About Lesson
VLSM
Variable length subnet mask (VLSM) is a computer networking technique to divide an IP network into subnets with different subnet masks
IPv4 Address Conservation
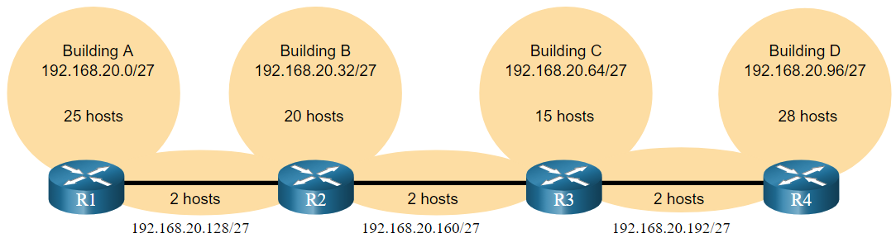
- Given the topology, 7 subnets are required (i.e, four LANs and three WAN links) and the largest number of host is in Building D with 28 hosts. A /27 mask would provide 8 subnets of 30 host IP addresses and therefore support this topology.

- However, the point-to-point WAN links only require two addresses and therefore waste 28 addresses each for a total of 84 unused addresses.

- Applying a traditional subnetting scheme to this scenario is not very efficient and is wasteful. VLSM was developed to avoid wasting addresses by enabling us to subnet a subnet.
VLSM
- The left side displays the traditional subnetting scheme (i.e., the same subnet mask) while the right side illustrates how VLSM can be used to subnet a subnet and divided the last subnet into eight /30 subnets.
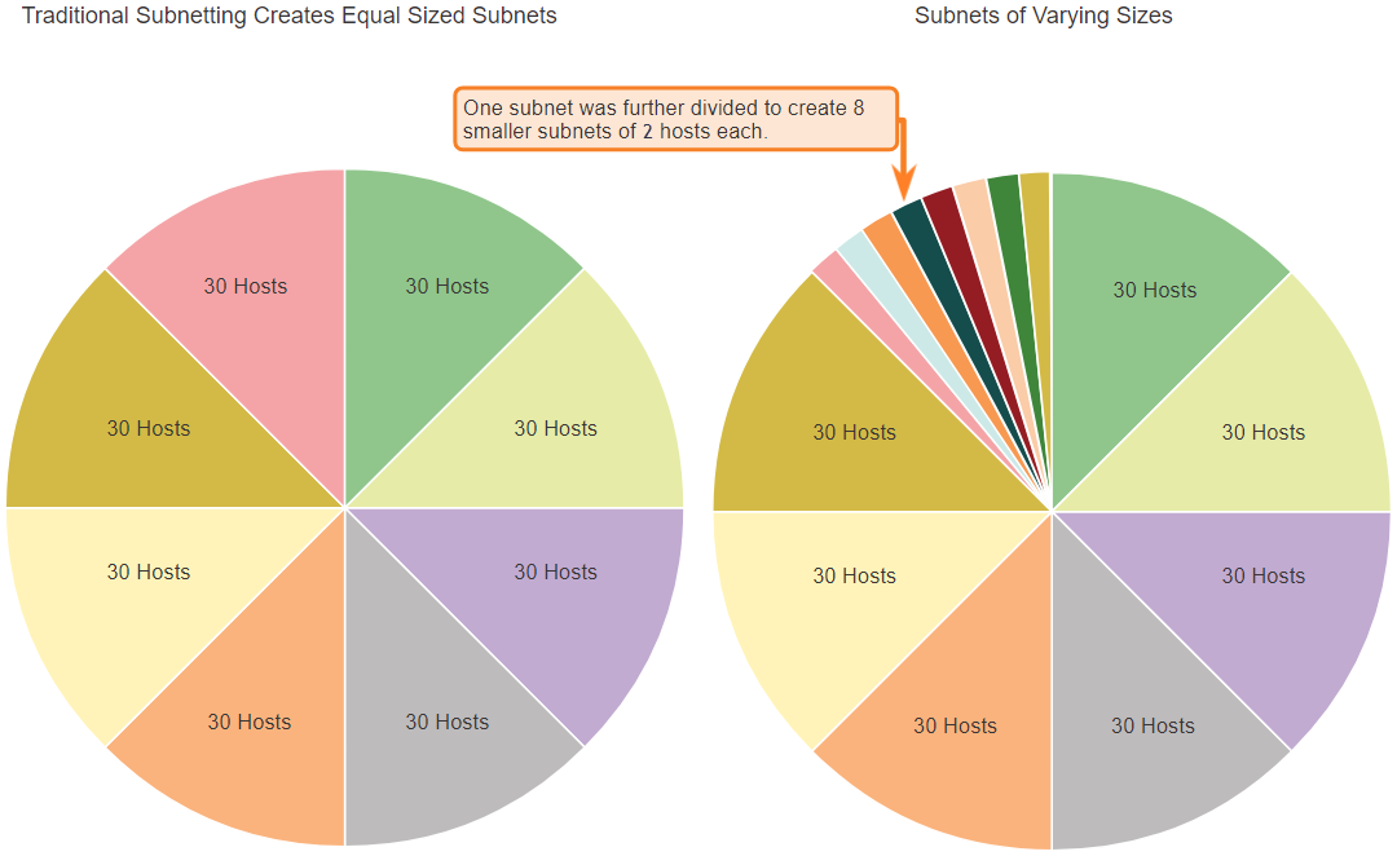
- When using VLSM, always begin by satisfying the host requirements of the largest subnet and continue subnetting until the host requirements of the smallest subnet are satisfied. The resulting topology with VLSM applied.
