About Lesson
Host and IOS Commands
Use host and IOS commands to acquire information about the devices in a network.
IP Configuration on a Windows Host
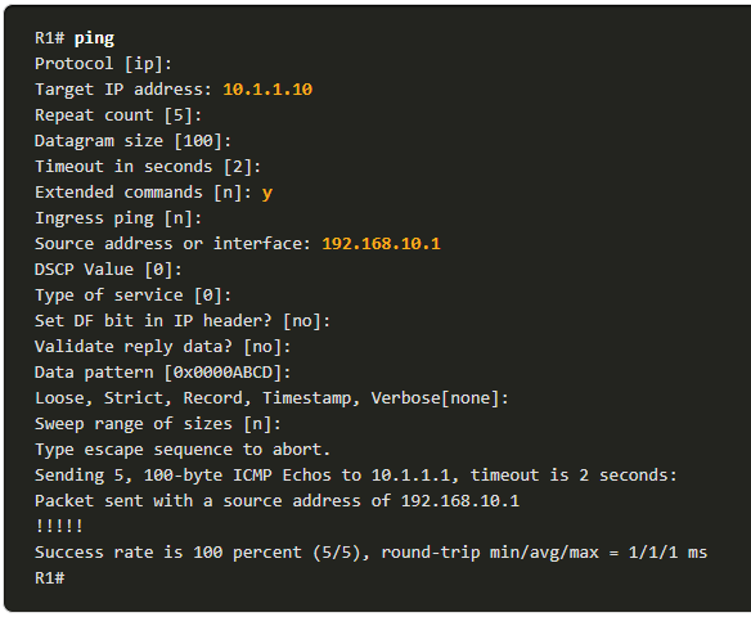
In Windows 10, you can access the IP address details from the Network and Sharing Center to quickly view the four important settings: address, mask, router, and DNS. Or you can issue the ipconfig command at the command line of a Windows computer.
- Use the ipconfig /all command to view the MAC address, as well as a number of details regarding the Layer 3 addressing of the device.
- If a host is configured as a DHCP client, the IP address configuration can be renewed using the ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew commands.
- The DNS Client service on Windows PCs also optimizes the performance of DNS name resolution by storing previously resolved names in memory. The ipconfig /displaydns command displays all of the cached DNS entries on a Windows computer system.

IP Configuration on a Linux Host
- Verifying IP settings using the GUI on a Linux machine will differ depending on the Linux distribution and desktop interface.
- On the command line, use the ifconfig command to display the status of the currently active interfaces and their IP configuration.
- The Linux ip address command is used to display addresses and their properties. It can also be used to add or delete IP addresses.
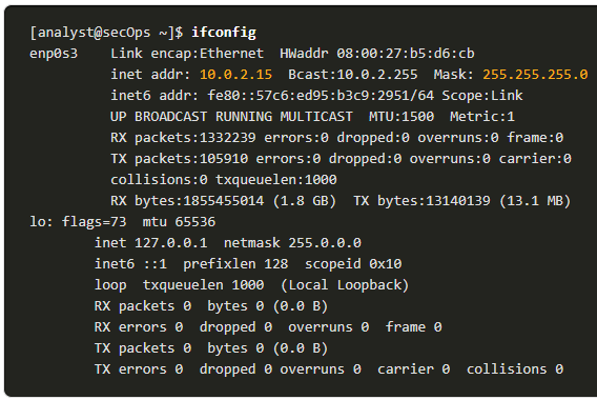
Note: The output displayed may vary depending on the Linux distribution.
IP Configuration on a macOS Host
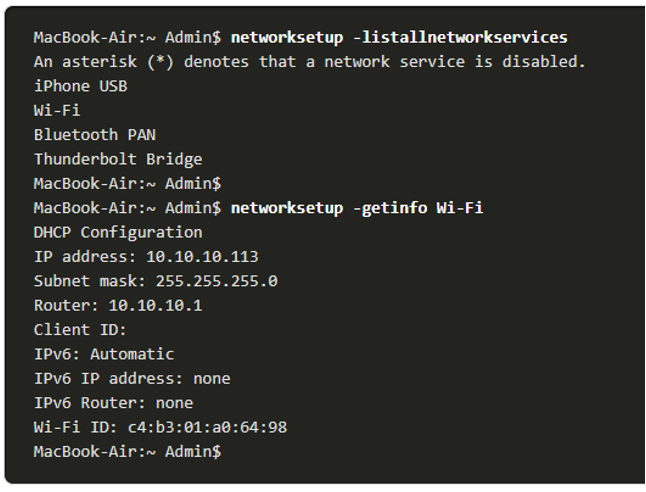
- In the GUI of a Mac host, open Network Preferences > Advanced to get the IP addressing information.
- The ifconfig command can also be used to verify the interface IP configuration at the command line.
- Other useful macOS commands to verify the host IP settings include networksetup -listallnetworkservices and the networksetup -getinfo <network service>.
The arp Command
The arp command is executed from the Windows, Linux, or Mac command prompt. The command lists all devices currently in the ARP cache of the host.
- The arp -a command displays the known IP address and MAC address binding. The ARP cache only displays information from devices that have been recently accessed.
- To ensure that the ARP cache is populated, ping a device so that it will have an entry in the ARP table.
- The cache can be cleared by using the netsh interface ip delete arpcache command in the event the network administrator wants to repopulate the cache with updated information.
Note: You may need administrator access on the host to be able to use the netsh interface ip delete arpcache command.
Common show Commands Revisited
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| show running-config | Verifies the current configuration and settings |
| show interfaces | Verifies the interface status and displays any error messages |
| show ip interface | Verifies the Layer 3 information of an interface |
| show arp | Verifies the list of known hosts on the local Ethernet LANs |
| show ip route | Verifies the Layer 3 routing information |
| show protocols | Verifies which protocols are operational |
| show version | Verifies the memory, interfaces, and licenses of the device |
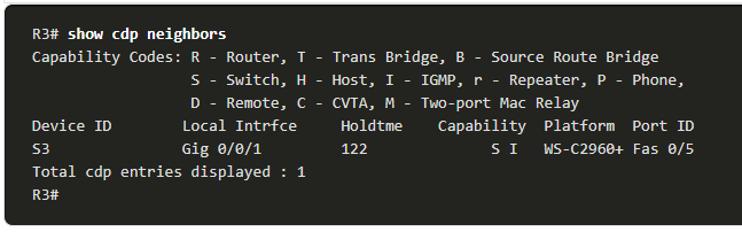
The show cdp neighbors Command
- CDP provides the following information about each CDP neighbor device:
-
- Device identifiers – The configured host name of a switch, router, or other device
- Address list – Up to one network layer address for each protocol supported
- Port identifier – The name of the local and remote port in the form of an ASCII character string, such as FastEthernet 0/0
- Capabilities list – Whether a specific device is a Layer 2 switch or a Layer 3 switch
- Platform – The hardware platform of the device.
- The show cdp neighbors detail command reveals the IP address of a neighboring device.
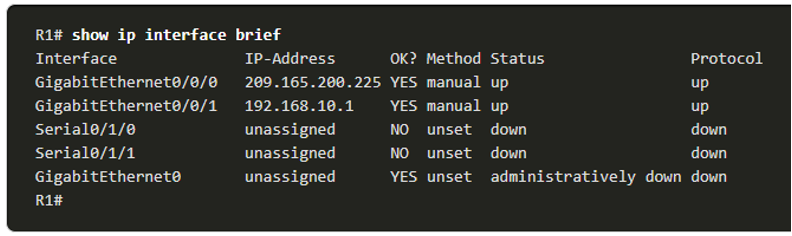
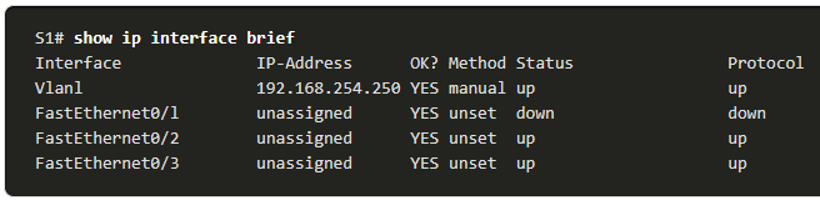
The show ip interface brief Command
- One of the most frequently used commands is the show ip interface brief command.
- This command provides a more abbreviated output than the show ip interface command.
- It provides a summary of the key information for all the network interfaces on a router.
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
|---|---|
| Devices in a Small Network | Identify the devices used in a small network. |
| Small Network Applications and Protocols | Identify the protocols and applications used in a small network. |
| Scale to Larger Networks | Explain how a small network serves as the basis of larger networks. |
| Verify Connectivity | Use the output of the ping and tracert commands to verify connectivity and establish relative network performance. |
| Host and IOS Commands | Use host and IOS commands to acquire information about the devices in a network. |
| Troubleshooting Methodologies | Describe common network troubleshooting methodologies. |
| Troubleshooting Scenarios | Troubleshoot issues with devices in the network. |
Other useful information
- Full CCNA Course
- CCNA Certificate Information
- 200-301 CCNA Exam Questions and Solutions
- 200-301 CCNA Exam Topics
Join the conversation