Link-State Announcements
how OSPF stores, communicates, and builds a topology from the link-state announcements (LSAs).
- When OSPF neighbors become adjacent, the LSDBs synchronize between the OSPF routers.
- As an OSPF router adds or removes a directly connected network link to or from its database, the router floods the link-state advertisement (LSA) out all active OSPF interfaces.
- The OSPF LSA contains a complete list of networks advertised from that router.
OSPF LSA Types for IPv4 Routing
OSPF uses six LSA types for IPv4 routing:
- Type 1, router LSA – Advertises the LSAs that originate within an area.
- Type 2, network LSA – Advertises a multi-access network segment attached to a DR.
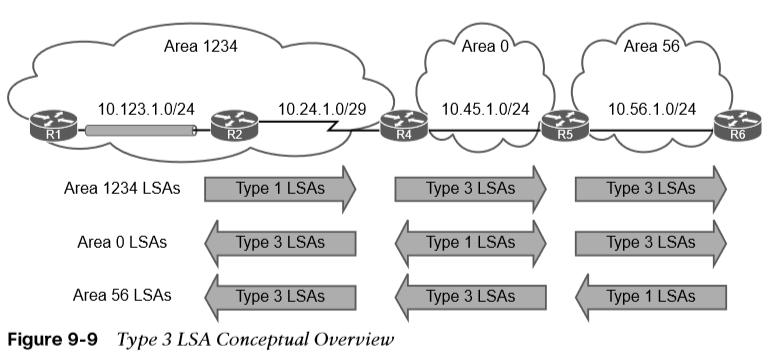
- Type 3, summary LSA – Advertises network prefixes originating from a different area.
- Type 4, ASBR summary LSA – Advertises a summary LSA for a specific ASBR.
- Type 5, AS external LSA – Advertises LSAs for routes that have been redistributed.
- Type 7, NSSA external LSA – Advertises redistributed routes in NSSAs.
LSA types 1, 2, and 3, which are used for building the SPF tree for intra-area and interarea routes, are explained in this section.
Components of the LSA
- LSA age and flooding: Every OSPF LSA includes an age that is entered into the local LSDB and that will increment by 1 every second. When a router’s OSPF LSA age exceeds 1800 seconds (30 minutes) for its networks, the originating router advertises a new LSA with the LSA age set to 0. The LSA is deemed invalid if age reaches 3600.
- LSA sequences: OSPF uses the sequence number to overcome problems caused by delays in LSA propagation in a network. The LSA sequence number is a 32-bit number for controlling versioning.
- LSA types: All routers within an OSPF area have an identical set of LSAs for that area. The ABRs maintain a separate set of LSAs for each OSPF area.
LSA Type 1: Router Link
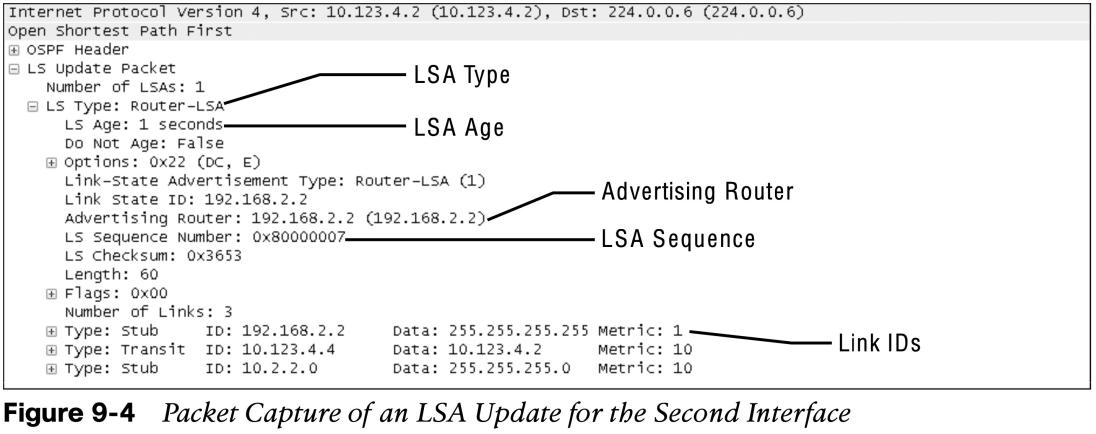
