About Lesson
Transportation of Data
Explain the purpose of the transport layer in managing the transportation of data in end-to-end communication.
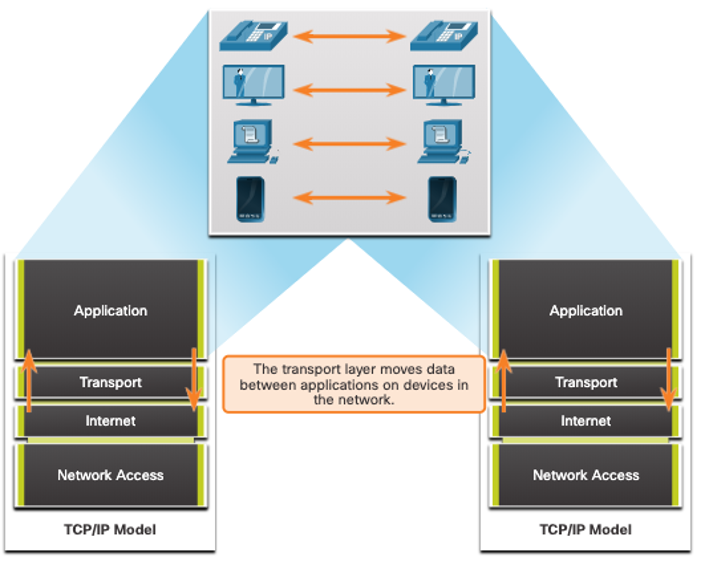
Role of the Transport Layer
The transport layer is:
- responsible for logical communications between applications running on different hosts.
- The link between the application layer and the lower layers that are responsible for network transmission.

Transport Layer Responsibilities
The transport layer has the following responsibilities:
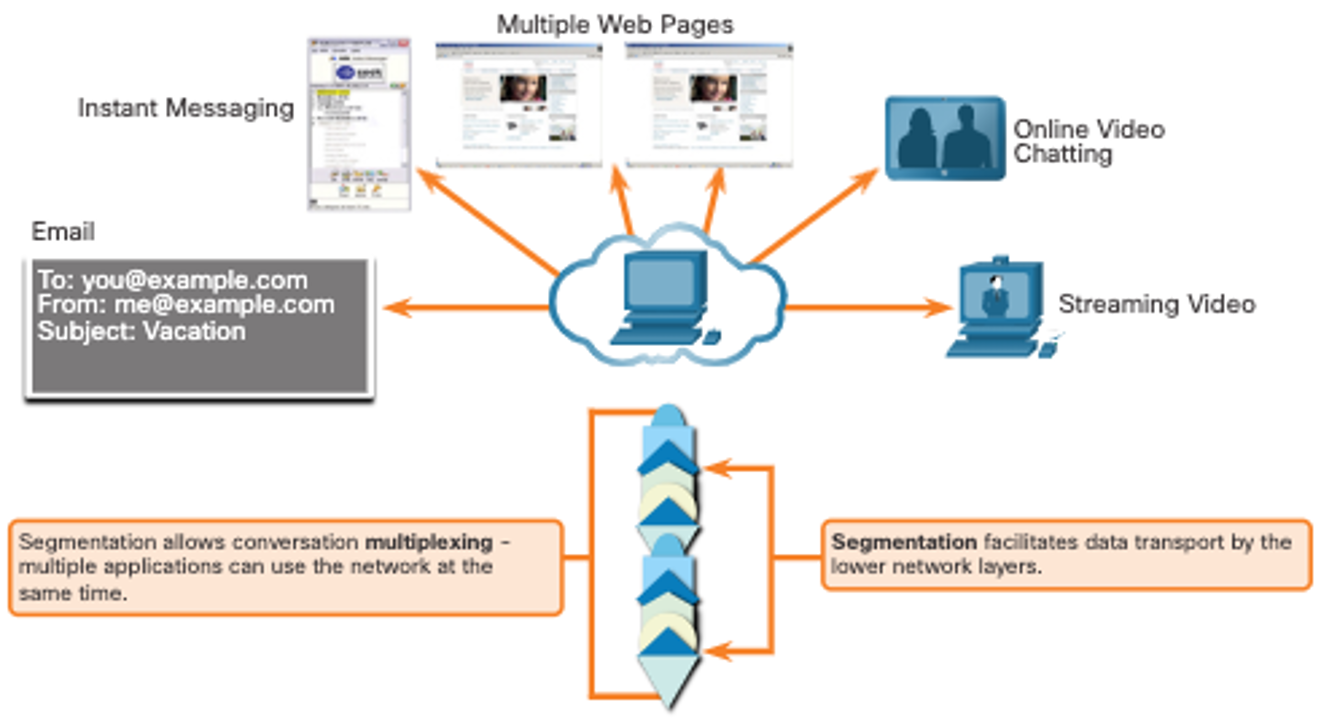
- Tracking individual conversations
- Segmenting data and reassembling segments
- Adds header information
- Identify, separate, and manage multiple conversations
- Uses segmentation and multiplexing to enable different communication conversations to be
- interleaved on the same network
Transport Layer Protocols
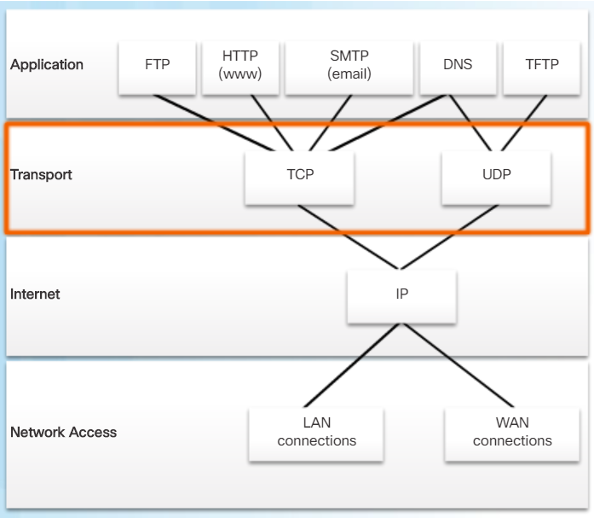
