Overview of ESXi
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Describe the ESXi host architecture
- Navigate the Direct Console User Interface (DCUI) to configure an ESXi host
- Recognize user account best practices
- Install an ESXi host
- Configure ESXi host settings
About ESXi
ESXi is a hypervisor that you can buy with vSphere or get in a free, downloadable version. ESXi has the following features:
- High security:
- —Host-based firewall
- —Memory hardening
- —Kernel module integrity
- —Trusted Platform Module (TPM 2.0)
- —UEFI secure boot
- —Encrypted core dumps
- Small disk footprint
- Quick boot for faster patching and upgrades
- Installable on hard disks, SAN LUNs, SSD, USB devices, SD cards, SATADOM, and diskless hosts
Configuring an ESXi Host
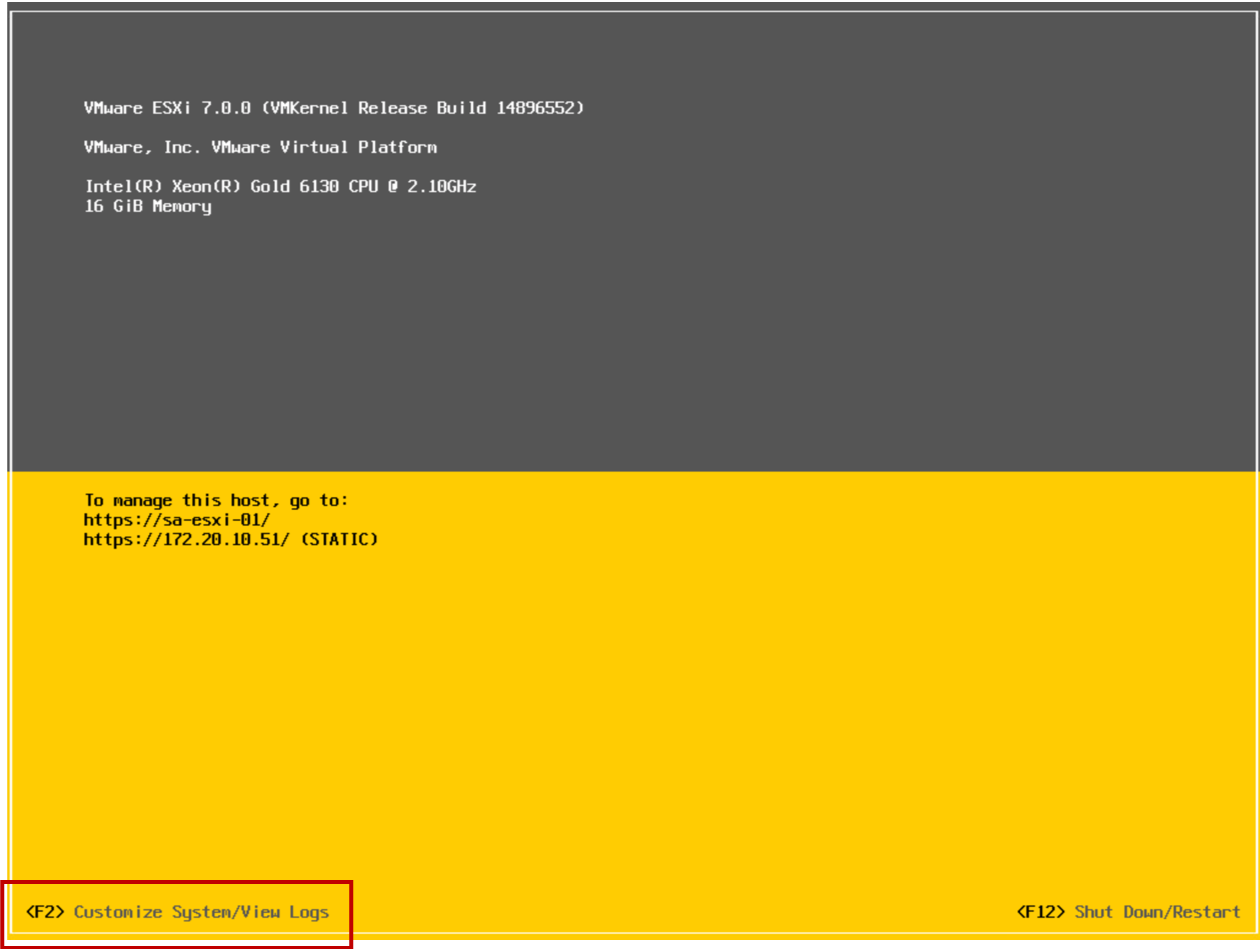
The DCUI is a text-based user interface with keyboard-only interaction. 
