About Lesson
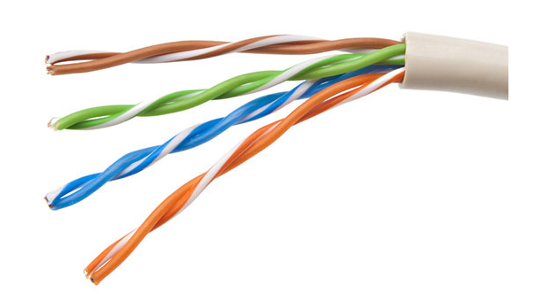
UTP Cabling
Explain how UTP cable is used in Ethernet networks.
Properties of UTP Cabling

- UTP has four pairs of color-coded copper wires twisted together and encased in a flexible plastic sheath. No shielding is used. UTP relies on the following properties to limit crosstalk:
-
- Cancellation – Each wire in a pair of wires uses opposite polarity. One wire is negative, the other wire is positive. They are twisted together and the magnetic fields effectively cancel each other and outside EMI/RFI.
- Variation in twists per foot in each wire – Each wire is twisted a different amount, which helps prevent crosstalk amongst the wires in the cable.
UTP Cabling Standards and Connectors
- Standards for UTP are established by the TIA/EIA. TIA/EIA-568 standardizes elements like:
- Cable Types
- Cable Lengths
- Connectors
- Cable Termination
- Testing Methods
- Electrical standards for copper cabling are established by the IEEE, which rates cable according to its performance. Examples include:
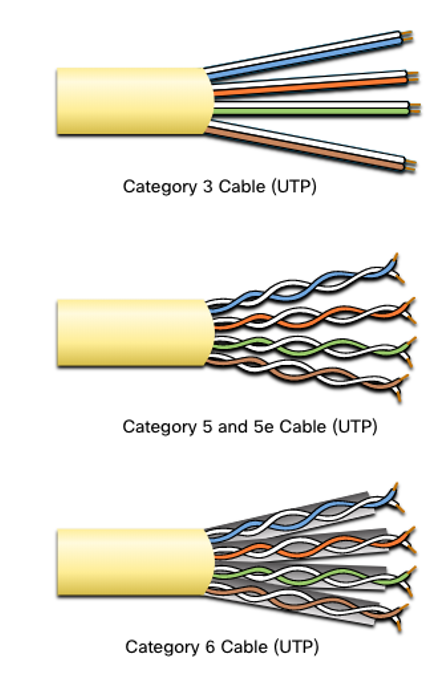
- Category 3
- Category 5 and 5e
- Category 6
Connectors

Straight-through and Crossover UTP Cables
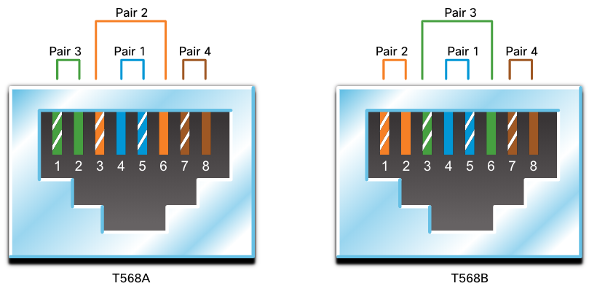
| Cable Type | Standard | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet Straight-through | Both ends T568A or T568B | Host to Network Device |
| Ethernet Crossover | One end T568A, other end T568B | Host-to-Host, Switch-to-Switch, Router-to-Router |
| Rollover | Cisco Proprietary | Host serial port to Router or Switch Console Port, using an adapter |
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
|---|---|
| Purpose of the Physical Layer | Describe the purpose and functions of the physical layer in the network. |
| Physical Layer Characteristics | Describe characteristics of the physical layer. |
| Copper Cabling | Identify the basic characteristics of copper cabling. |
| UTP Cabling | Explain how UTP cable is used in Ethernet networks. |
| Fiber-Optic Cabling | Describe fiber optic cabling and its main advantages over other media. |
| Wireless Media | Connect devices using wired and wireless media. |
Other useful information
- Full CCNA Course
- CCNA Certificate Information
- 200-301 CCNA Exam Questions and Solutions
- 200-301 CCNA Exam Topics
Join the conversation