OSPF Path Selection
how OSPF makes path selection choices for routes learned within the OSPF routing domain.
- OSPF executes Dijkstra’s shortest path first (SPF) algorithm to create a loop-free topology of shortest paths.
- All routers use the same logic to calculate the shortest path for each network.
- Path selection prioritizes paths by using the following logic: intra-area, interarea, and external routes (which involves additional logic and not covered here)
Intra-Area Routes
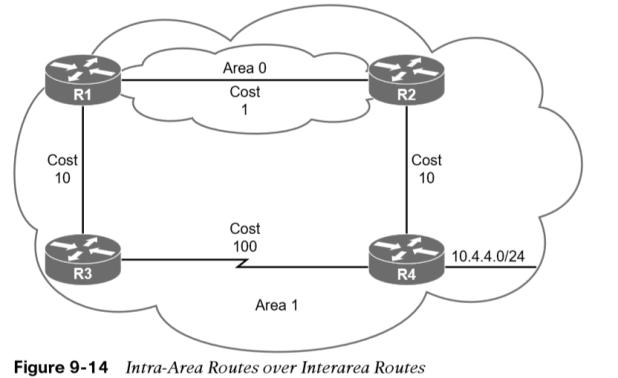
Routes advertised via a type 1 LSA for an area are always preferred over type 3 LSAs. If multiple intra-area routes exist, the path with the lowest total path metric is installed in the OSPF Routing Information Base (RIB), which is then presented to the router’s global RIB. If there is a tie in metric, both routes install into the OSPF RIB.  In Figure 9-14, R1 is computing the route to 10.4.4.0/24. Instead of taking the faster Ethernet connection, R1 takes the path across the slower serial link to R4 because that is the intra-area path.
In Figure 9-14, R1 is computing the route to 10.4.4.0/24. Instead of taking the faster Ethernet connection, R1 takes the path across the slower serial link to R4 because that is the intra-area path. 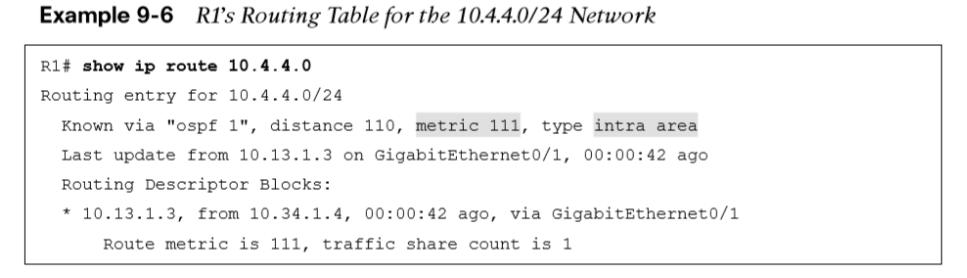 In Example 9-6, notice that the metric is 111 and that the intra-area path was selected over the interarea path with the lower total path metric.
In Example 9-6, notice that the metric is 111 and that the intra-area path was selected over the interarea path with the lower total path metric.
Interarea Routes and Equal Cost Multipathing
The next priority for selecting a path to a network is selection of the path with the lowest total path metric to the destination. If there is a tie in metric, both routes install into the OSPF RIB. All interarea paths for a route must go through Area 0 to be considered. In Figure 9-15, R1 is computing the path to R6. R1 uses the path R1–R3–R5–R6 because its total path metric is 35 versus the R1–R2–R4–R6 path, with a metric of 40. 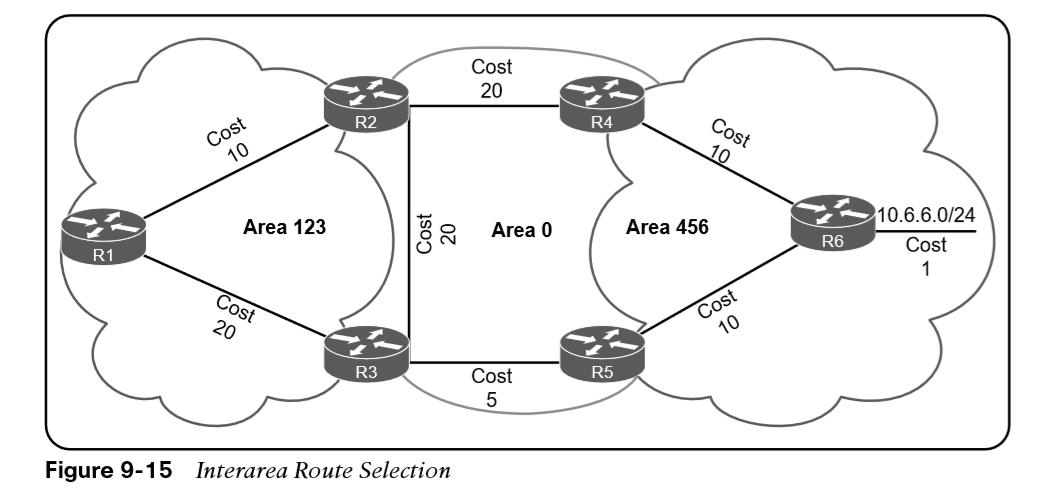 If OSPF identifies multiple paths in the path selection algorithms, those routes are installed into the routing table as equal-cost multipathing (ECMP) routes. The default maximum number of ECMP paths is four paths. Other useful information:
If OSPF identifies multiple paths in the path selection algorithms, those routes are installed into the routing table as equal-cost multipathing (ECMP) routes. The default maximum number of ECMP paths is four paths. Other useful information: