OSPFv3 Configurations
the configuration and verification of an OSPFv3 environment.
Configuration Steps:
- Step 1. Initialize the routing process with the command ‘ipv6 unicast-routing’.
- Step 2. Define the 32-bit router ID within the OSPFv3 router process.
- Step 3. (Optional) Initialize the address family – enabled automatically when OSPFv3 is enabled on an interface.
- Step 4. Enable OSPFv3 on an interface using a process-id and area-id.
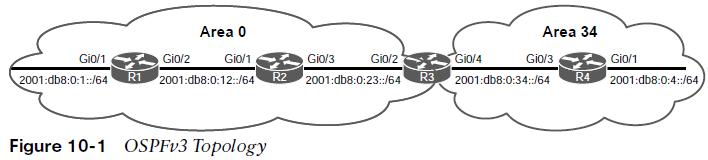
OSPFv3 Topology
Area 0 consists of R1, R2, and R3, and Area 34 contains R3 and R4. R3 is the ABR. 
Example OSPFv3 Configuration
Earlier versions of IOS used the commands ipv6 router ospf for initialization of the OSPF process and ipv6 ospf process-id area area-id for identification of the interface. These commands are considered legacy and should be migrated to the current practice such as ospfv3 process-id ipv6 area area-id in the R1 & R2 configurations, as highlighted below. 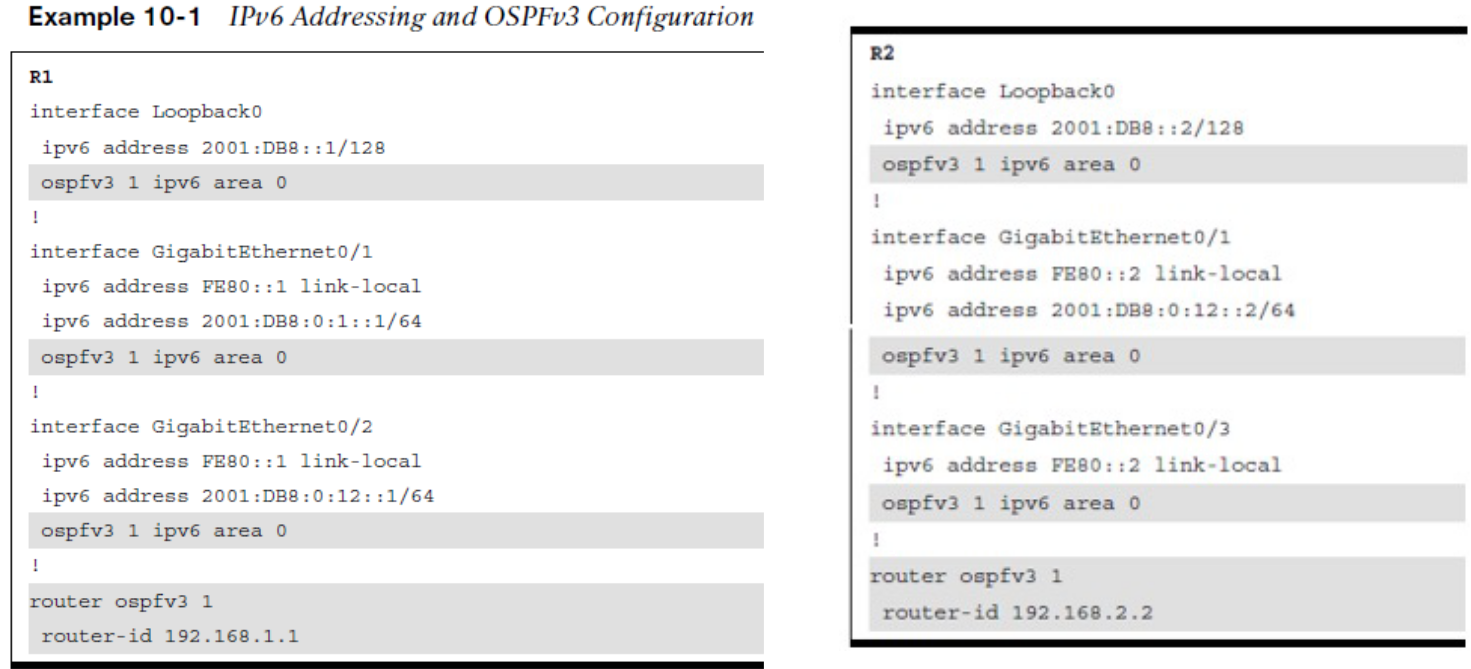 R3 & R4 configurations steps are highlighted below.
