Creating Virtual Machine Snapshots
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Take a snapshot of a virtual machine
- Manage multiple snapshots
- Delete virtual machine snapshots
- Consolidate snapshots
VM Snapshots

- With snapshots, you can preserve the state of the VM so that you can repeatedly return to the same state.
- For example, if problems occur during the patching or upgrading process, you can stop the process and revert to the previous state.
- VM snapshots are not recommended as a VM backup strategy.
Taking Snapshots
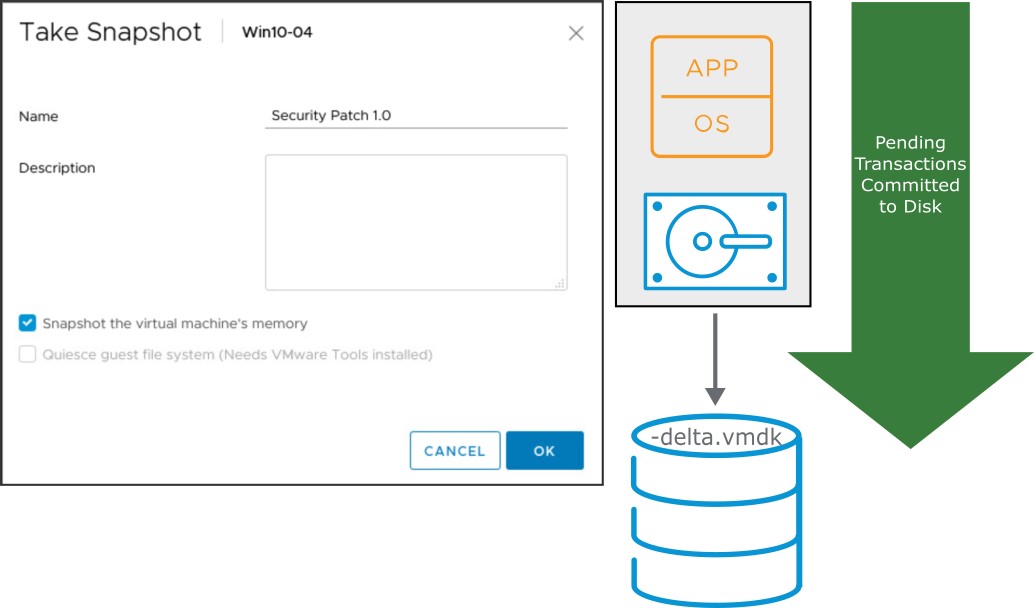
You can take a snapshot while a VM is powered on, powered off, or suspended. A snapshot captures the following items:
- VM configuration
- VM memory state (optional)
- Virtual disks
A snapshot capture does not include Independent virtual disks (persistent and nonpersistent).
Types of Snapshots
A delta or child disk is created when you create a snapshot:
- On the VMFS datastore, the delta disk is a sparse disk.
- Delta disks use different sparse formats depending on the type of datastore.
