
About Lesson
Ports and Addresses
Explain how devices communicate across network media.
- The use of IP addresses is the primary means of enabling devices to locate one another and establish end-to-end communication on the internet.
- The structure of an IPv4 address is called dotted decimal notation and is represented by four decimal numbers between 0 and 255.
- An IPv4 subnet mask is a 32-bit value that differentiates the network portion of the address from the host portion. Coupled with the IPv4 address, the subnet mask determines to which subnet the device is a member.
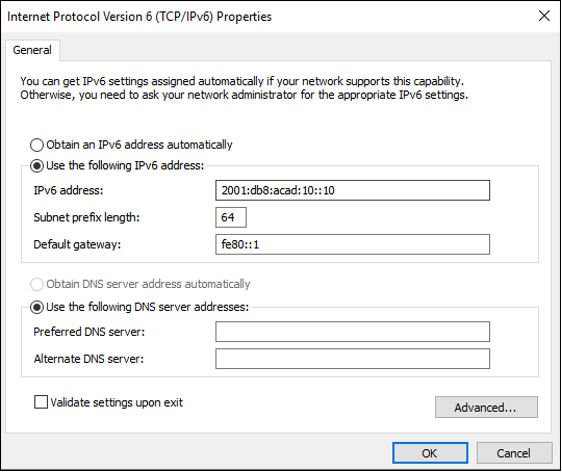
- The default gateway address is the IP address of the router that the host will use to access remote networks, including the internet.

- IPv6 addresses are 128 bits in length and written as a string of hexadecimal values. Every four bits is represented by a single hexadecimal digit; for a total of 32 hexadecimal values. Groups of four hexadecimal digits are separated by a colon “:”.
- IPv6 addresses are not case-sensitive and can be written in either lowercase or uppercase.
Interfaces and Ports
- Network communications depend on end user device interfaces, networking device interfaces, and the cables that connect them. Types of network media include twisted-pair copper cables, fiber-optic cables, coaxial cables, or wireless.
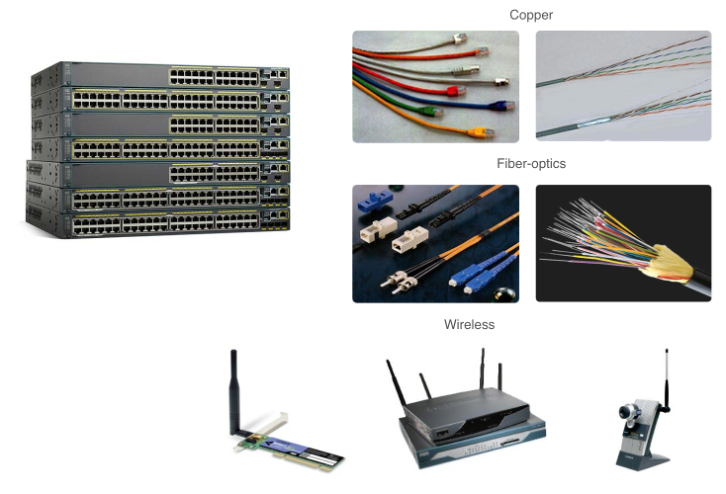

- Different types of network media have different features and benefits. Some of the differences between various types of media include:
-
- Distance the media can successfully carry a signal
- Environment in which the media is to be installed
- Amount of data and the speed at which it must be transmitted
- Cost of the media and installation
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
|---|---|
| Cisco IOS Access | Explain how to access a Cisco IOS device for configuration purposes. |
| Cisco IOS Navigation | Explain how to navigate Cisco IOS to configure network devices. |
| Cisco IOS Command Structure | Describe the command structure of Cisco IOS software. |
| Basic Cisco Device Configuration | Configure a Cisco IOS device using CLI. |
| Save Cisco IOS Configurations | Use IOS commands to save the running configuration. |
| Ports and Addresses | Explain how devices communicate across network media. |
| Configure IP Addressing | Configure a host device with an IP address. |
Other useful information
- Full CCNA Course
- CCNA Certificate Information
- 200-301 CCNA Exam Questions and Solutions
- 200-301 CCNA Exam Topics
Join the conversation