
Additional Spanning Tree Protection Mechanisms
protection mechanisms such as root guard, BPDU guard, and STP loop guard.
- A network forwarding loop occurs when there are multiple active paths between two devices. Broadcast and multicast traffic are forwarded out every switch port continuing the forwarding loop.
- The network’s throughput is drastically effected as the switches are processing numerous frames.
- The switches CPU utilization will be high and memory space will be consumed. The switches might crash and users will likely notice the impact on the network.
Additional Spanning Tree Protection Mechanisms
Common issues for Layer 2 forwarding loops:
- STP is disabled on a switch.
- A load balancer is misconfigured and sends traffic out multiple ports with the same MAC address.
- A virtual switch that bridges two physical ports.
- End users using an unmanaged switch or hub.
Root Guard
Root guard is an STP feature that prevents a configured port from becoming a root port.
- It does this by placing the port in an ErrDisabled state if a superior BDPU is received on that port.
- Root guard placed on designated ports towards other switches that should never become root bridges.
- Root guard is enabled on a port-by-port basis.
Use the spanning-tree guard root to enable root guard.
STP Portfast
- disables the topology notification (TCN) generation and causes access ports that come up to bypass the learning and listening states and enter the forwarding state immediately. If a BPDU is received on a portfast-enabled port, the portfast functionality is removed from that port.
| Command | Description |
| spanning-tree portfast | Interface command to enable portfast on aspecific access port |
| spanning-tree portfast default | Global command to enable portfast on allaccess ports |
| spanning-tree portfast disable | Disable portfast on a port |
| spanning-tree portfast trunk | Command used on trunk links to enableportfast*This command should only be used withports connected to a single host. |
STP Portfast Examples

BPDU Guard
BPDU guard is a safety mechanism that shuts down ports configured with STP portfast upon receiving a BPDU.
| Command | Description |
| spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default | Global command to enable BPDU guard on all STP portfast ports |
| spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default{enable | disable} | Interface command to enables or disable BPDUguard on a specific interface |
| show spanning-tree interface interface-id detail | Displays whether BPDU guard is enabled for thespecified interface |