| Snapshot Type | Notes | Filename | Block Size |
| VMFSsparse | VMFS5 with virtual disks smaller than 2 TB | #-delta.vmdk | 512 bytes |
| SEsparse |
|
#-sesparse.vmdk | 4 KB |
| vsanSparse | vSAN | Delta object | 4 MB |
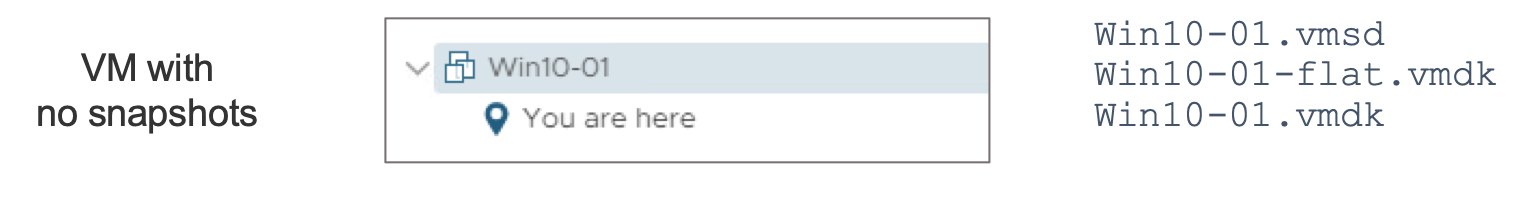
VM Snapshot Files
 A snapshot consists of a set of files:
A snapshot consists of a set of files:
- -Snapshot#.vmsn: Configuration state
- -Snapshot#.vmem: Memory state (optional)
- -00000#.vmdk: Disk descriptor
- -00000#-delta.vmdk: VMFS5 delta
- -00000#-sesparse.vmdk: VMFS6 delta
- .vmsd: Stores names, descriptions, and relationships for all the VM’s snapshots
