
About Lesson
9.2 ARP
ARP Overview
A device uses ARP to determine the destination MAC address of a local device when it knows its IPv4 address.  ARP provides two basic functions:
ARP provides two basic functions:
- Resolving IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses
- Maintaining an ARP table of IPv4 to MAC address mappings
ARP Functions
To send a frame, a device will search its ARP table for a destination IPv4 address and a corresponding MAC address.
- If the packet’s destination IPv4 address is on the same network, the device will search the ARP table for the destination IPv4 address.
- If the destination IPv4 address is on a different network, the device will search the ARP table for the IPv4 address of the default gateway.
- If the device locates the IPv4 address, its corresponding MAC address is used as the destination MAC address in the frame.
- If there is no ARP table entry is found, then the device sends an ARP request.
Removing Entries from an ARP Table
Entries in the ARP table are not permanent and are removed when an ARP cache timer expires after a specified period of time. The duration of the ARP cache timer differs depending on the operating system. ARP table entries can also be removed manually by the administrator. 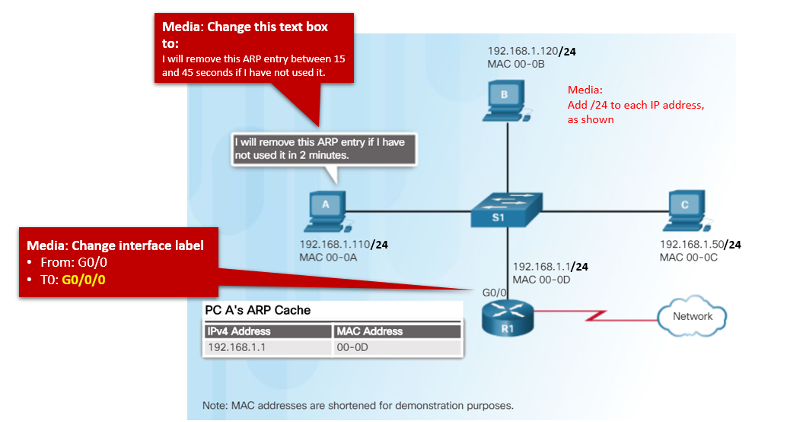
ARP Tables on Networking Devices
The show ip arp command displays the ARP table on a Cisco router.  The arp –a command displays the ARP table on a Windows 10 PC.
The arp –a command displays the ARP table on a Windows 10 PC. 
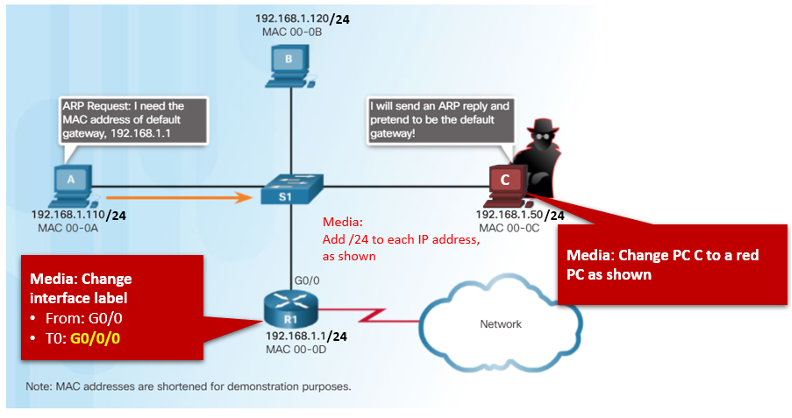
ARP Issues – ARP Broadcasting and ARP Spoofing
- ARP requests are received and processed by every device on the local network.
- Excessive ARP broadcasts can cause some reduction in performance.
- ARP replies can be spoofed by a threat actor to perform an ARP poisoning attack.
- Enterprise level switches include mitigation techniques to protect against ARP attacks.
Join the conversation