Software Defined WAN (SDWAN)
This section defines the benefits of SD-WAN over traditional WANs as well as the components and features of the Cisco SD-WAN solution, including the orchestration plane, management plane, control plane, and data plane.
Managing enterprise networks is becoming more complex, with customers embracing a multicloud approach, applications moving to the cloud, mobile and IoT devices growing exponentially in the network, and the internet edge moving to the branch. This digital transformation is powering the adoption of SD-WAN by customers looking to do the following:
- Lower costs and reduce risks with simple WAN automation and orchestration.
- Extend their enterprise networks (such as branch or on-premises) seamlessly into the public cloud.
- Provide optimal user experience for SaaS applications.
- Leverage a transport-independent WAN for lower cost and higher diversity. This means the underlay network can be any type of IP-based network, such as the internet, MPLS, 3G/4G LTE, satellite, or dedicated circuits.
- Enhance application visibility and use that visibility to improve performance with intelligent path control to meet SLAs for business-critical and real-time applications.
- Provide end-to-end WAN traffic segmentation and encryption for protecting critical enterprise compute resources.
SD-WAN Solutions
Cisco currently offers two Software Defined WAN (SD-WAN) solutions:
- Cisco SD-WAN (based on Viptela) – This is the preferred solution for organizations that require an SD-WAN solution with cloud-based initiatives that provides granular segmentation, advanced routing, advanced security, and complex topologies while connecting to cloud instances.
- Meraki SD-WAN – This is the recommended solution for organizations that require unified threat management (UTM) solutions with SD-WAN functionality or that are existing Cisco Meraki customers looking to expand to SD-WAN. UTM is an all-in-one security solution delivered in a single appliance and typically includes the following security features: firewall, VPN, intrusion prevention, antivirus, antispam, and web content filtering.
Cisco SD-WAN Architecture
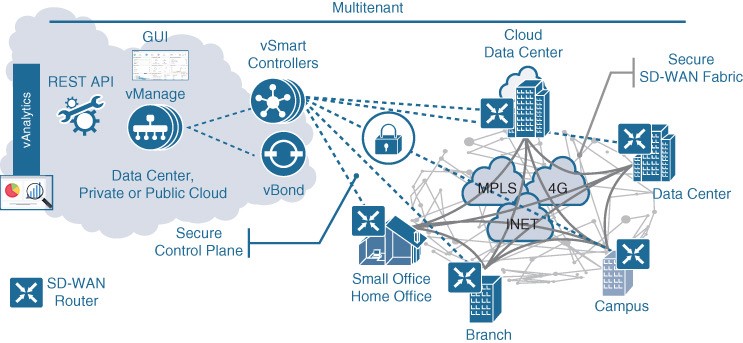
Cisco SD-WAN (based on Viptela) is a cloud-delivered overlay WAN architecture that facilitates digital and cloud transformation for enterprises. It addresses all the customer requirements mentioned earlier. Figure 23-13 shows how SD-WAN can be used to provide secure connectivity to remote offices, branch offices, campus networks, data centers, and the cloud over any type of IP-based underlay transport network, such as the internet, 3G/4G LTE, and MPLS. It also illustrates how some of the components to manage the SD-WAN fabric can be deployed on a data center, private cloud, or public cloud.

Figure 23-13 SD-WAN Solution Architecture
Cisco SD-WAN Solution
The Cisco SD-WAN solution has four main components and an optional analytics service:
- vManage NMS – The vManage NMS is a single pane of glass network management system (NMS) GUI that is used to configure and manage the full SD-WAN solution. It enables centralized provisioning and simplifies network changes.
- vSmart Controller – vSmart controllers have pre-installed credentials that allow them to authenticate every SD-WAN router that comes online. These credentials ensure that only authenticated devices are allowed access to the SD-WAN fabric. After successful authentication, each vSmart controller establishes a permanent DTLS tunnel to each SD-WAN router in the SD-WAN fabric and uses these tunnels to establish Overlay Management Protocol (OMP) neighbor relationships with each SD-WAN router. OMP is a proprietary routing protocol similar to BGP that can advertise routes, next hops, keys, and policy information needed to establish and maintain the SD-WAN fabric.
Cisco SD-WAN Routers (vEdge and cEdge): Cisco SD-WAN routers deliver the essential WAN, security, and multicloud capabilities of the Cisco SD-WAN solution. They are available as hardware, software, cloud, or virtualized routers that sit at the perimeter of a site, such as a remote office, branch office, campus, or data center. SD-WAN routers support standard router features, such as OSPF, BGP, ACLs, QoS, and routing policies, in addition to the SD-WAN overlay control and data plane functions. There are two different SD-WAN router options available for the Cisco SD-WAN solution:
- vEdge: The original Viptela platforms running Viptela software.
- cEdge: Viptela software integrated with Cisco IOS-XE. This is supported on CSR, ISR, ASR1K, ENCS, and the cloud-enabled CSRv and ISRv platforms.
A main differentiator between SD-WAN cEdge routers and vEdge routers is that cEdge routers support advanced security features, as demonstrated in Table 23-2.
| Feature | cEdge | vEdge |
| Cisco AMP and AMP Threat Grid | Yes | No |
| Enterprise Firewall | Yes | Yes |
| Cisco Umbrella DNS Security | Yes | Yes |
| URL filtering | Yes | No |
| The Snort intrusion prevention system (IPS) | Yes | No |
| Embedded platform security (including the Cisco Trust Anchor module) | Yes | No |
Table 23-2 SD-WAN Router Advanced Security Feature Comparison
vBond Orchestrator
The vBond orchestrator authenticates the vSmart controllers and the SD-WAN routers and orchestrates connectivity between them. It is the only device that must have a public IP address so that all SD-WAN devices in the network can connect to it. A vBond orchestrator is an SD-WAN router that only performs vBond orchestrator functions. The major components of the vBond orchestrator are:
- Control plane connection – Each vBond orchestrator has a permanent control plane connection over a DTLS tunnel with each vSmart controller.
- NAT traversal – The vBond orchestrator facilitates the initial orchestration between SD-
WAN routers and vSmart controllers when one or both of them are behind NAT devices.
- Load balancing – In a domain with multiple vSmart controllers, the vBond orchestrator automatically performs load balancing of SD-WAN routers across the vSmart controllers when routers come online.
vAnalytics
vAnalytics is an optional analytics and assurance service that has many advanced capabilities, including the following:
- Visibility into applications and infrastructure across the WAN
- Forecasting and what-if analysis
- Intelligent recommendations
These capabilities benefit SD-WAN in ways that are not possible without v Analytics. For example, if a branch office is experiencing latency or loss on its MPLS link, vAnalytics detects it and compare that latency or loss with information on other organizations in the area that it is also monitoring to see if they are also having that same issue in their circuits. If they are, vAnalytics can then report the issue with confidence to the SPs. vAnalytics can also help predict how much bandwidth is truly required for any location. This aids in deciding whether a circuit can be downgraded to a lower bandwidth to reduce costs.
Cisco Software Defined WAN (SD-WAN) Cloud OnRamp
- Traditional enterprise WAN architectures are not designed for the cloud. As organizations adopt more SaaS applications such as Office 365 and public cloud infrastructures such as AWS and Microsoft Azure, the current network infrastructure poses major problems related to the level of complexity and end-user experience. The Cisco SD-WAN solution includes a set of functionalities addressing optimal cloud SaaS application access and IaaS connectivity, called Cloud OnRamp.
- Cloud OnRamp delivers the best application quality of experience (QoE) for SaaS applications by continuously monitoring SaaS performance across diverse paths and selecting the best-performing path based on performance metrics (jitter, loss, and delay). In addition, it simplifies hybrid cloud and multicloud IaaS connectivity by extending the SDWAN fabric to the public cloud while at the same time increasing high availability and scale.
Cloud OnRamp for SaaS
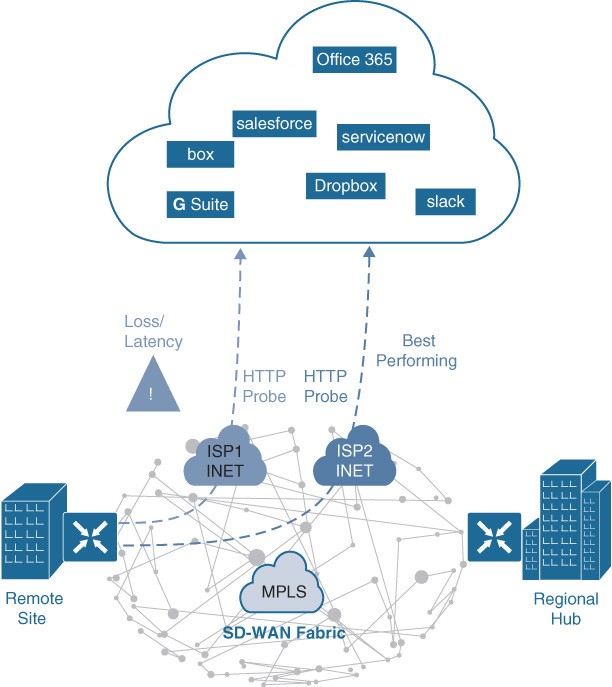
Figure 23-14 Cloud OnRamp for SaaS with Dual DIA
- Figure 23-14 illustrates a remote site with dual direct internet access (DIA) circuits from two different internet service providers (ISP1 and ISP2).
