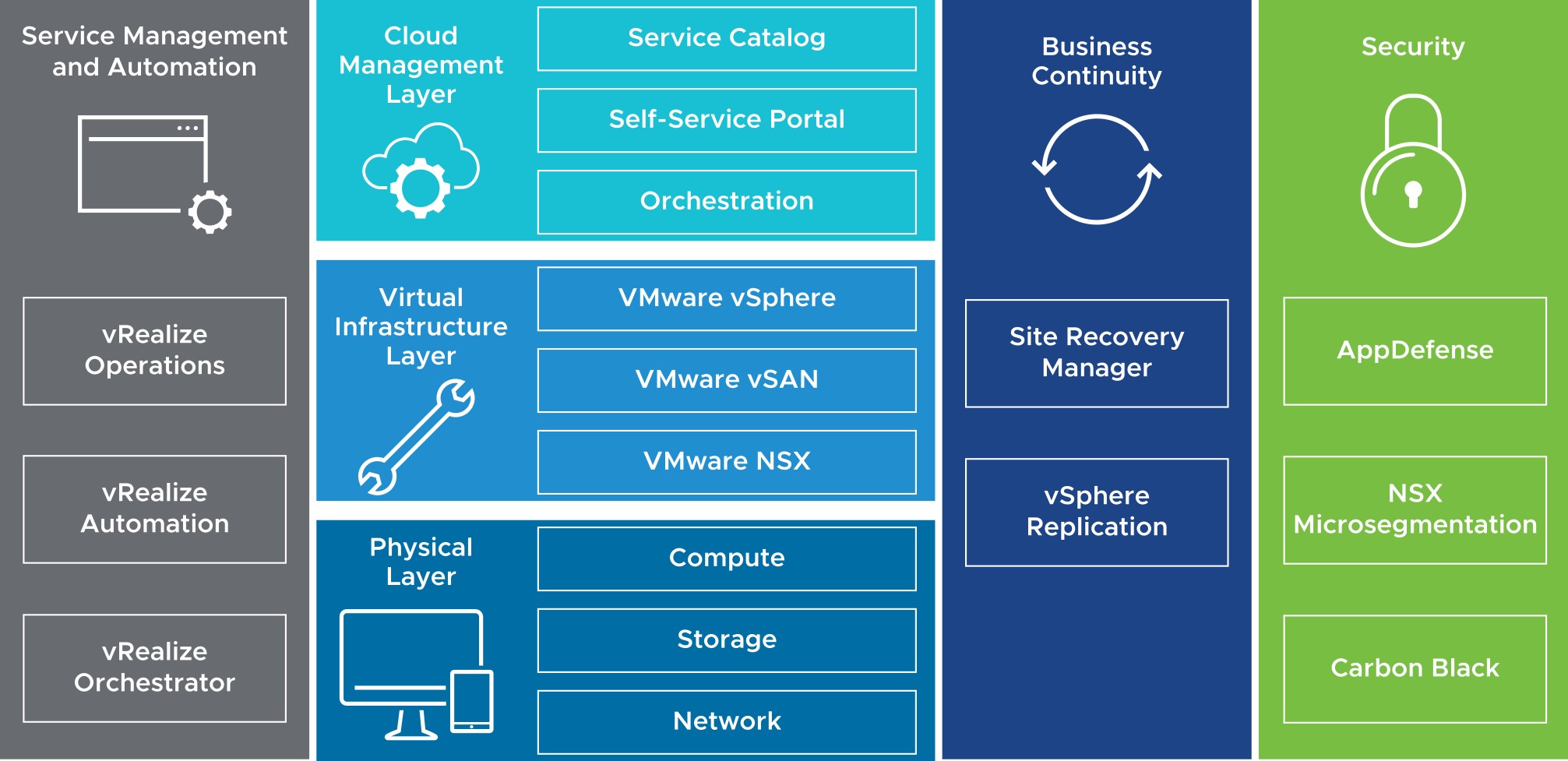
vSphere and Cloud Computing
Cloud computing exploits the efficient pooling of an on-demand, self-managed, and virtual infrastructure. 
About VMware Skyline
VMware Skyline is a proactive support technology that provides predictive analysis and proactive recommendations to help you avoid problems. VMware Skyline provides the following benefits:
- Issue avoidance: • Personalized recommendations:
- —Proactively identifies potential issues
- —Resolution is specific to your environment. based on environment-specific • No additional cost: configuration, details, and usage.
- —You receive additional value with your —Resolves issues before they occur, current support subscription (Basic, improving environment reliability and Production, or Premier support). stability.
- Shortens time to resolution:
- —Environment-specific, data-driven analytics accelerate problem resolution.
VMware Skyline Family
The VMware Skyline family includes Skyline Health and Skyline Advisor.
Skyline Health
All VMware Customers Key capabilities:
- vSphere and vSAN findings
- Available in the vSphere Client
- Supports vSphere 6.7 U1 and later
Skyline Advisor
Production and Premier Support Customers Key capabilities:
- Supports vSphere, vSAN, NSX for vSphere, vRealize Operations Manager, and VMware Horizon
- Supports vSphere 5.5 and later
- Tags VMware Validated Design, VxRail, and VMware Cloud Foundation deployments
- Automates log transfers with Log Assist
- Uses cloud-based ID and access Premier Support Customers
Key capabilities:
- Advanced findings and reporting
- Tailored remediation plans
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, Overview of vSphere and Virtual Machines, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Explain basic virtualization concepts
- Describe how vSphere fits into the software-defined data center and the cloud infrastructure
- Describe how to proactively manage your vSphere environment