VM Snapshot Files Example (1)
VM Snapshot Files Example (2)

VM Snapshot Files Example (3)

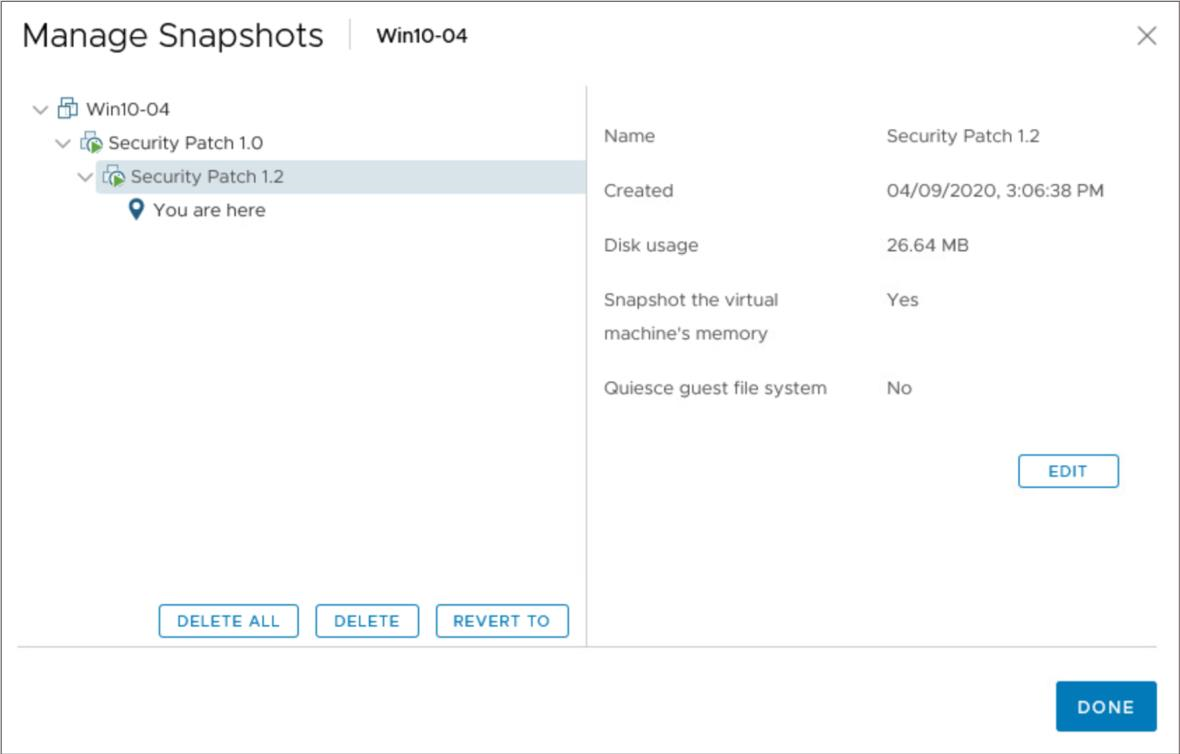
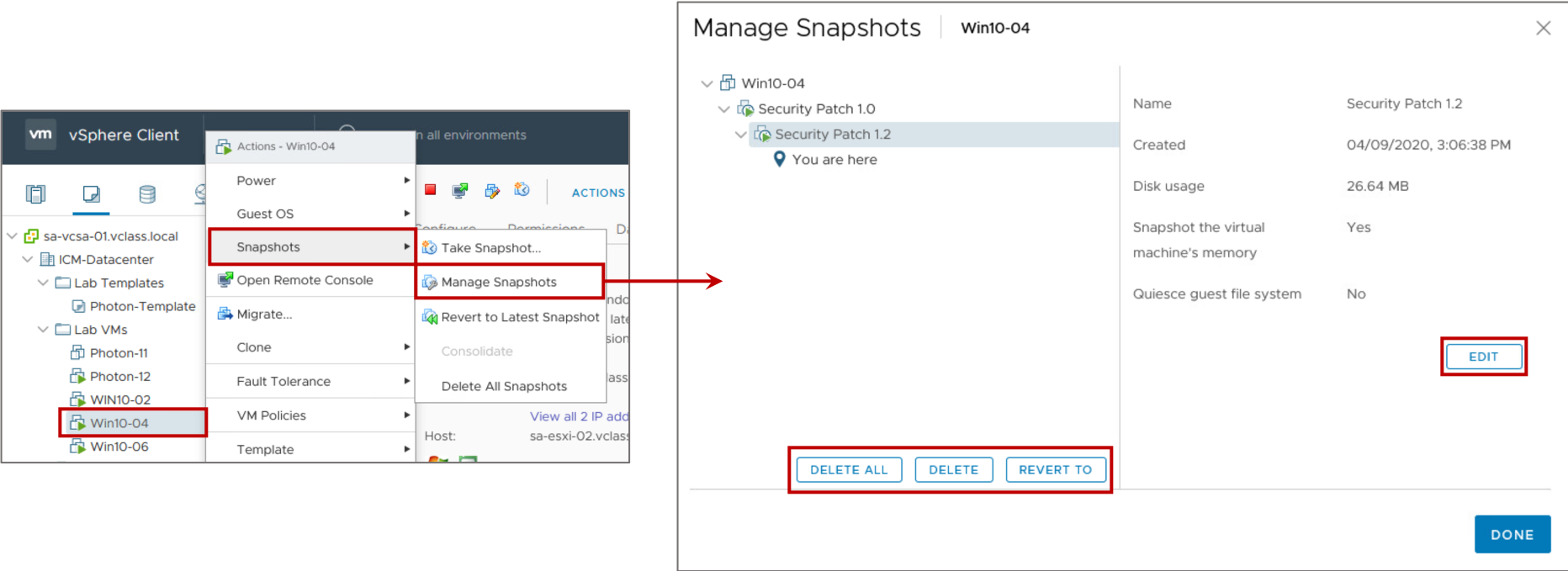
Managing Snapshots
In the vSphere Client, you can view snapshots for the active VM and take edit, delete, and revert to actions.
Deleting VM Snapshots (1)
If you delete a snapshot one or more levels above the You are here level, the snapshot state is deleted. In this example, the snap01 data is committed into the parent (base disk), and the foundation for snap02 is retained.