Configuring an ESXi Host: Root Access
Administrators use the DCUI to configure root access settings:
- Set a root password (complex passwords only).
- Enable or disable lockdown mode:
- —Limits management of the host to vCenter Server
- —Can be configured only for hosts managed by a vCenter Server instance
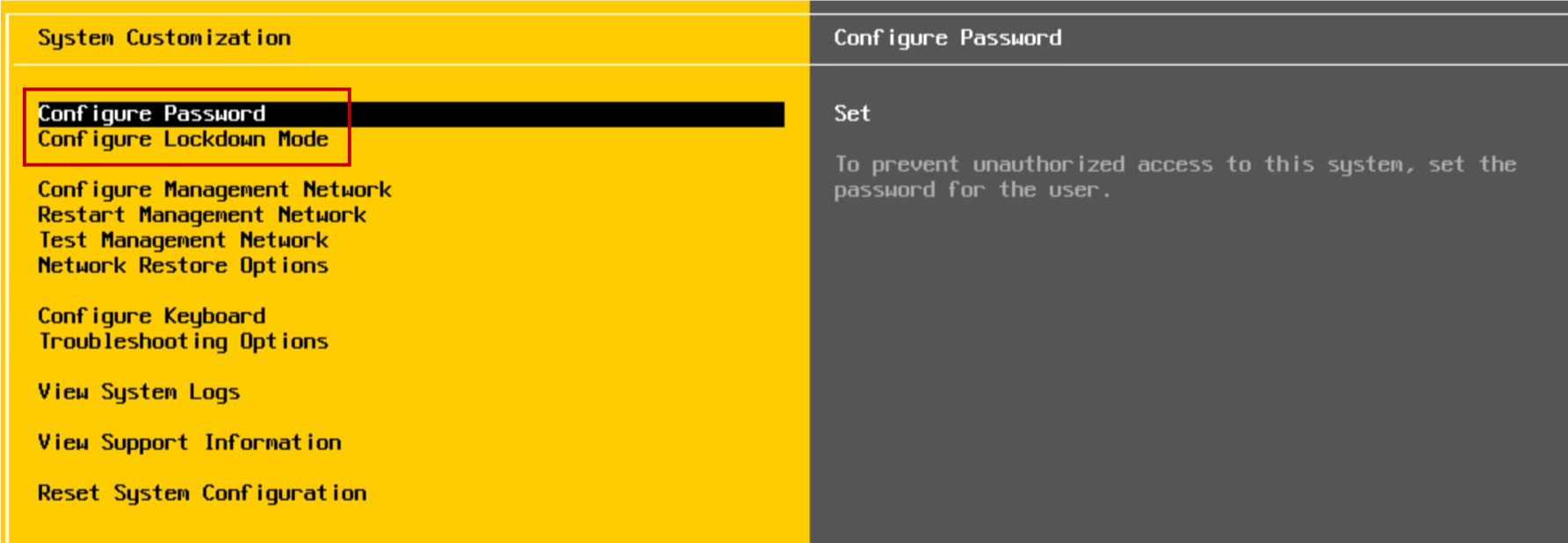
Configuring an ESXi Host: Management Network
Using the DCUI, you can modify network settings:
- Host name
- IP configuration (IP address, subnet mask, default gateway)
- DNS servers
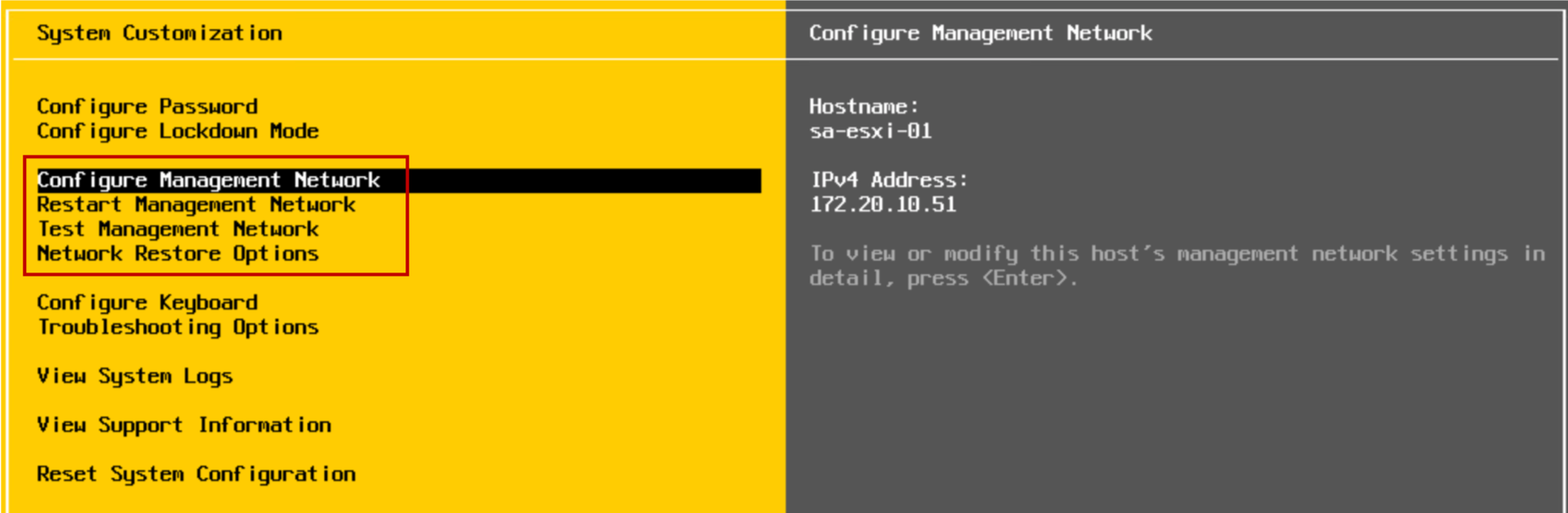
Configuring an ESXi Host: Other Settings
Using the DCUI, you can configure the keyboard layout, enable troubleshooting services, view support information, and view system logs. 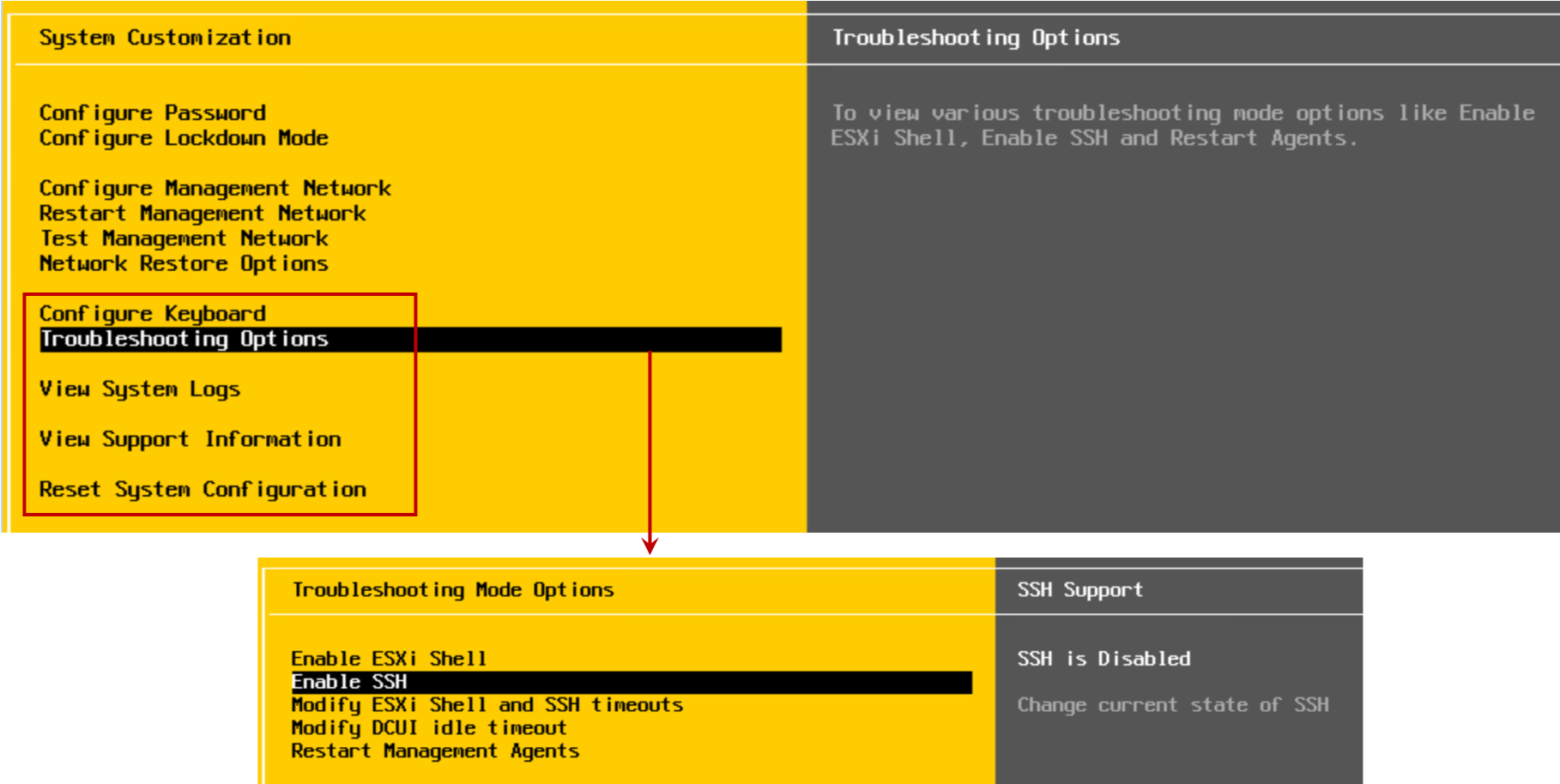
Controlling Remote Access to an ESXi Host
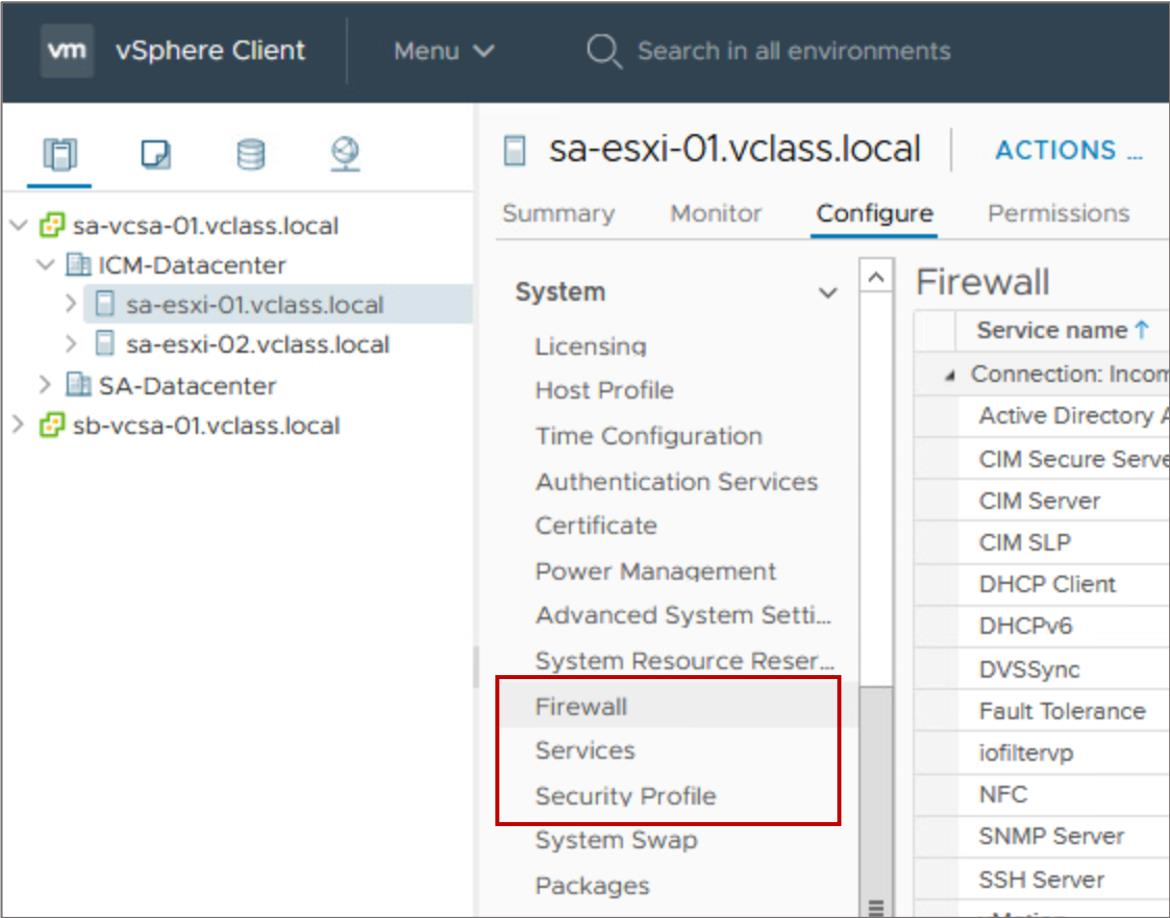
You can use the vSphere Client to customize essential security settings that control remote access to an ESXi host:
- The ESXi firewall is enabled by default:
- —The firewall blocks incoming and outgoing traffic, except for the traffic that is enabled in the host’s firewall settings.
