Introduction to vSphere HA
Learner Objectives
After completing this Introduction to vSphere HA lesson lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Identify options for configuring a highly available vSphere environment
- Describe how vSphere HA responds when an ESXi host, a virtual machine, or an application fails
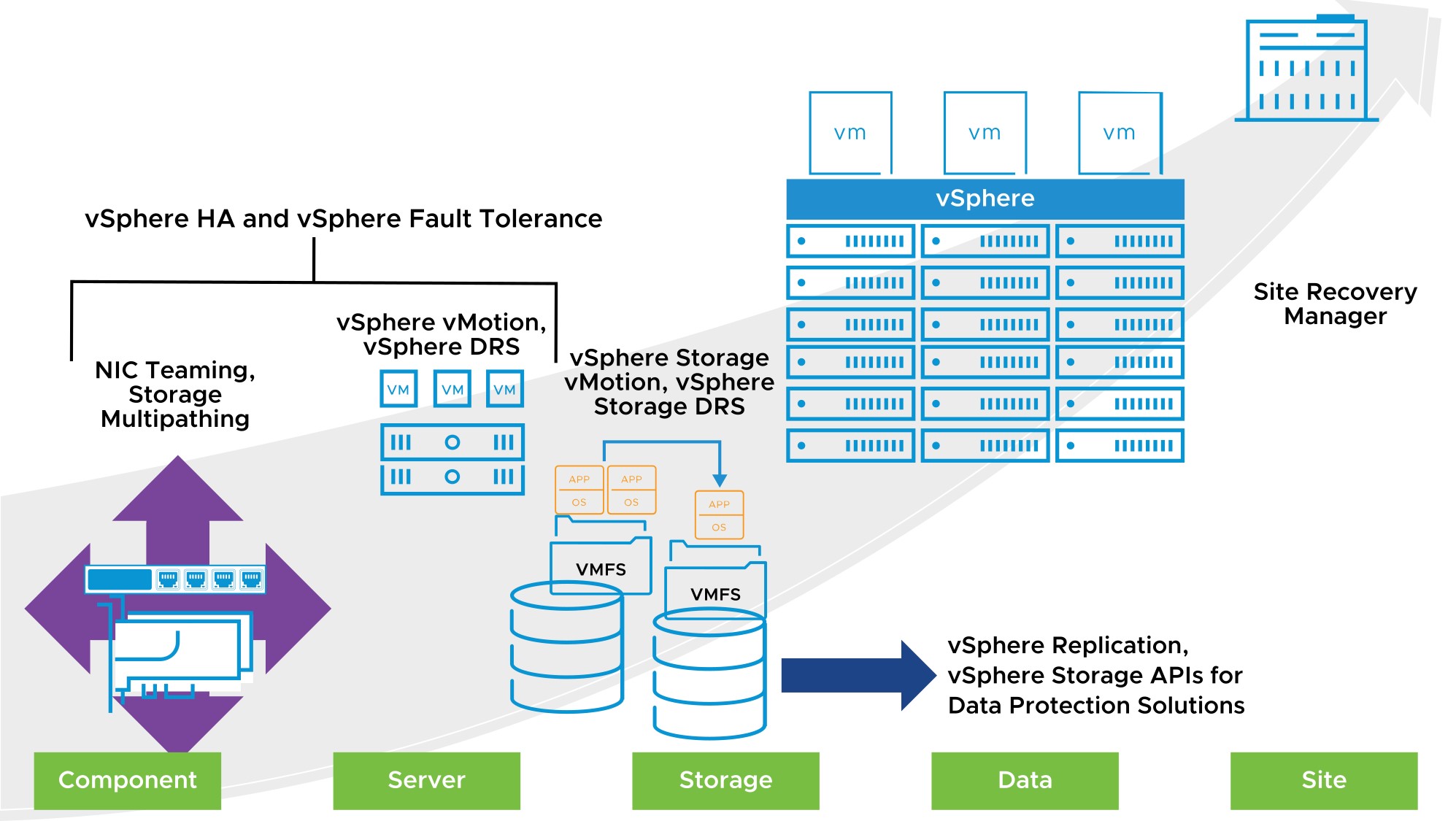
Protection at Every Level
With vSphere, you can reduce planned downtime, prevent unplanned downtime, and recover rapidly from outages. 
About vSphere HA
vSphere HA provides rapid recovery from outages and cost-effective high availability for applications running in VMs. vSphere HA protects application availability in several ways.
| Protects Against | How Does vSphere HA Provide Protection? |
| ESXi host failure | By restarting the VMs on other hosts within the cluster |
| VM failure | By restarting the VM when a VMware Tools heartbeat is not received within a set time |
| Application failure | By restarting the VM when an application heartbeat is not received within a set time |
| Datastore accessibility failure | By restarting the affected VMs on other hosts that still can access the datastores. |
| Network isolation | By restarting VMs if their host becomes isolated on the management or vSAN network. This protection is provided even if the network becomes partitioned. |
vSphere HA Scenario: ESXi Host Failure
When a host fails, vSphere HA restarts the impacted VMs on other hosts in the cluster. 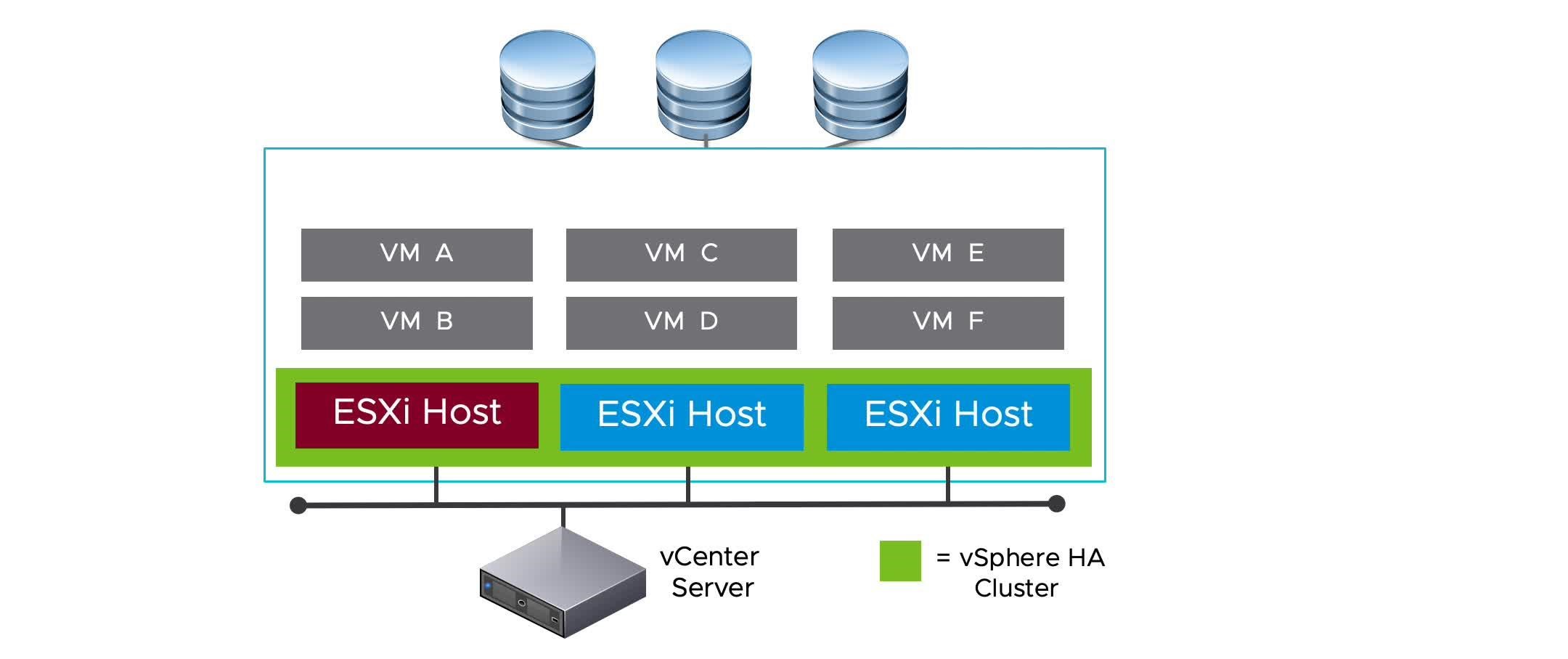
vSphere HA Scenario: Guest Operating System Failure
When a VM stops sending heartbeats or the VM process (vmx) fails unexpectedly, vSphere HA resets the VM. 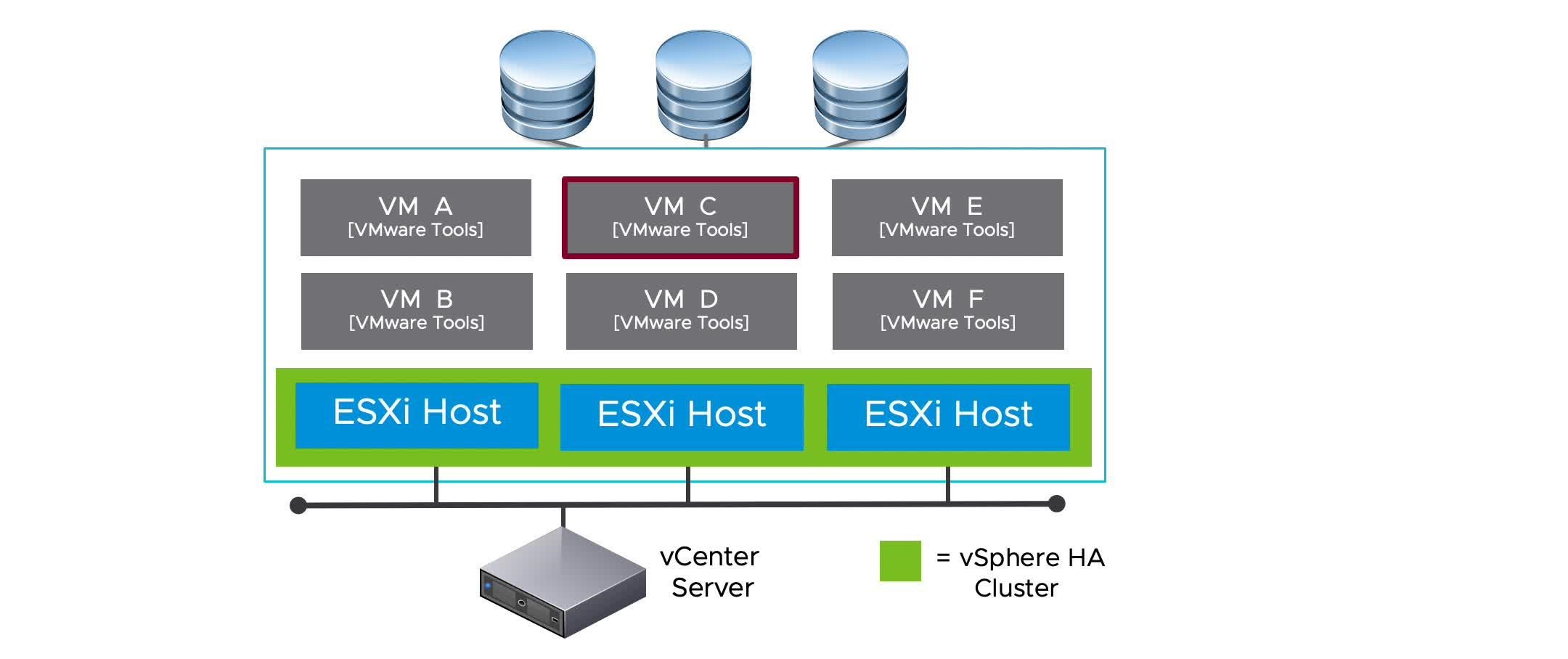
vSphere HA Scenario: Application Failure
When an application fails, vSphere HA restarts the impacted VM on the same host. 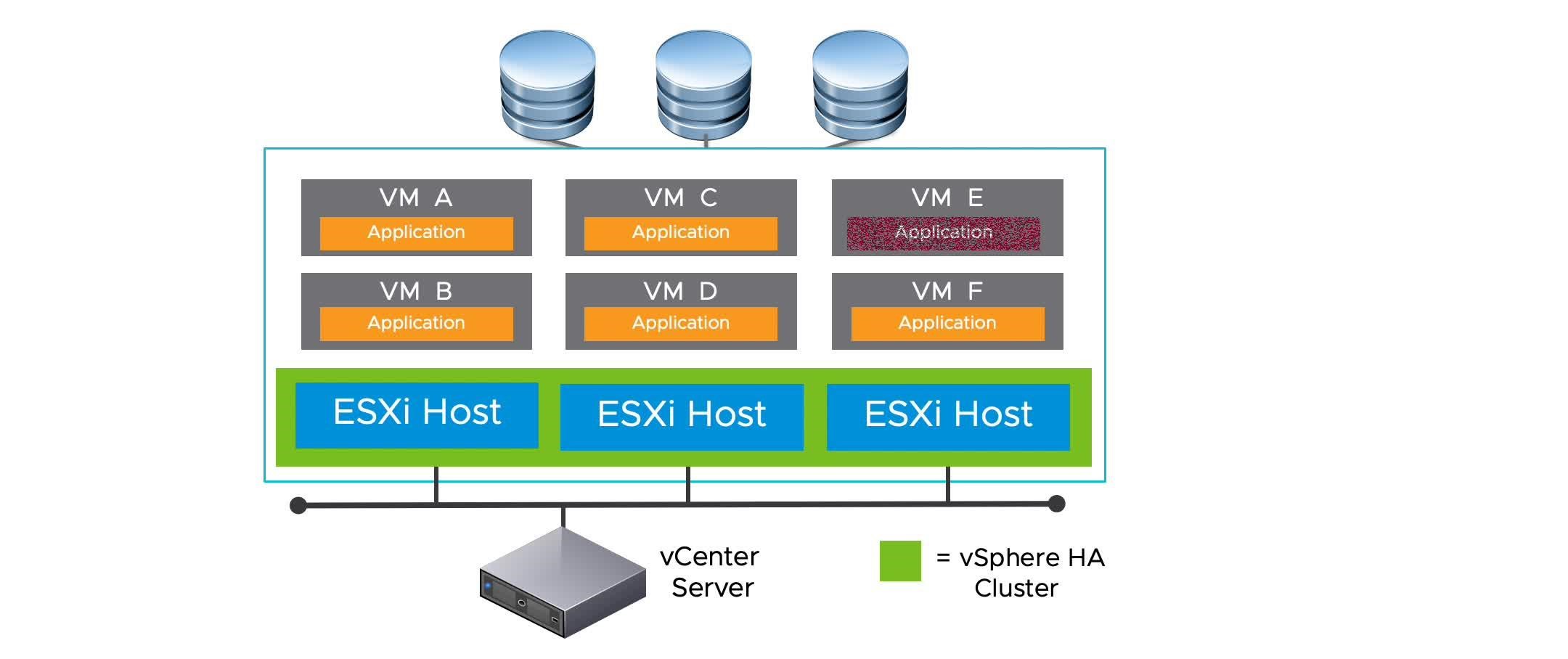
vSphere HA Scenario: Datastore Accessibility Failures
If VM Component Protection (VMCP) is enabled, vSphere HA can detect datastore accessibility failures and provide automated recovery for affected VMs. You can determine the response that vSphere HA makes to such a failure, ranging from the creation of event alarms to VM restarts on other hosts:
- All paths down (APD):
- Recoverable.
- Represents a transient or unknown accessibility loss.
- Response can be either Issue events, Power off and restart VMs – Conservative restart policy, or Power off and restart VMs – Aggressive restart policy.
- Permanent device loss (PDL):
- Unrecoverable loss of accessibility.
- Occurs when a storage device reports that the datastore is no longer accessible by the host.