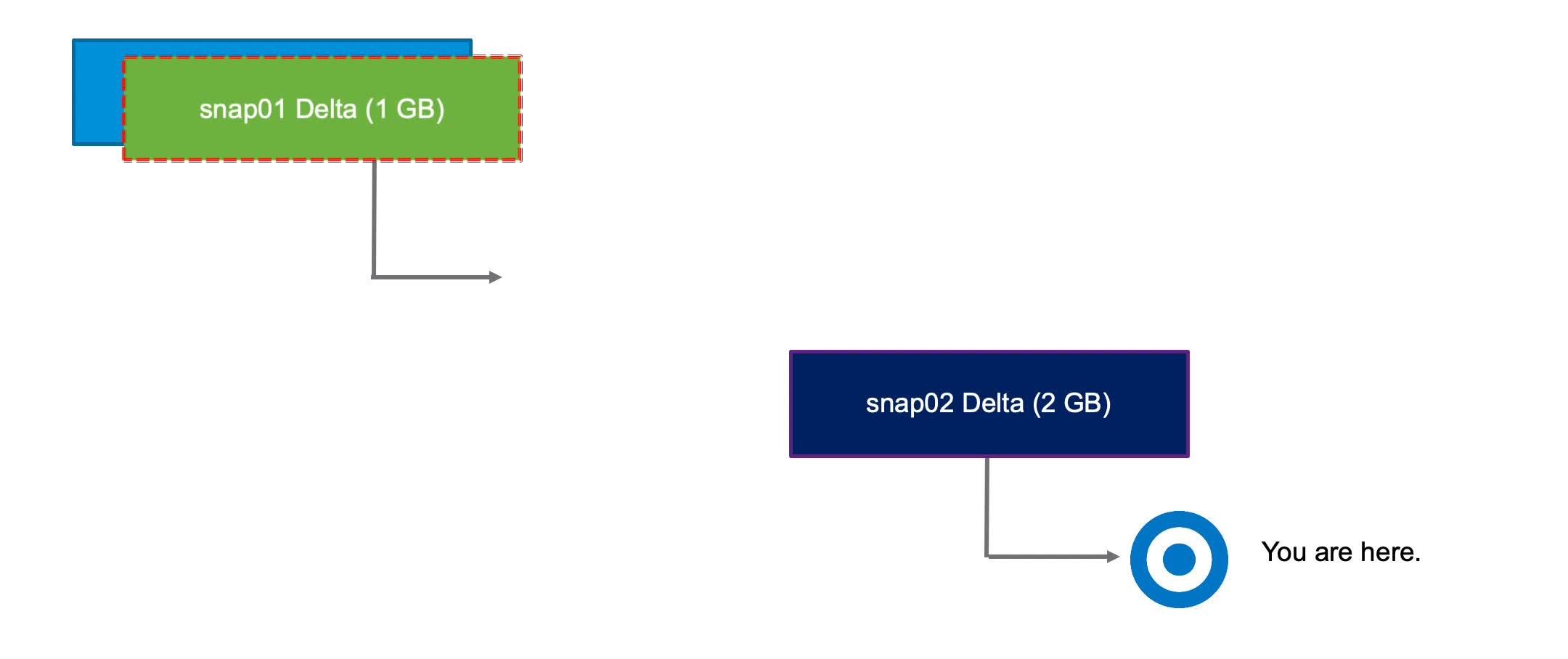
Deleting VM Snapshots (2)
If you delete the latest snapshot, the changes are committed to its parent. The snap02 data is committed into snap01 data, and the snap02 -delta.vmdk file is deleted. 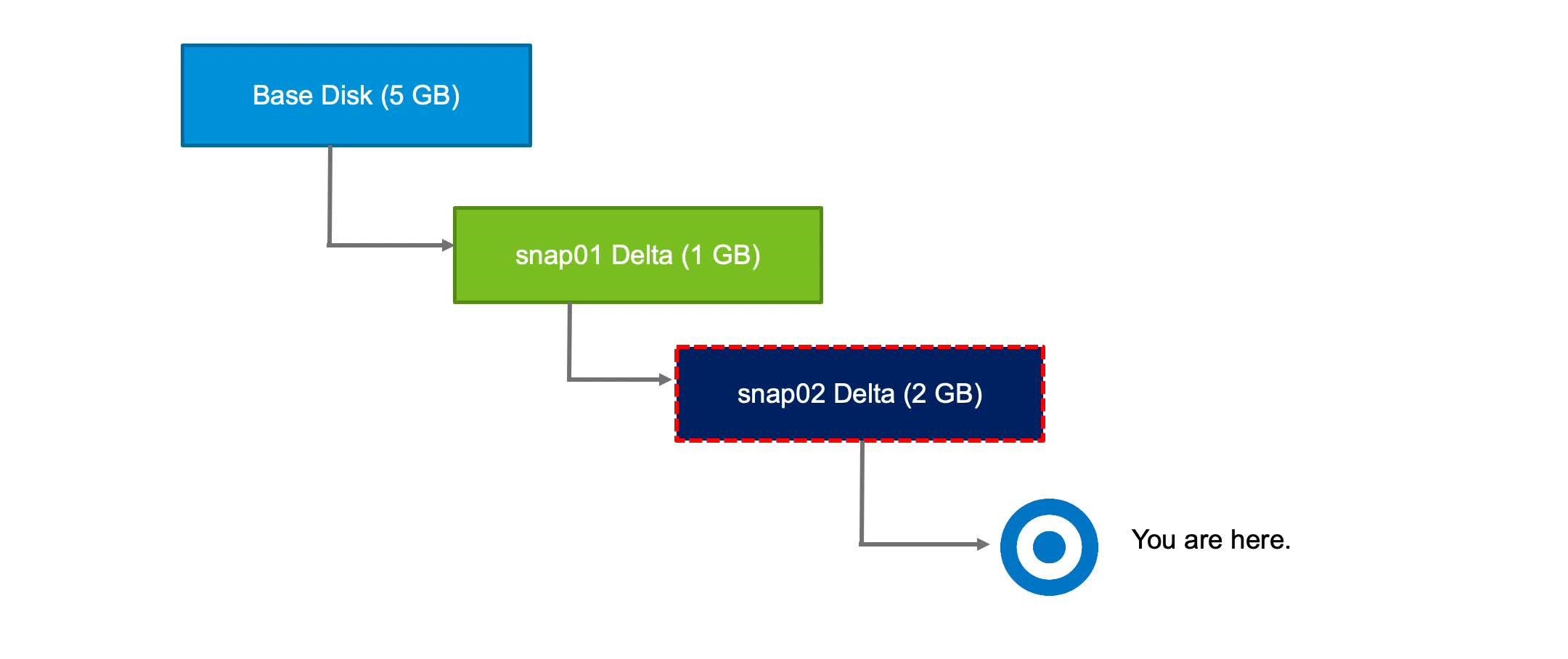
Deleting VM Snapshots (3)
If you delete a snapshot one or more levels below the You are here level, subsequent