- IP does not specify how the delivery or transportation of the packets takes place.
- Transport layer protocols specify how to transfer messages between hosts, and are responsible for managing reliability requirements of a conversation.
- The transport layer includes the TCP and UDP protocols.
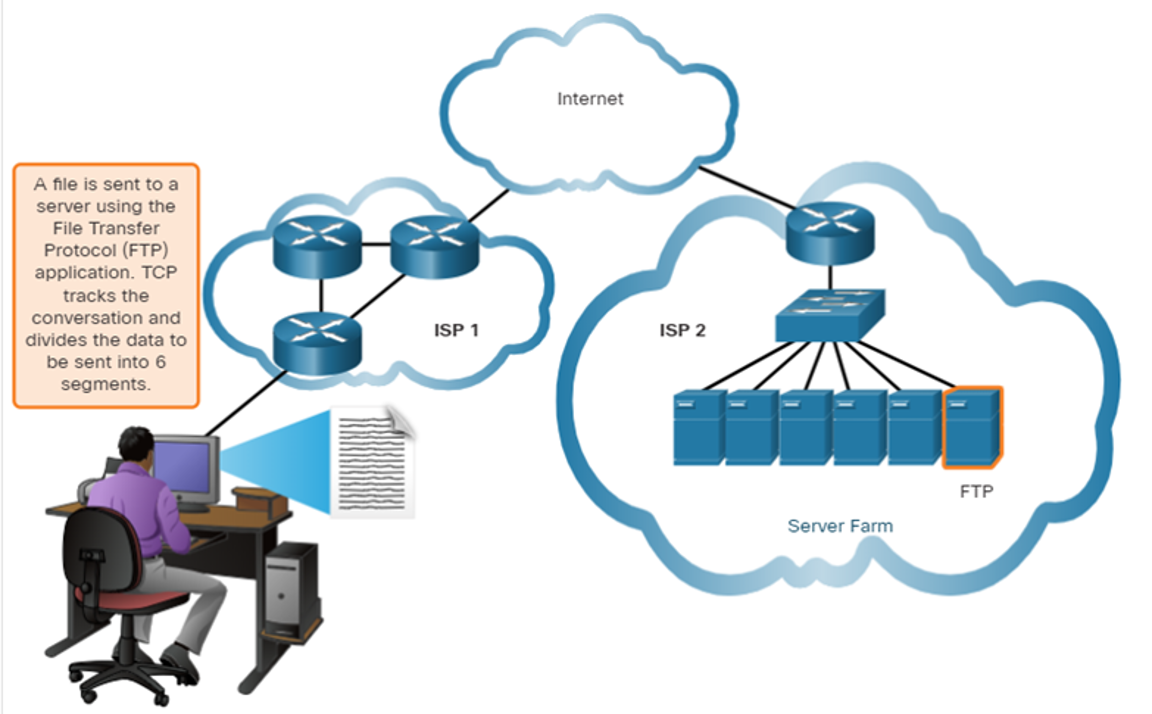
Transmission Control Protocol
TCP provides reliability and flow control. TCP basic operations:
- Number and track data segments transmitted to a specific host from a specific application
- Acknowledge received data
- Retransmit any unacknowledged data after a certain amount of time
- Sequence data that might arrive in wrong order
- Send data at an efficient rate that is acceptable by the receiver
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
UDP provides the basic functions for delivering datagrams between the appropriate applications, with very little overhead and data checking.
- UDP is a connectionless protocol.
- UDP is known as a best-effort delivery protocol because there is no acknowledgment that the data is received at the destination.
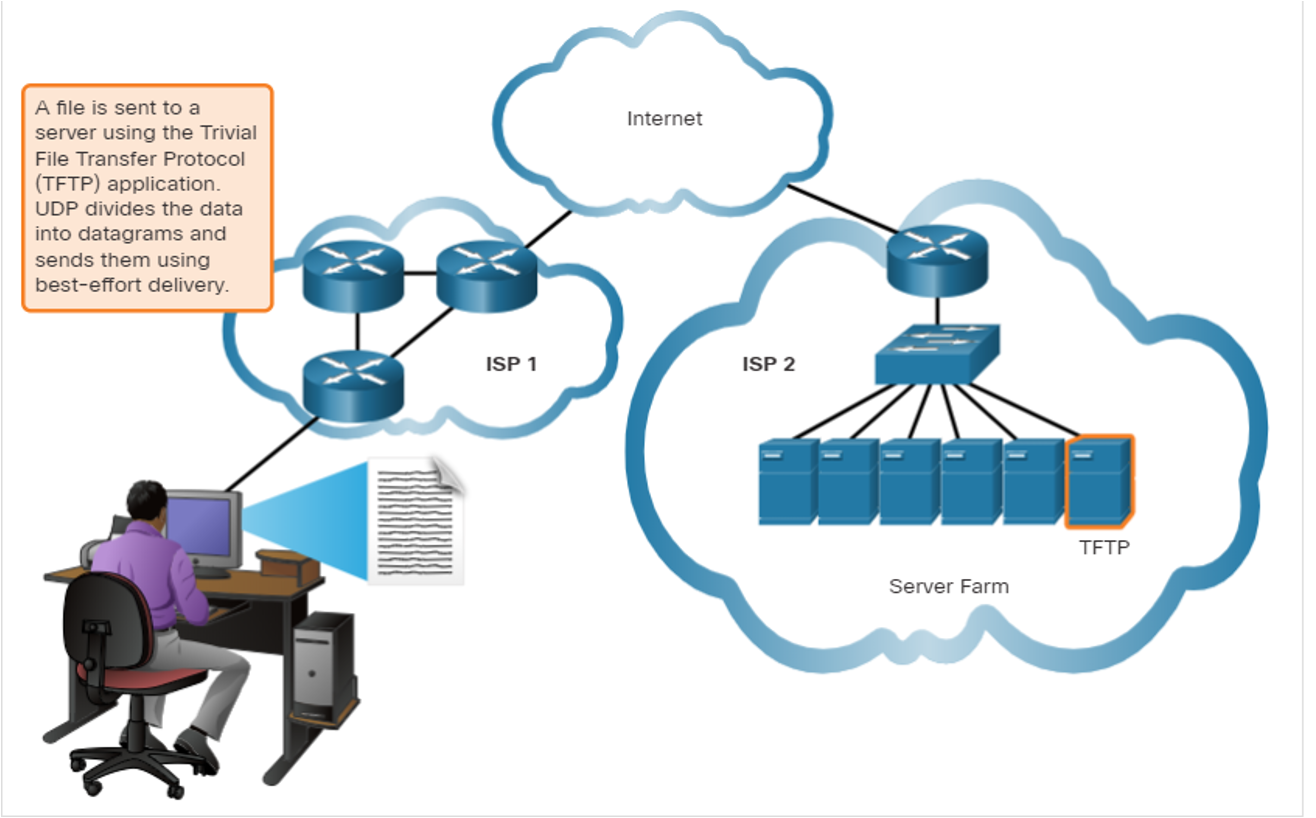
The Right Transport Layer Protocol for the Right Application
- UDP is also used by request-and-reply applications where the data is minimal, and retransmission can be done quickly.