- Services, such as the NTP client and the SSH client, can be managed by the administrator.
- Lockdown mode prevents remote users from logging in to the host directly. The host is accessible only through the DCUI or vCenter Server.
Managing User Accounts: Best Practices
When assigning user accounts to access ESXi hosts or vCenter Server systems, ensure that you follow these security guidelines:
- Strictly control root privileges to ESXi hosts.
- Create strong root account passwords that have at least eight characters. Use special characters, case changes, and numbers. Change passwords periodically.
- Manage ESXi hosts centrally through the vCenter Server system by using the appropriate vSphere client.
- Minimize the use of local users on ESXi hosts:
- —Add the ESXi hosts to Active Directory and add the relevant administrator users to the ESX Admins domain group. Users in the ESX Admins domain group have root privileges on ESXi hosts, by default.
- —If local users are created, manage them centrally using the esxcli command in the vSphere CLI.
- ESXi Host as an NTP Client
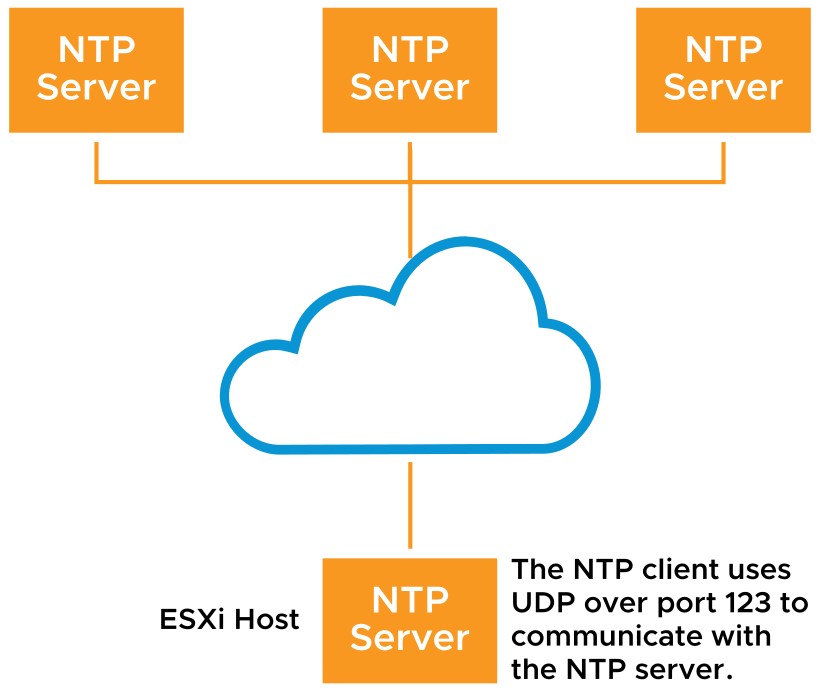
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a client-server protocol used to synchronize a computer’s clock to a time reference. NTP is important:
- For accurate performance graphs
- For accurate time stamps in log messages
- So that virtual machines have a source to synchronize with
An ESXi host can be configured as an NTP client. It can synchronize time with an NTP server on the Internet or your corporate NTP server.
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, Overview of ESXi, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Describe the ESXi host architecture
- Navigate the Direct Console User Interface (DCUI) to configure an ESXi host
- Recognize user account best practices
- Install an ESXi host
- Configure ESXi host settings
Key Points
- Virtual machines are hardware independent.
- VMs share the physical resources of the ESXi host on which they reside.
- vSphere abstracts CPU, memory, storage, and networking for VM use.
- The ESXi hypervisor runs directly on the host.