snapshots are deleted, and you can no longer return to those states. The snap02 data is deleted. 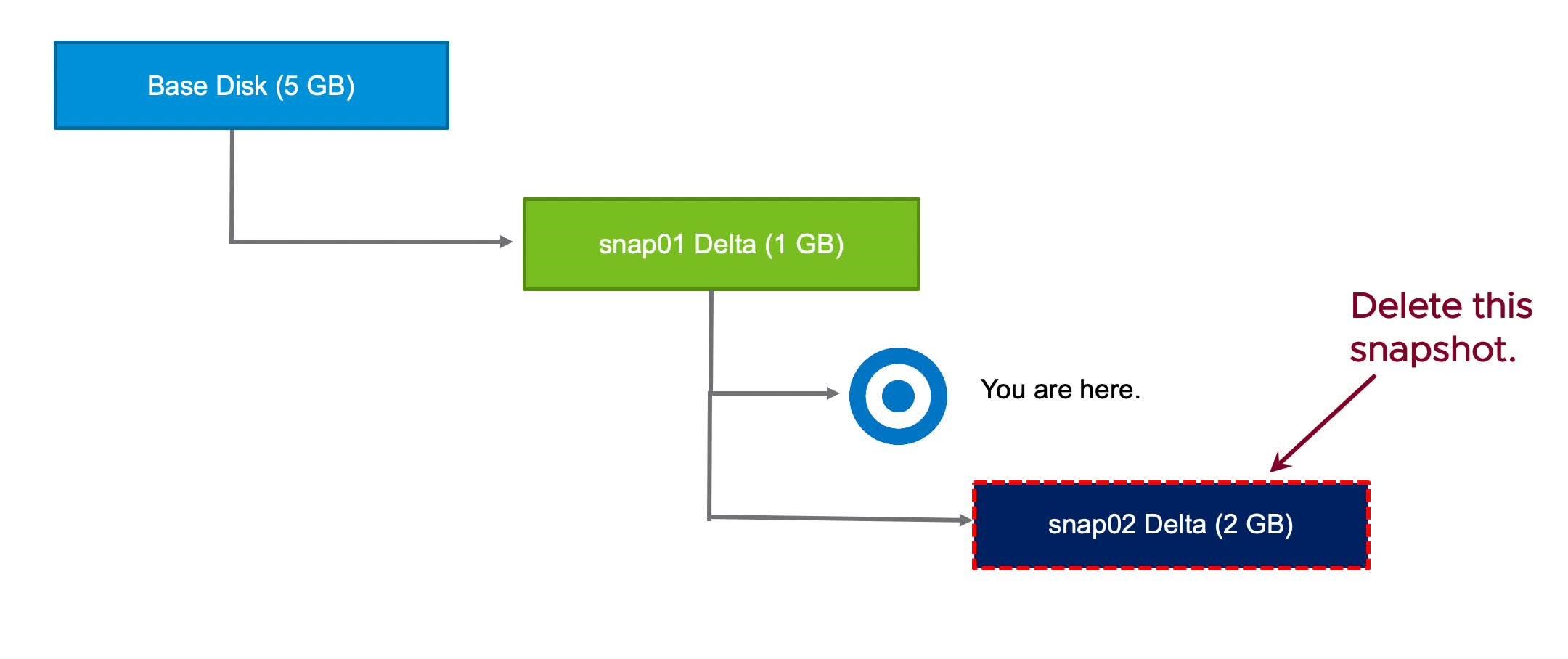
Deleting All VM Snapshots
The delete-all-snapshots mechanism uses storage space efficiently. The size of the base disk does not increase. Snap01 is committed to the base disk before snap02 is committed. 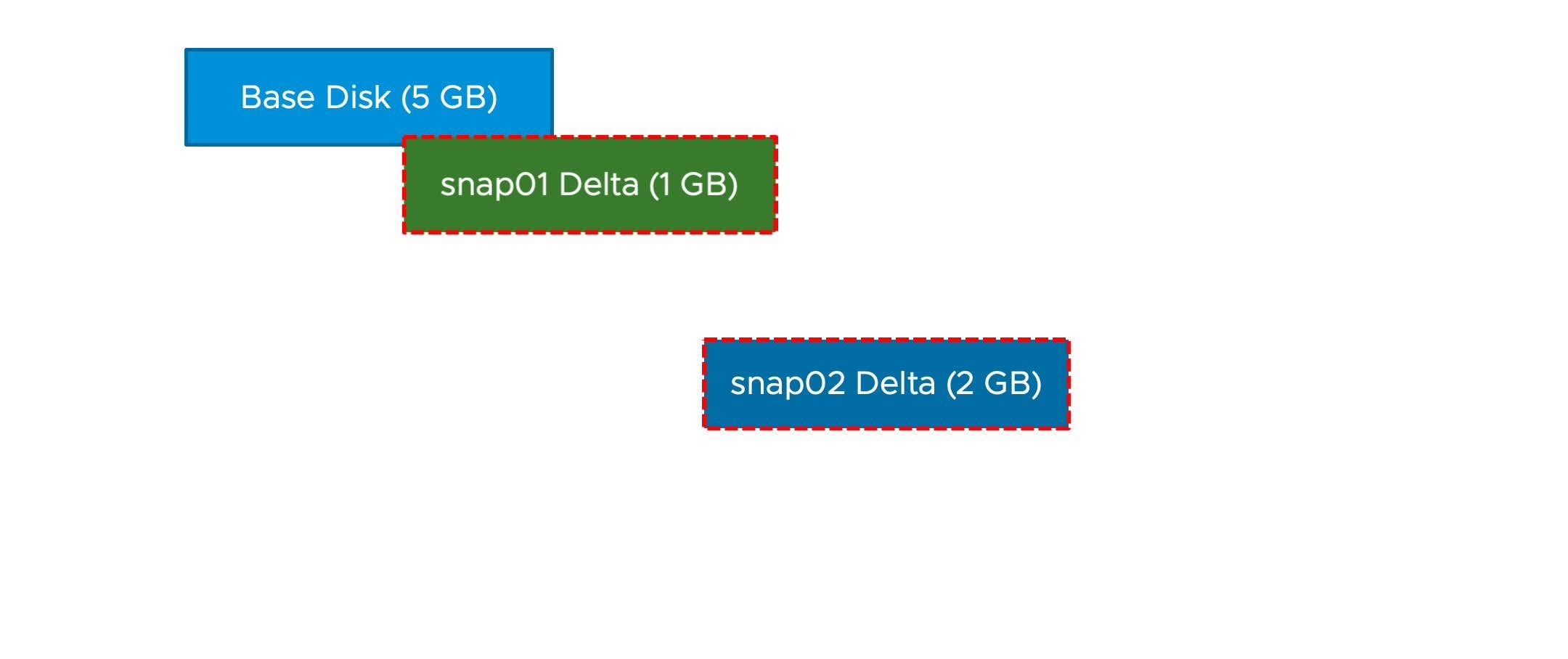