- If it is important that all the data arrives and that it can be processed in its proper sequence, TCP is used as the transport protocol.
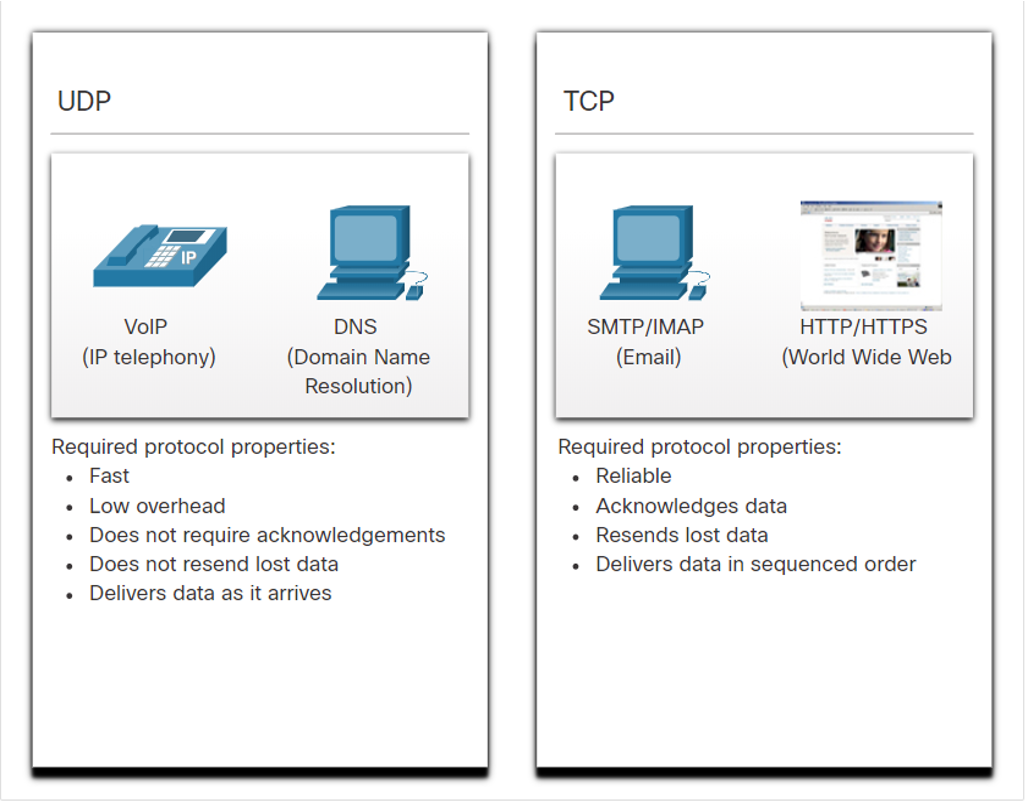
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
|---|---|
| Transportation of Data | Explain the purpose of the transport layer in managing the transportation of data in end-to-end communication. |
| TCP Overview | Explain characteristics of TCP. |
| UDP Overview | Explain characteristics of UDP. |
| Port Numbers | Explain how TCP and UDP use port numbers. |
| TCP Communication Process | Explain how TCP session establishment and termination processes facilitate reliable communication. |
| Reliability and Flow Control | Explain how TCP protocol data units are transmitted and acknowledged to guarantee delivery. |
| UDP Communication | Compare the operations of transport layer protocols in supporting end-to-end communication. |
Other useful information
Join the conversation