Note: BPDU Guard is typically configured with all host-facing ports that are enabled with portfast.
BPDU Guard Examples
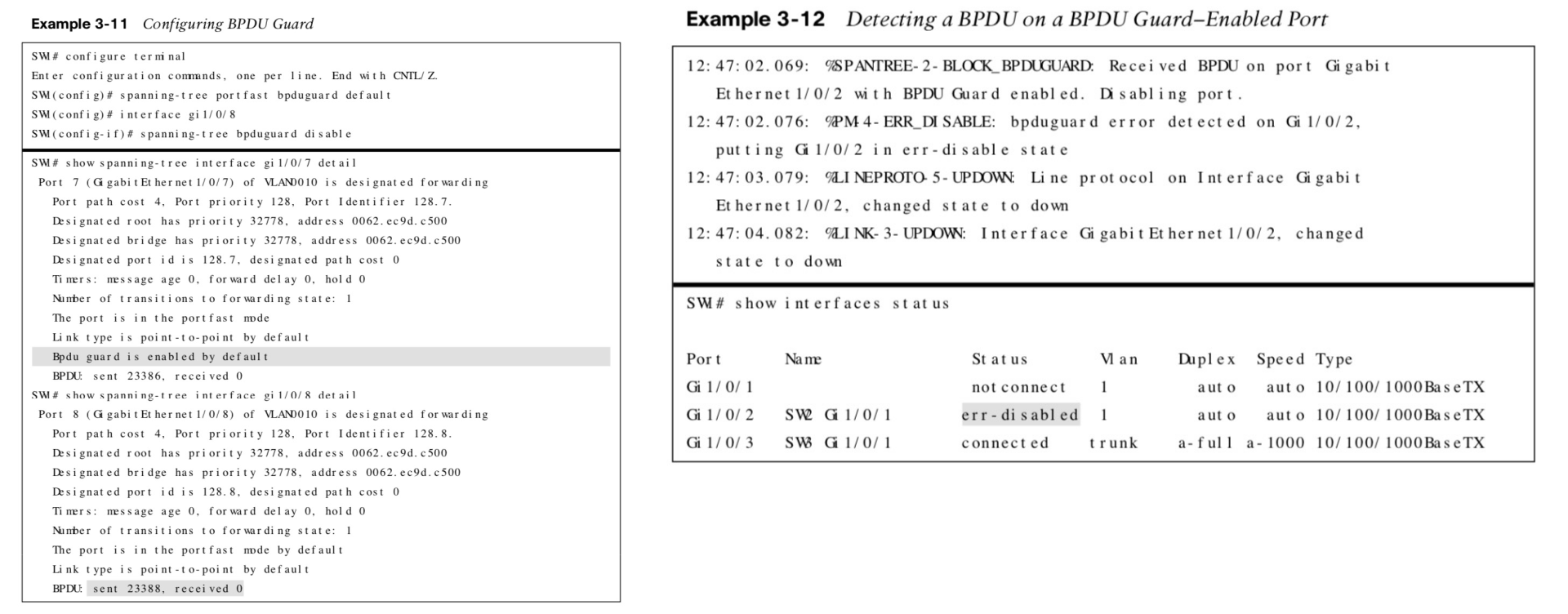
BPDU Guard Error Recovery
The Error Recovery service can be used to reactivate ports that are shut down. Ports that are put into the ErrDisabled mode due to BPDU guard do not automatically restore themselves.
| Command | Description |
| errdisable recovery cause bpduguard | Recovers ports shutdown by BPDUguard |
| errdisable recovery interval time-seconds | The period that Error Recovery checks |
BPDU Guard Error Recovery Example
 Note: The Error Recovery service operates every 300 seconds (5 minutes). This can be changed from 5 to 86,000 seconds with the global command errdisable recovery interval time
Note: The Error Recovery service operates every 300 seconds (5 minutes). This can be changed from 5 to 86,000 seconds with the global command errdisable recovery interval time
BPDU Filter
BPDU filter blocks BPDUs from being transmitted out of a port. It can be enabled globally or on a specific interface.
Global BPDU filter:
spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default With the global BPDU configuration the port sends a series of 10 – 12 BPDUs. If the switch receives any BPDUs, it checks to identify which switch is more preferred.
- The preferred switch doesn’t process any BPDUs but still passes them along to inferior switches.
- A non-preferred switch processes the BPDUs that are received but doesn’t transmit any BPDUs to superior switches.
Interface-specific BPDU filter:
Spanning-tree bpdufilter enable With the interface-specific BPDU configuration the port does not send any BPDUs on an ongoing basis. If the remote port has BPDU guard, that generally shuts down the port as a loop prevention mechanism.
Verifying a BPDU Filter

Problems with Unidirectional Links
Network devices that utilize fiber-optic cables for connectivity can encounter unidirectional traffic flows if one strand is broken. BPDUs will not able to be transmitted causing other switches on the network to eventually time out the existing root port and change root ports resulting in a forwarding loop. Two solutions to problems with unidirectional links:
- STP LoopGuard
- Unidirectional Link Detection
Loop Guard
- Prevents any alternative or root ports from becoming designated ports due to loss of BPDUs on the root port. Loop guard places the original port into an ErrDisabled while BPDUs are not being received and transitions back through the STP states when it begins receiving BPDUs again.