About Snapshot Consolidation
Snapshot consolidation is a method for committing a chain of delta disks to the base disks when the Snapshot Manager shows that no snapshots exist but the delta disk files remain on the datastore. Snapshot consolidation resolves problems that might occur with snapshots:
- The snapshot descriptor file is committed correctly, and the Snapshot window shows that all the snapshots are deleted.
- The snapshot files (-delta.vmdk) are still part of the VM.
- Delta disk files continue to expand until the datastore on which the VM is located runs out of space.
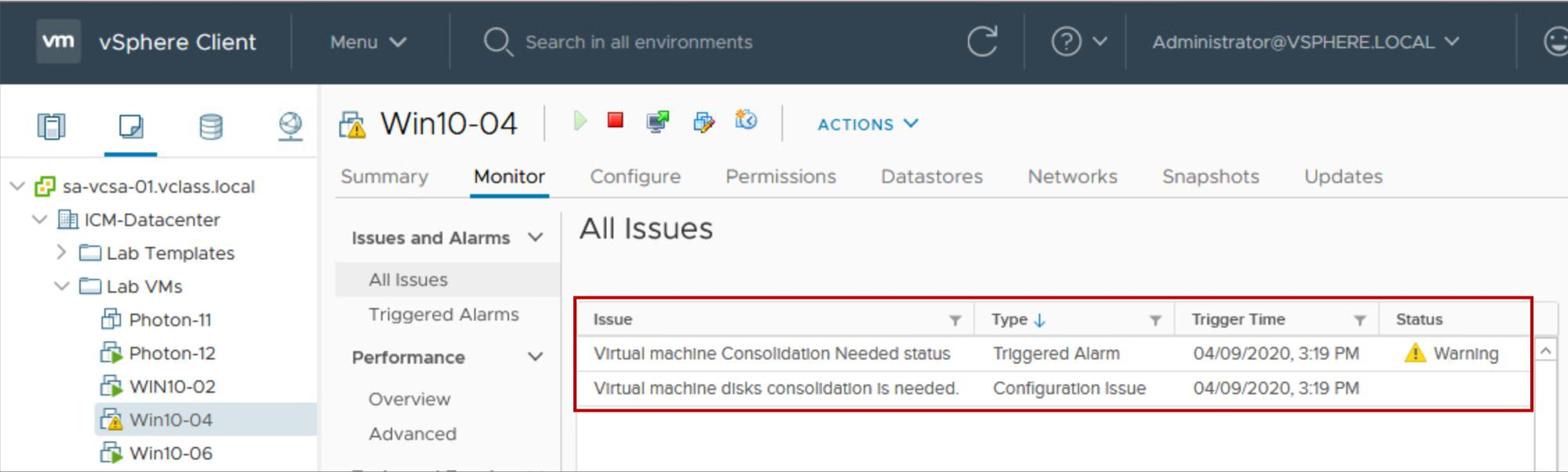
Discovering When to Consolidate Snapshots
On the Monitor tab under All Issues for the VM, a warning notifies you that a consolidation is required.