- When Cloud OnRamp for SaaS is configured for an SaaS application on vManage, the SD-WAN router at the remote site starts sending small HTTP probes to the SaaS application through both DIA circuits to measure latency and loss. Based on the results, the SD-WAN router will know which circuit is performing (in this case, ISP2) and sends the SaaS application traffic out that circuit.
- The process of probing continues, and if a change in performance characteristics of ISP2’s DIA circuit occurs, the remote site SD-WAN router makes an appropriate forwarding decision.
Cloud OnRamp for SaaS (Cont.)
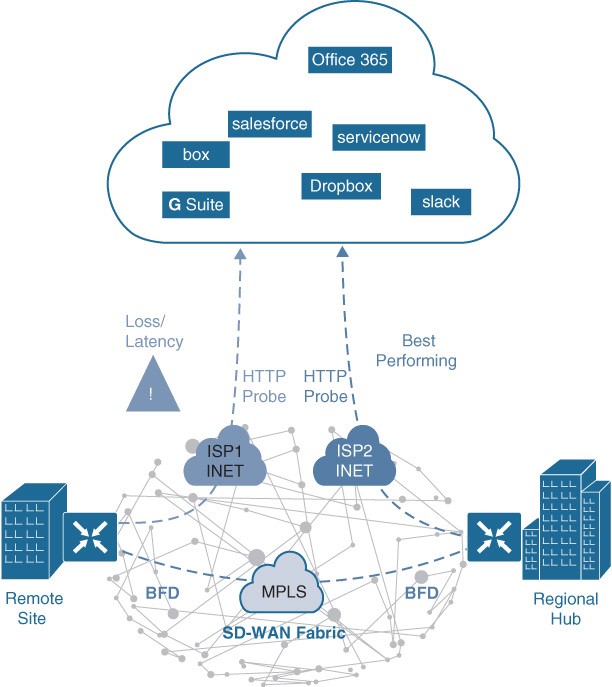
Figure 23-15 Cloud OnRamp for SaaS DIA and Gateway
Figure 23-15 illustrates another example of Cloud OnRamp for SaaS. In this case, the remote site has a single DIA circuit to ISP1 and an SD-WAN fabric DTLS session to the regional hub. Much as in the previous case, Cloud OnRamp for SaaS can be configured on the vManage NMS and become active on the remote site SD-WAN router. However, in this case, Cloud OnRamp for SaaS also gets enabled on the regional hub SD-WAN router and is designated as the gateway node. Quality probing service via HTTP toward the cloud SaaS application of interest starts on both the remote site SD-WAN and the regional hub SD-WAN.
Cloud OnRamp for IaaS
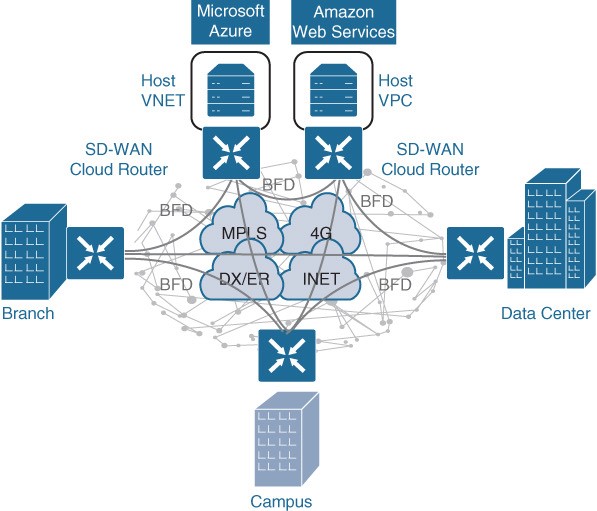
Figure 23-16 Cloud OnRamp for IaaS
With the Cisco SD-WAN solution, ubiquitous connectivity, zero-trust security, end-to-end segmentation, and application-aware QoS policies can be extended into the IaaS environments by using SD-WAN cloud routers, as illustrated in Figure 23-16. The transport-independent capability of the Cisco SD-WAN solution allows the use of a variety of connectivity methods by securely extending the SD-WAN fabric into the public cloud environment across any underlay transport network. These include the internet, MPLS, 3G/4G LTE, satellite, and dedicated circuits such as AWS’s DX and Microsoft Azure’s ER.