Every OSPF router advertises a type 1 LSA. Type 1 LSAs are the essential building blocks within the LSDB. A type 1 LSA entry exists for each OSPF-enabled link. Type 1 LSAs for an area are shown with the command show ip ospf database router. Figure 9-5 shows that in this example, the type 1 LSAs are not advertised outside Area 1234, which means the underlying topology in an area is invisible to other areas. 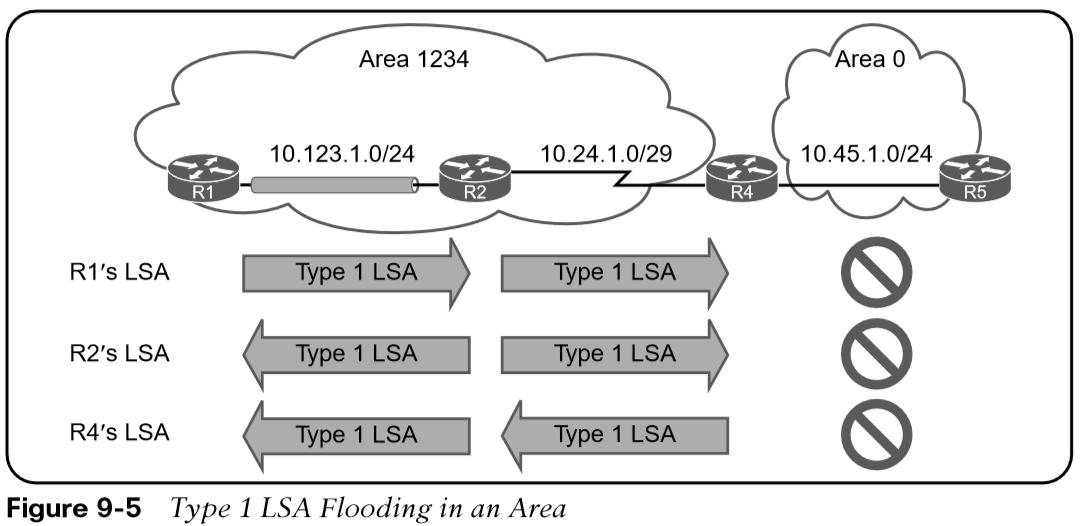 The initial fields of each type 1 LSA indicate the RID for the LSA’s advertising router, age, sequence, link count, and link ID. Every OSPF-enabled interface is listed under the number of links for each router.
The initial fields of each type 1 LSA indicate the RID for the LSA’s advertising router, age, sequence, link count, and link ID. Every OSPF-enabled interface is listed under the number of links for each router.
LSA Type 2: Network Link
A type 2 LSA represents a multi-access network segment that uses a DR. The DR always advertises the type 2 LSA and identifies all the routers attached to that network segment. If a DR has not been elected, a type 2 LSA is not present in the LSDB because the corresponding type 1 transit link type LSA is a stub. Like type 1 LSAs, type 2 LSAs are not flooded outside the originating OSPF area. 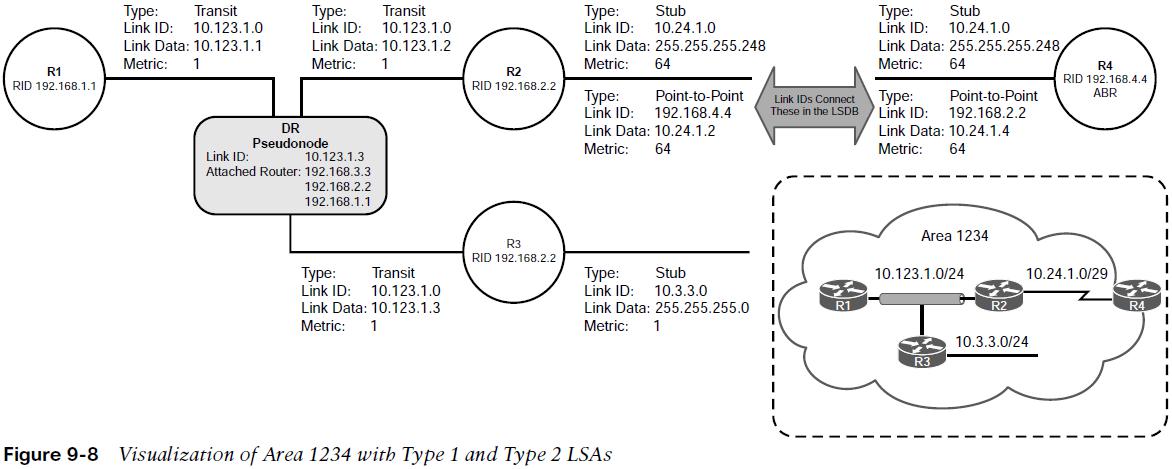 Detailed type 2 LSA information is shown with the command show ip ospf database network.
Detailed type 2 LSA information is shown with the command show ip ospf database network.
LSA Type 3: Summary Link
Type 3 LSAs represent networks from other areas. The role of the ABRs is to participate in multiple OSPF areas and ensure that the networks associated with type 1 LSAs are reachable in the non-originating OSPF areas. 
LSA Type 3: Summary Link
The advertising router for type 3 LSAs is the last ABR that advertises the prefix. The metric within the type 3 LSA uses the following logic:
- If the type 3 LSA is created from a type 1 LSA, it is the total path metric to reach the originating router in the type 1 LSA.
- If the type 3 LSA is created from a type 3 LSA from Area 0, it is the total path metric to the ABR plus the metric in the original type 3 LSA.
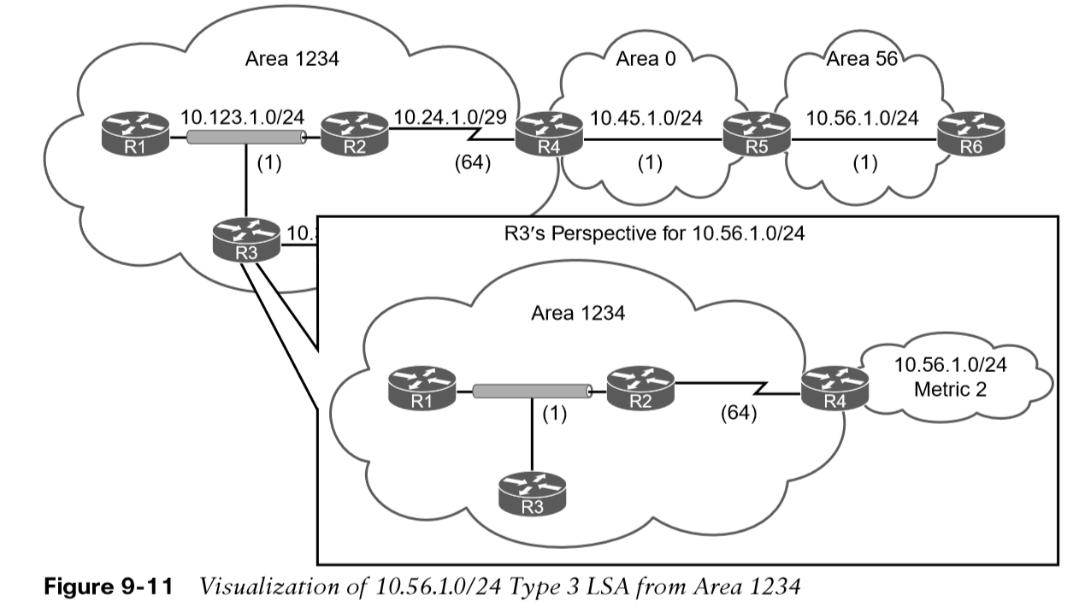
The type 3 LSA contains the link-state ID (network number), the subnet mask, the IP address of the advertising ABR, and the metric for the network prefix. 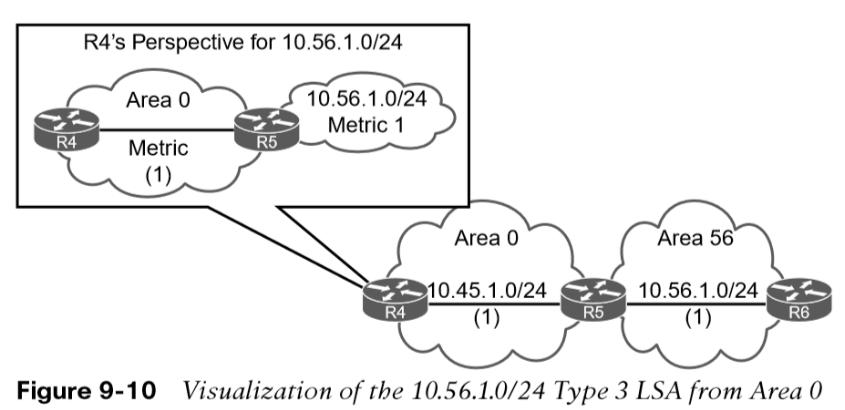 Figure 9-10 provides R4’s perspective of the type 3 LSA created by ABR (R5) for the 10.56.1.0/24 network. The total path metric to 10.56.1.0/24 is 2. Figure 9-11 provides R3’s perspective of the type 3 LSA created by ABR (R4) for the 10.56.1.0/24 network.
Figure 9-10 provides R4’s perspective of the type 3 LSA created by ABR (R5) for the 10.56.1.0/24 network. The total path metric to 10.56.1.0/24 is 2. Figure 9-11 provides R3’s perspective of the type 3 LSA created by ABR (R4) for the 10.56.1.0/24 network.
- R3 does not know if the 10.56.1.0/24 network is directly attached to the ABR (R4) or multiple hops away.
- R3 knows that its metric to the ABR (R4) is 65 and that the type 3 LSA already has a metric of 2, so its total path metric to reach the 10.56.1.0/24 network is 67.
 Other useful information:
Other useful information:
- Full ENCOR Course
- CCNP Enterprise Certificate Information
- 350-401 ENCOR Exam Questions and Solutions
- 350-401 ENCOR Exam Topics