R3 & R4 configurations steps are highlighted below. 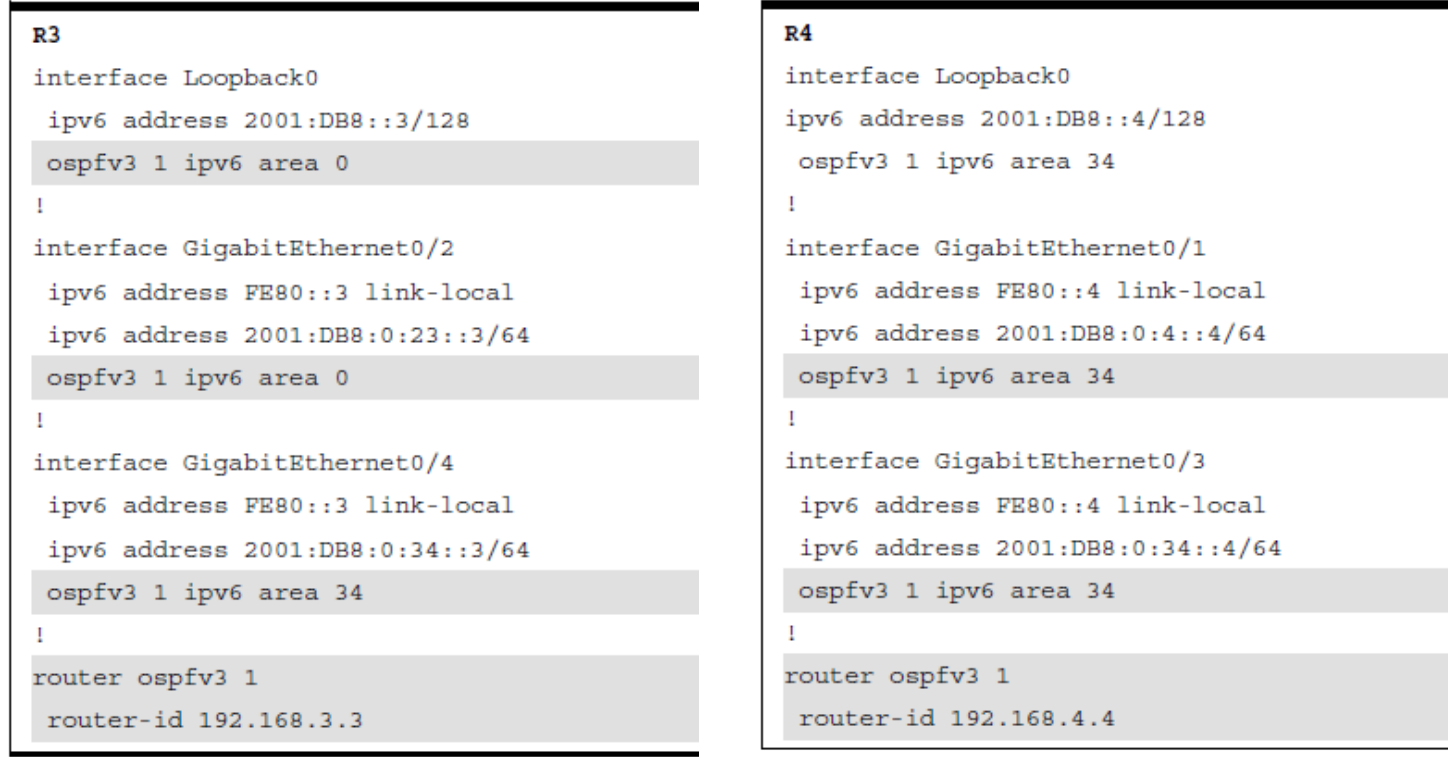
OSPFv3 Verification – Neighbor Adjacency
To view the R3 OSPFv3 Neighbor Adjacency the show opsfv3 ipv6 neighbor command is used. Neighbors router-id is displayed, OSPFv3 priority, state of the connection, and the interface the neighbor is learned on. 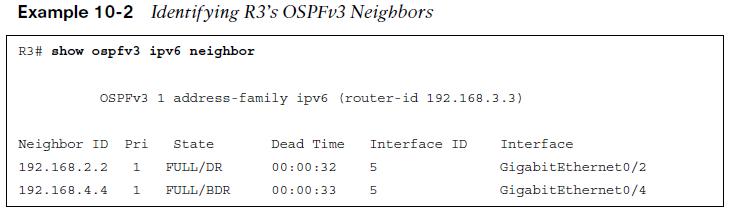
OSPFv3 Verification
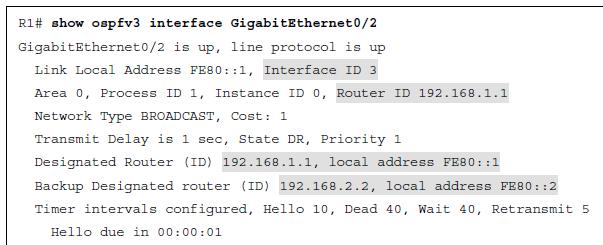
 Verifying the OSPFv3 interface information provides the following:
Verifying the OSPFv3 interface information provides the following:
- Interface ID
- Router ID
- DR and Backup DR
- Neighbor Adjacency
OSPFv3 Interface Verification
To show a brief listing of the interfaces participating in OSPFv3 Routing on R3 use the show ospfv3 interface brief command. Important information includes the Interface, the area the interface belongs to, and the role of the router on the link (State) 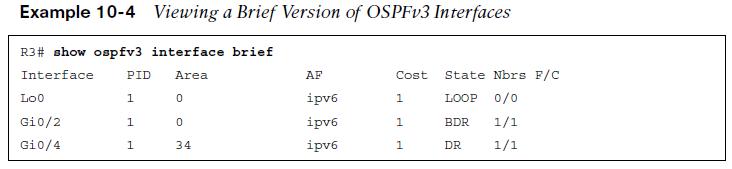
OSPFv3 Routing Verification
 Output from the OSPFv3 routing table showing both Intra-Area routes (O) and Inter-Area routes (OI) using the command show ipv6 route ospf.
Output from the OSPFv3 routing table showing both Intra-Area routes (O) and Inter-Area routes (OI) using the command show ipv6 route ospf.
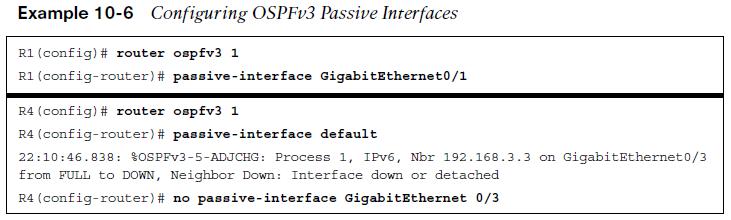
OSPFv3 Passive Interface
OSPFv3 supports marking an interface as passive. The command is placed under the OSPFv3 process or under the specific address family. Placing the command under the global process cascades the setting to both address families.
- The passive interface can be set explicitly to an interface (R1 configuration).
- The passive interface can be set as default (R4 configuration).
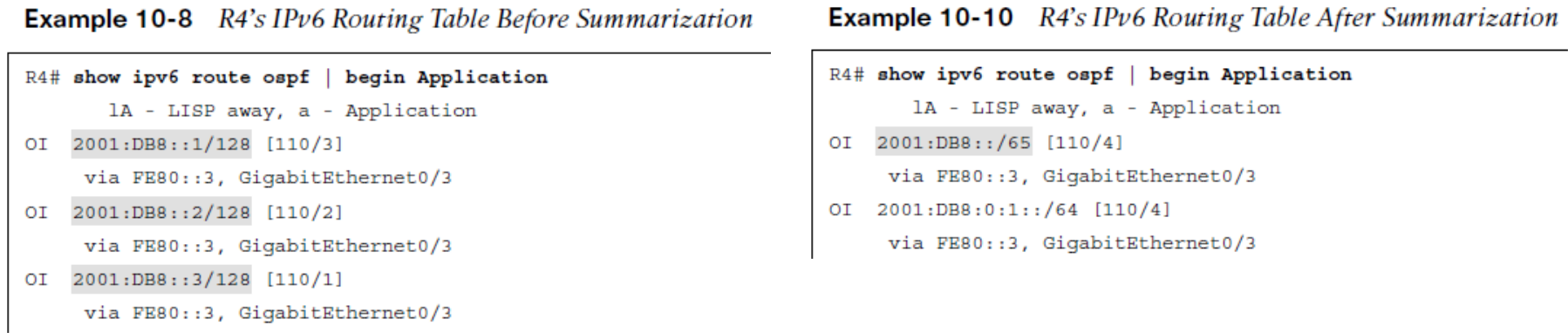
OSPFv3 Route Summarization
Route summarization reduces the number of route entries on the neighboring router. 
