About Lesson
WAN and LAN topologies
Compare the characteristics of media access control methods on WAN and LAN topologies.
Physical and Logical Topologies
The topology of a network is the arrangement and relationship of the network devices and the interconnections between them.
There are two types of topologies used when describing networks:
- Physical topology – shows physical connections and how devices are interconnected.
- Logical topology – identifies the virtual connections between devices using device interfaces and IP addressing schemes.
WAN Topologies
There are three common physical WAN topologies:
- Point-to-point – the simplest and most common WAN topology. Consists of a permanent link between two endpoints.
- Hub and spoke – similar to a star topology where a central site interconnects branch sites through point-to-point links.
- Mesh – provides high availability but requires every end system to be connected to every other end system.
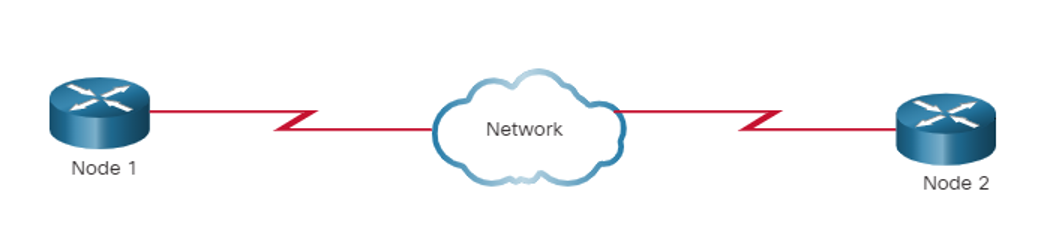
Point-to-Point WAN Topology
- Physical point-to-point topologies directly connect two nodes.
- The nodes may not share the media with other hosts.
- Because all frames on the media can only travel to or from the two nodes, Point-to-Point WAN protocols can be very simple.
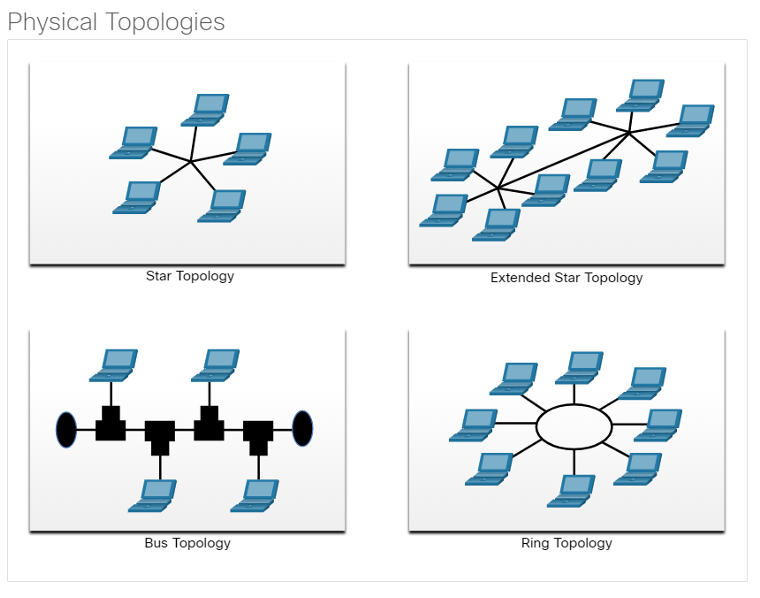
LAN Topologies
End devices on LANs are typically interconnected using a star or extended star topology. Star and extended star topologies are easy to install, very scalable and easy to troubleshoot.
Early Ethernet and Legacy Token Ring technologies provide two additional topologies:
- Bus – All end systems chained together and terminated on each end.
- Ring – Each end system is connected to its respective neighbors to form a ring.

Half and Full Duplex Communication
Half-duplex communication
- Only allows one device to send or receive at a time on a shared medium.
- Used on WLANs and legacy bus topologies with Ethernet hubs.
Full-duplex communication
- Allows both devices to simultaneously transmit and receive on a shared medium.
- Ethernet switches operate in full-duplex mode.
Access Control Methods
Contention-based access
- All nodes operating in half-duplex, competing for use of the medium. Examples are:
- Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) as used on legacy bus-topology Ethernet.
- Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) as used on Wireless LANs.
Controlled access
- Deterministic access where each node has its own time on the medium.
- Used on legacy networks such as Token Ring and ARCNET.
Contention-Based Access – CSMA/CD
CSMA/CD – Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection
- Used by legacy Ethernet LANs.
- Operates in half-duplex mode where only one device sends or receives at a time.
- Uses a collision detection process to govern when a device can send and what happens if multiple devices send at the same time.
CSMA/CD collision detection process:
- Devices transmitting simultaneously will result in a signal collision on the shared media.
- Devices detect the collision.
- Devices wait a random period of time and retransmit data.
CSMA/CA – Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance
- Used by IEEE 802.11 WLANs.
- Operates in half-duplex mode where only one device sends or receives at a time.
- Uses a collision avoidance process to govern when a device can send and what happens if multiple devices send at the same time.
CSMA/CA collision avoidance process:
- When transmitting, devices also include the time duration needed for the transmission.
- Other devices on the shared medium receive the time duration information and know how long the medium will be unavailable.
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
|---|---|
| Purpose of the Data Link Layer | Describe the purpose and function of the data link layer in preparing communication for transmission on specific media. |
| WAN and LAN topologies | Compare the characteristics of media access control methods on WAN and LAN topologies. |
| Data Link Frame | Describe the characteristics and functions of the data link frame. |
Other useful information
- Full CCNA Course
- CCNA Certificate Information
- 200-301 CCNA Exam Questions and Solutions
- 200-301 CCNA Exam Topics
Join the conversation