| Command | Description |
| spanning-tree loopguard default | Global command to enable loop guard |
| spanning-tree guard loop | Interface command to enable loop guard |
| show spanning-tree inconsistent-ports | Shows ports in the inconsistent state due to the portnot receiving BPDUs |
Note: Loop guard shouldn’t be enabled on portfast- enabled ports because it directly conflicts with root/alternate port logic
STP Loop Guard Examples
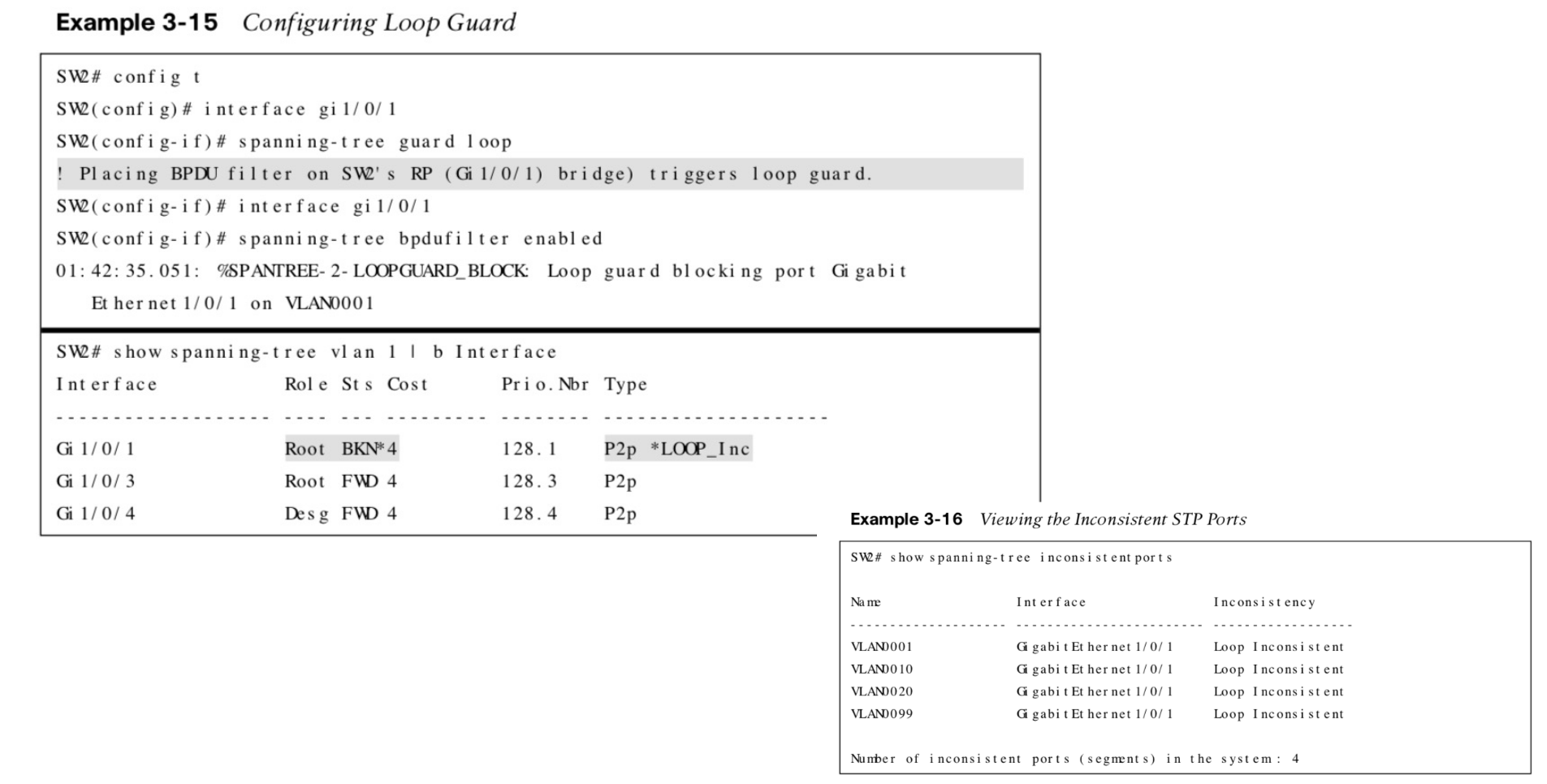
Unidirectional Link Detection
Allows for the bidirectional monitoring of fiber-optic cables. UDLD operates in two modes:
- Normal – If a frame not acknowledged, the link considered undetermined and the port remains active.
- Aggressive – If a frame is not acknowledged, the switch sends another 8 packets in 1 second intervals. If those packets aren’t acknowledged, the port is placed into an error state.