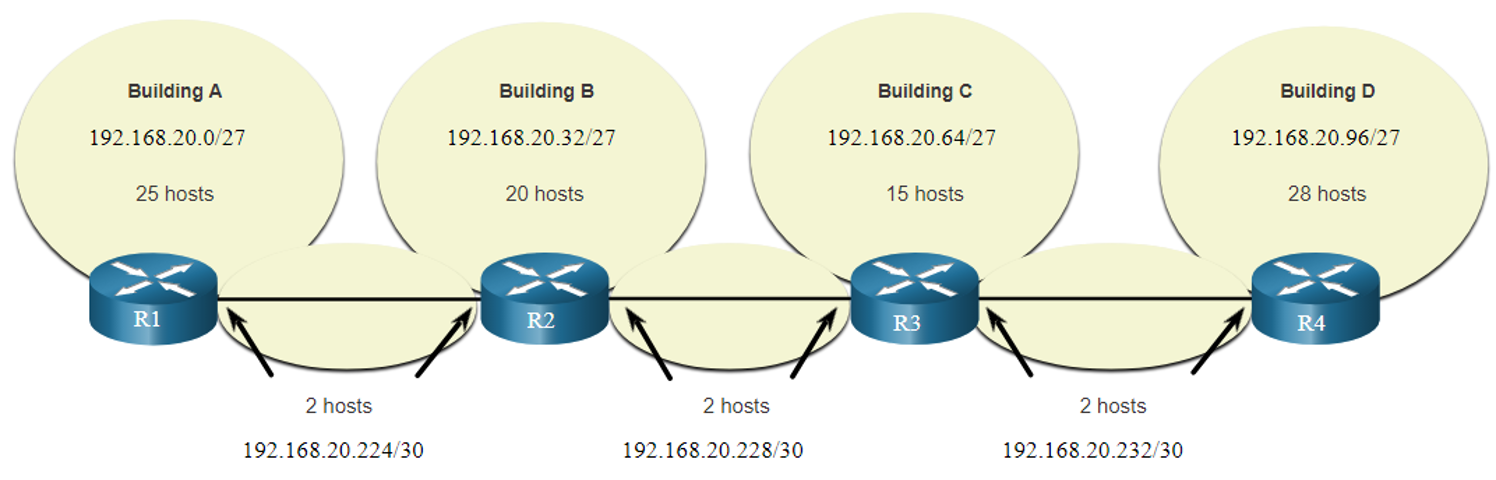
VLSM Topology Address Assignment
Using VLSM subnets, the LAN and inter-router networks can be addressed without unnecessary waste as shown in the logical topology diagram. 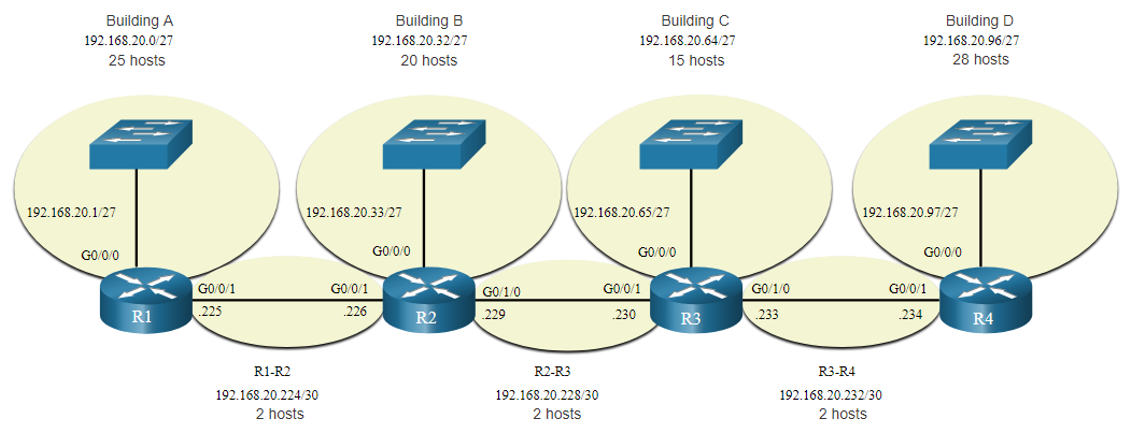
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Address Structure | Describe the structure of an IPv4 address including the network portion, the host portion, and the subnet mask. |
| IPv4 Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast | Compare the characteristics and uses of the unicast, broadcast, and multicast IPv4 addresses. |
| Types of IPv4 Addresses | Explain public, private, and reserved IPv4 addresses. |
| Network Segmentation | Explain how subnetting segments a network to enable better communication. |
| Subnet an IPv4 Network | Calculate IPv4 subnets for a /24 prefix. |
| VLSM | Variable length subnet mask is a computer networking technique to divide an IP network into subnets with different subnet masks |
Other useful information
Join the conversation