Consolidating Snapshots
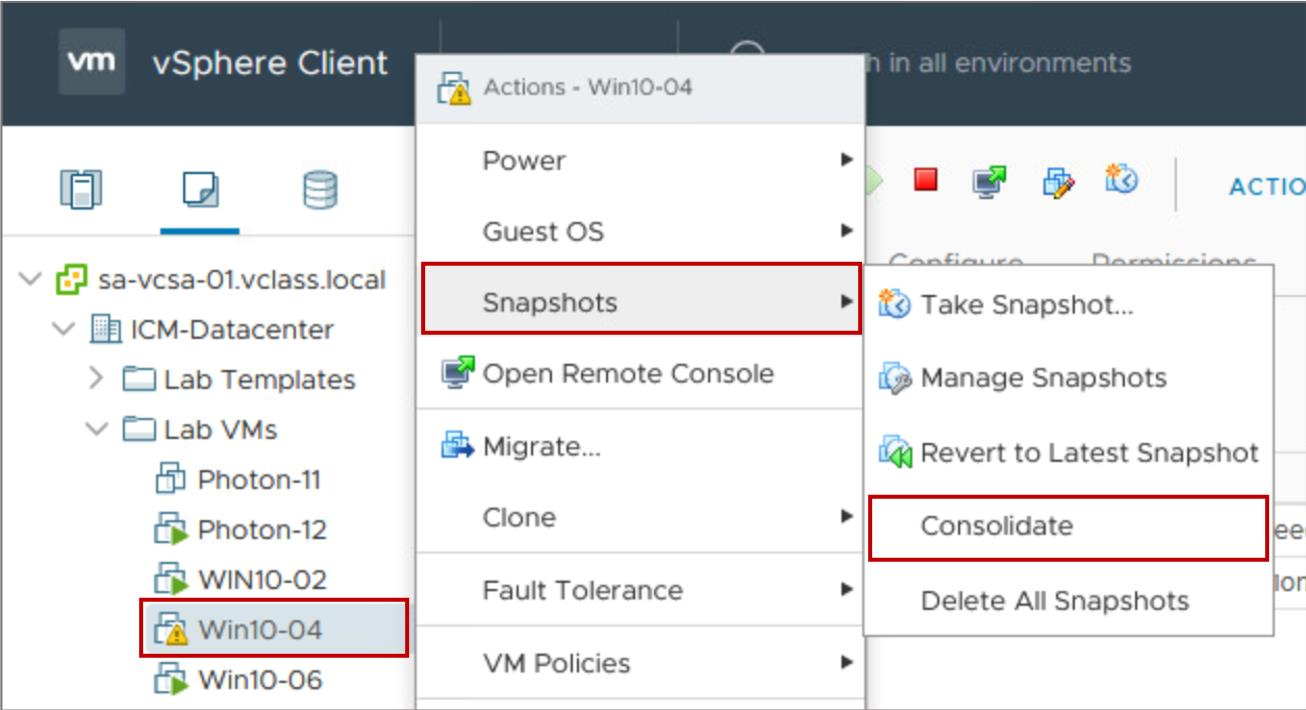
- After the snapshot consolidation warning appears, you can use the vSphere Client to consolidate the snapshots.
- All snapshot delta disks are committed to the base disks.
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this Creating Virtual Machine Snapshots lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Take a snapshot of a virtual machine
- Manage multiple snapshots
- Delete virtual machine snapshots
- Consolidate snapshots