- Response can be either Issue events or Power off and restart VMs.
vSphere HA Scenario: Protecting VMs Against Network Isolation vSphere HA restarts VMs if their host becomes isolated on the management or vSAN network. 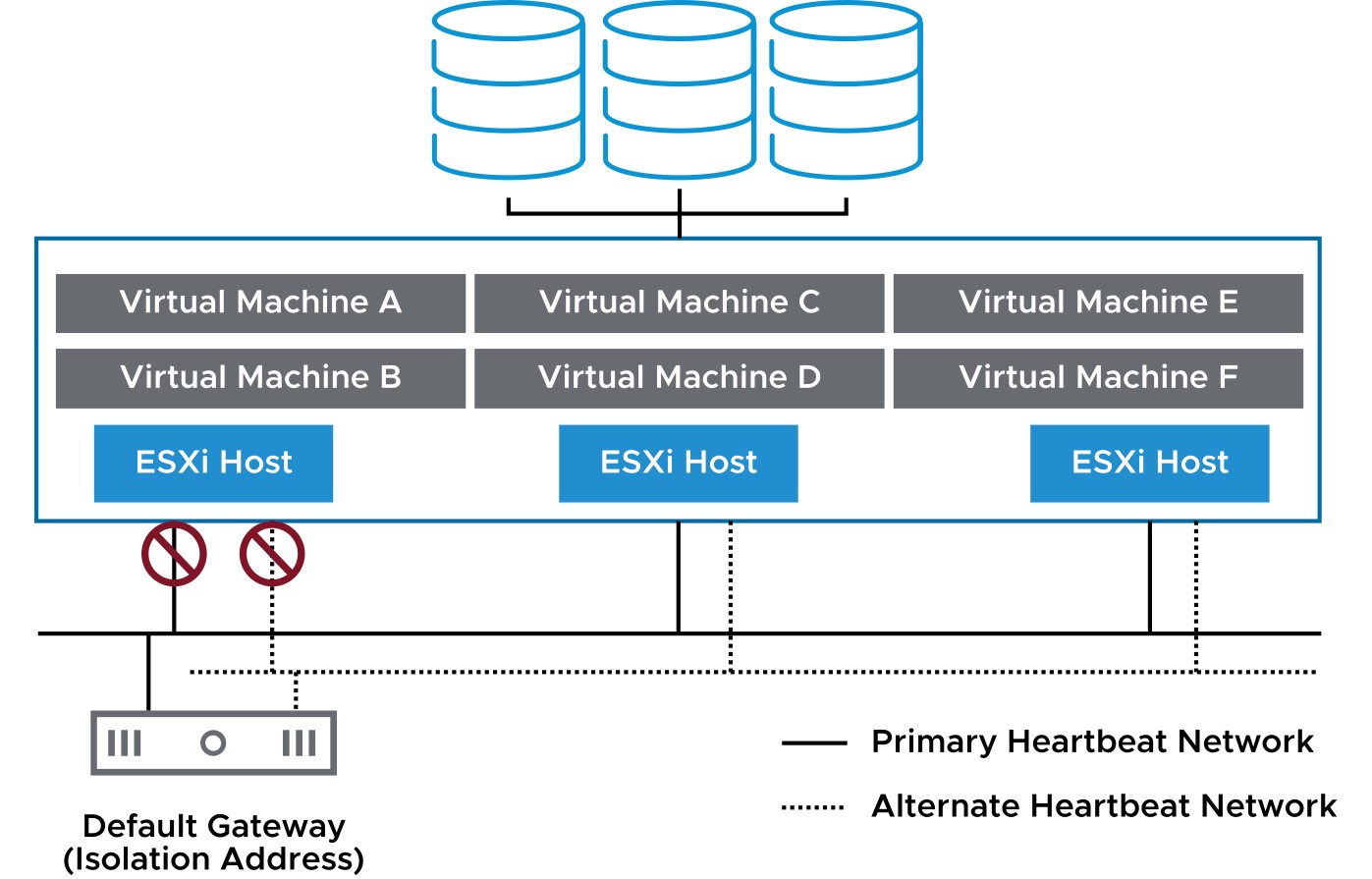
Host network isolation occurs when a host is still running, but it can no longer observe traffic from vSphere HA agents on the management network:
- The host tries to ping the isolation addresses. An isolation address is an IP address or FQDN that can be manually specified (the default is the host’s default gateway).
- If pinging fails, the host declares that it is isolated from the network.
- This protection is provided even if the network becomes partitioned.
Importance of Redundant Heartbeat Networks
Redundant heartbeat networks ensure reliable failure detection and minimize the chance of host isolation scenarios. In a vSphere HA cluster, heartbeats have the following characteristics:
- They are sent between the master host and the subordinate hosts.
- They are used to determine whether a master host or a subordinate host has failed.
- They are sent over a heartbeat network.
Redundancy Using NIC Teaming
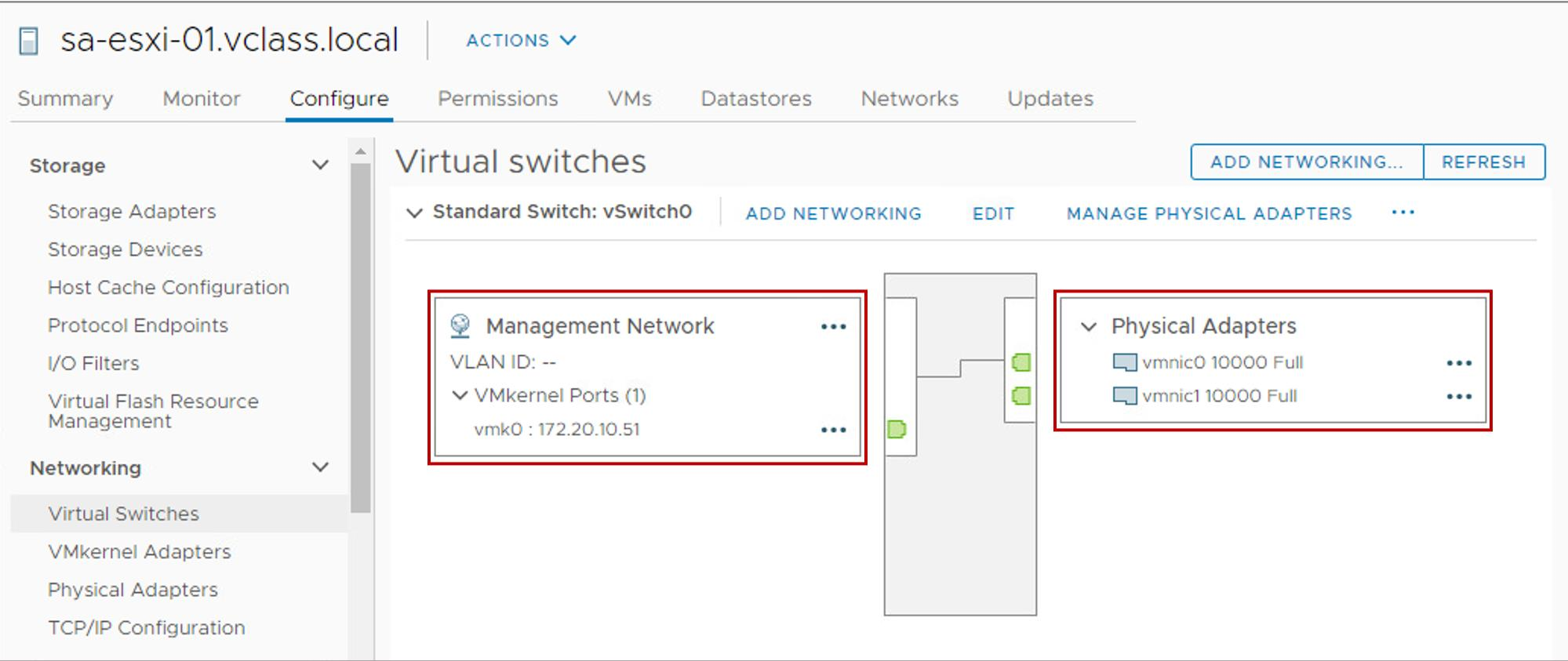
A heartbeat network is implemented in the following ways:
- By using a VMkernel port that is marked for management
- By using a VMkernel port that is marked for vSAN traffic when vSAN is in use You can use NIC teaming to create a redundant heartbeat network on ESXi hosts.
Redundancy Using Additional Networks
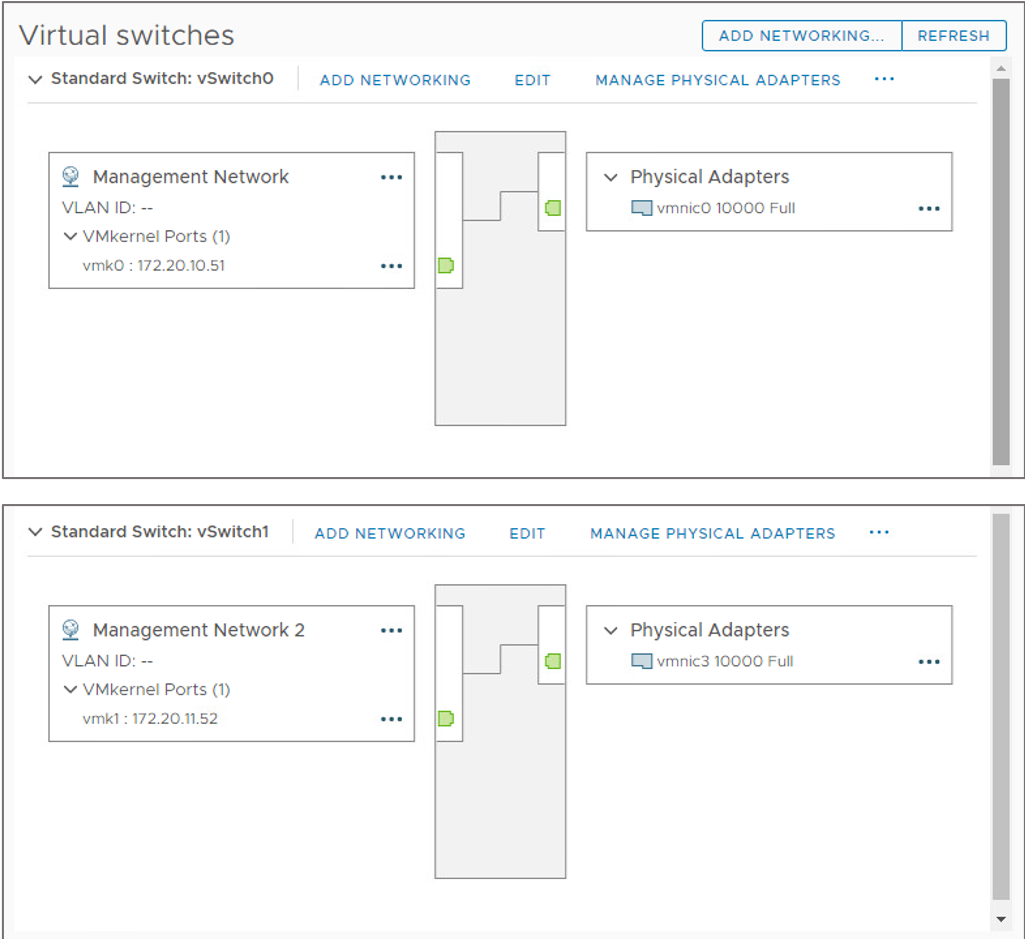
You can create redundancy by configuring more heartbeat networks.
On each ESXi host, create a second VMkernel port on a separate virtual switch with its own physical adapter.
Redundant management networking supports the reliable detection of failures and prevents isolation or partition conditions from occurring, because heartbeats can be sent over multiple networks.
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this Introduction to vSphere HA lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Identify options for configuring a highly available vSphere environment
- Describe how vSphere HA responds when an ESXi host, a virtual machine, or an application fails