OSPFv3 Verify Network Type
Configuration changes may be necessary for a dynamically learned network type. As shown in Example 10-11 the R2 G0/3 interface is shown as a BROADCAST network type. Based on the topology it should be a point-to-point. 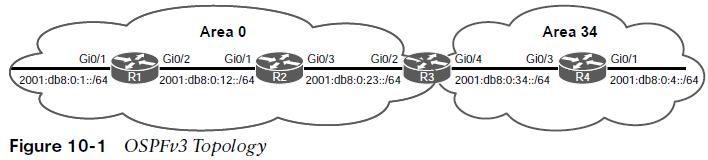
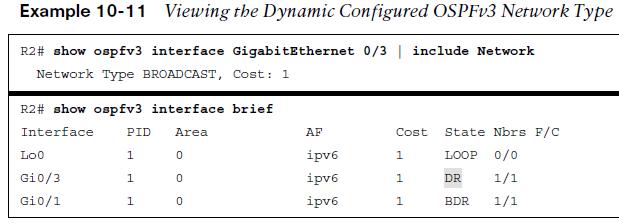
OSPFv3 Change Network Type
When changes are made to the network type it is necessary to change both ends of the link to match. The change is made directly on the interface. 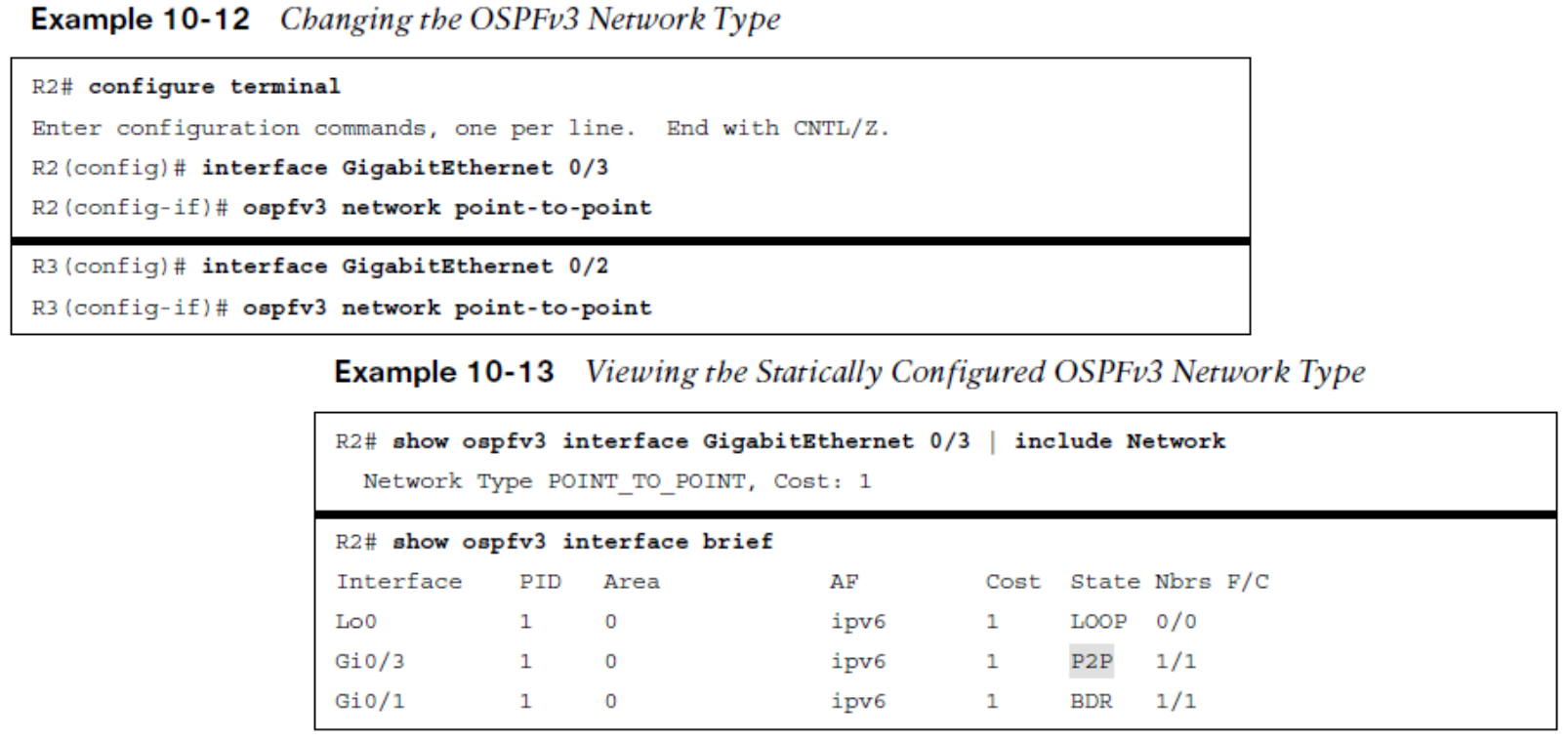 Other useful information:
Other useful information:
- Full ENCOR Course
- CCNP Enterprise Certificate Information
- 350-401 ENCOR Exam Questions and Solutions
- 350-401 ENCOR Exam Topics