UDLD Commands
| Command | Description |
| udld enable [aggressive] | Global command to enable UDLD. *Optionalaggressive keyword sets the mode to aggressive. |
| udld port [aggressive] | Interface command to enable UDLD *Optionalaggressive keyword sets the mode to aggressive. |
| udld port disable | Disable UDLD on a specific interface |
| udld recovery [interval time] | Enables UDLD recovery. The time default value is 5minutes. |
| show udld neighbors | Displays the status of UDLD neighborship |
| ushow udld interface-id | Displays detailed information about UDLD |
Configuring & Verifying UDLD Examples
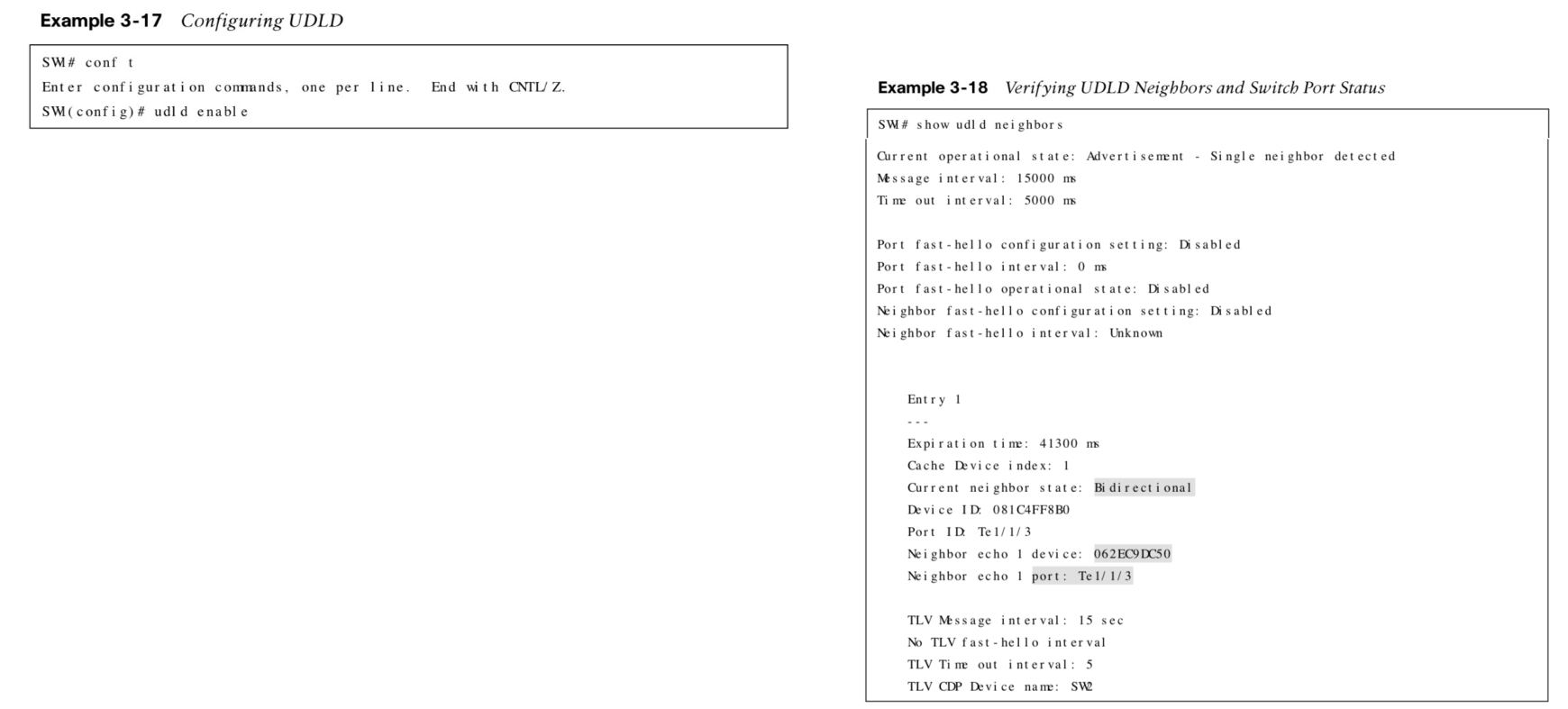
Other useful information: