Discontiguous Networks
demonstrates a discontiguous network and explains why such a network cannot distribute routes to all areas properly.
- The simplest fix for a discontiguous network is to ensure that Area 0 is contiguous.
Discontiguous Network Example
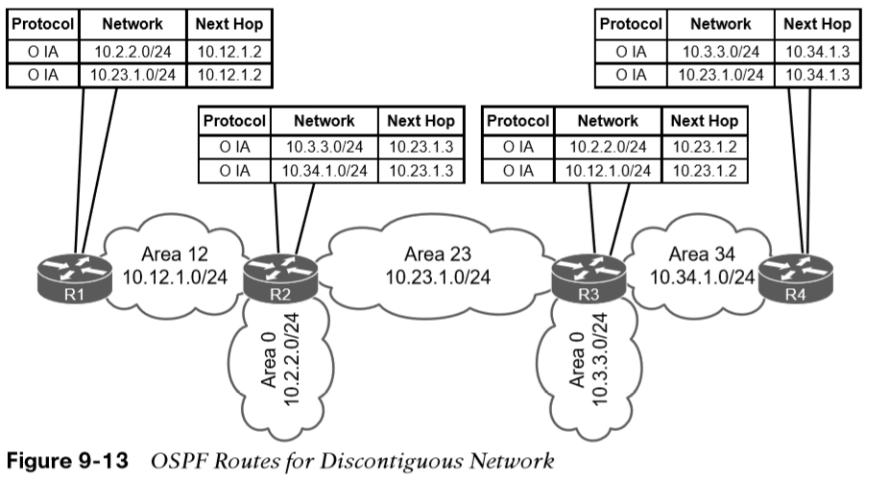
 An OSPF network with this design is discontiguous because interarea traffic is trying to cross a nonbackbone area. It looks like routes in the routing tables on R2 and R3 in Figure 9-13 are being advertised across area 23. The 10.34.1.0/24 network was advertised into OSPF by R3 and R4 as a type 1 LSA. R3 is an ABR and converts Area 34’s 10.34.1.0/24 type 1 LSA into a type 3 LSA in Area 0. R3 uses the type 3 LSA from Area 0 to generate the type 3 LSA for Area 23. R2 is able to install the type 3 LSA from Area 23 into its routing table. Note: To assume that the 10.34.1.0/24 route learned by Area 23 would then advertise into R2’s Area 0 and then propagate to Area 12, would be wrong.
An OSPF network with this design is discontiguous because interarea traffic is trying to cross a nonbackbone area. It looks like routes in the routing tables on R2 and R3 in Figure 9-13 are being advertised across area 23. The 10.34.1.0/24 network was advertised into OSPF by R3 and R4 as a type 1 LSA. R3 is an ABR and converts Area 34’s 10.34.1.0/24 type 1 LSA into a type 3 LSA in Area 0. R3 uses the type 3 LSA from Area 0 to generate the type 3 LSA for Area 23. R2 is able to install the type 3 LSA from Area 23 into its routing table. Note: To assume that the 10.34.1.0/24 route learned by Area 23 would then advertise into R2’s Area 0 and then propagate to Area 12, would be wrong.
Rules ABRs Use for Creating Type 3 LSAs
There are three fundamental rules ABRs use the for creating type 3 LSAs:
- Type 1 LSAs received from an area create type 3 LSAs into the backbone area and nonbackbone areas.
- Type 3 LSAs received from Area 0 are created for the nonbackbone area.
- Type 3 LSAs received from a nonbackbone area only insert into the LSDB for the source area. ABRs do not create a type 3 LSA for the other areas (including a segmented Area 0).
The simplest fix for a discontiguous network is to ensure that Area 0 is contiguous. There are other functions, like virtual link or usage of GRE tunnels that are not covered in this course. Real-life scenarios of discontiguous networks involve Area 0 becoming partitioned due to hardware failures. Other useful information: