vSphere Storage Concepts
Learner Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Recognize vSphere storage technologies
- Identify types of datastores
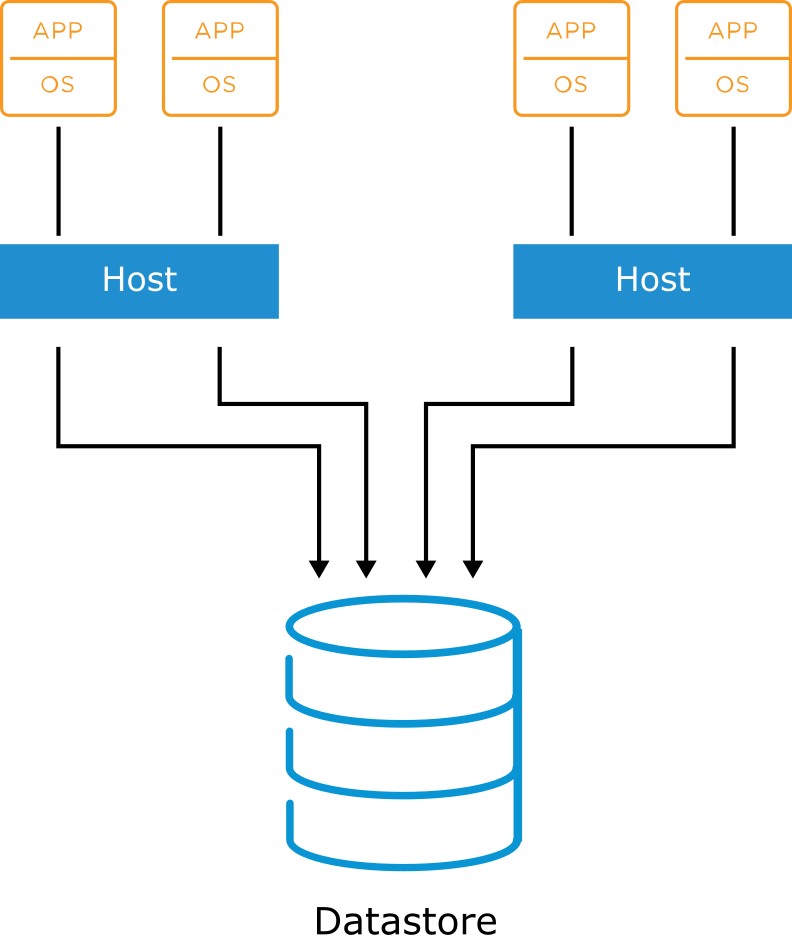
About Datastores

A datastore is a logical storage unit that can use disk space on one physical device or span several physical devices.
Datastores are used to hold VM files, VM templates, and ISO images.
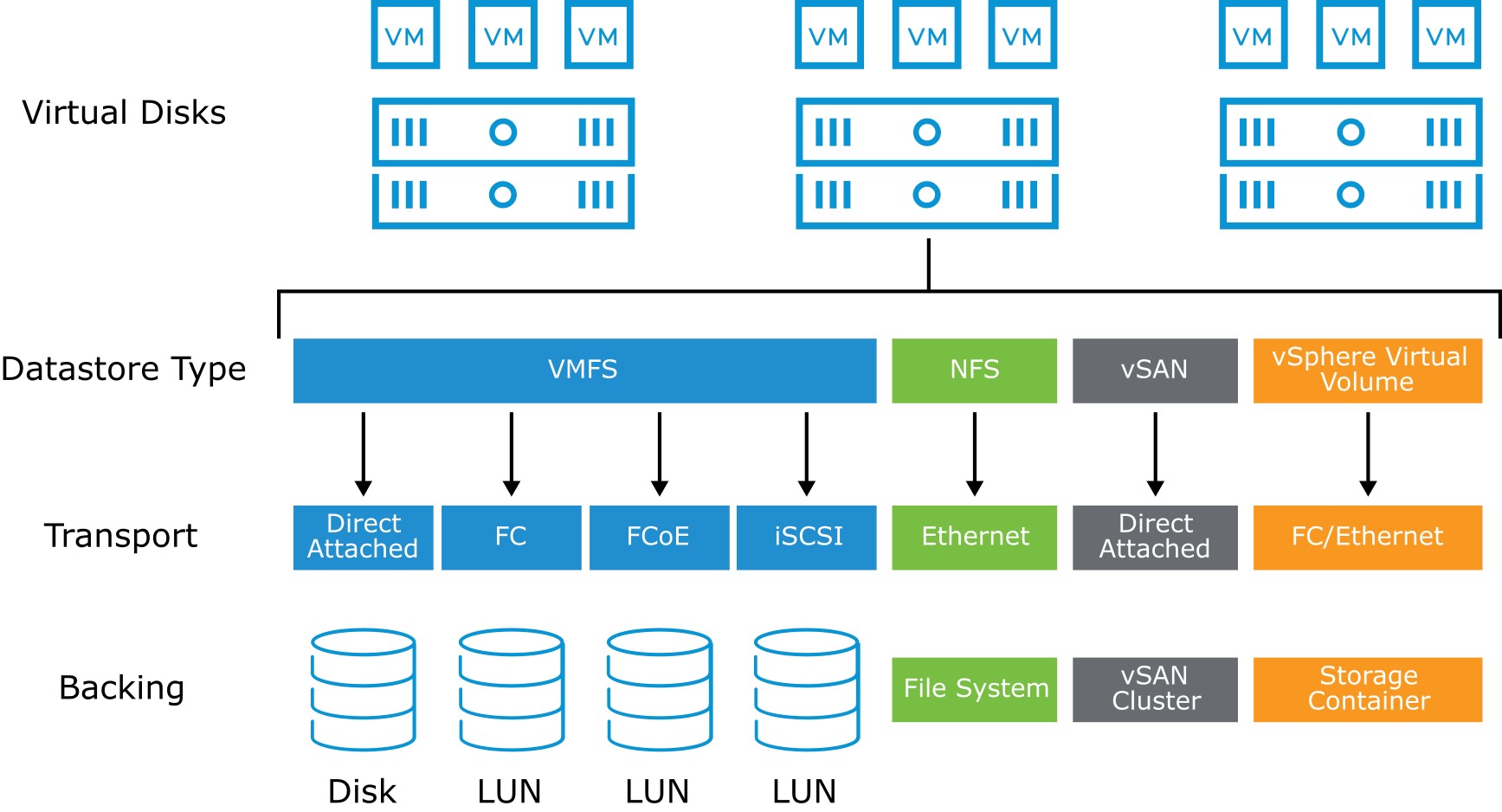
vSphere supports the following types of datastores:
- VMFS
- NFS
- vSAN
- vSphere Virtual Volumes
Storage Overview
ESXi hosts should be configured with shared access to datastores.
Storage Protocol Overview
Each datastore uses a protocol with varying support features.
| Datastore Type | Storage Protocol | Boot from SAN Support | vSphere vMotion Support | vSphere HA Support | vSphere DRS Support |
| VMFS | Fibre Channel | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| FCoE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| iSCSI | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| iSER/NVMe-oF (RDMA) | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| DAS (SAS, SATA, NVMe) | N/A | Yes* | No | No | |
| NFS | NFS | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| vSphere Virtual Volumes | FC/Ethernet (iSCSI, NFS) | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| vSAN Datastore | vSAN | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
About VMFS
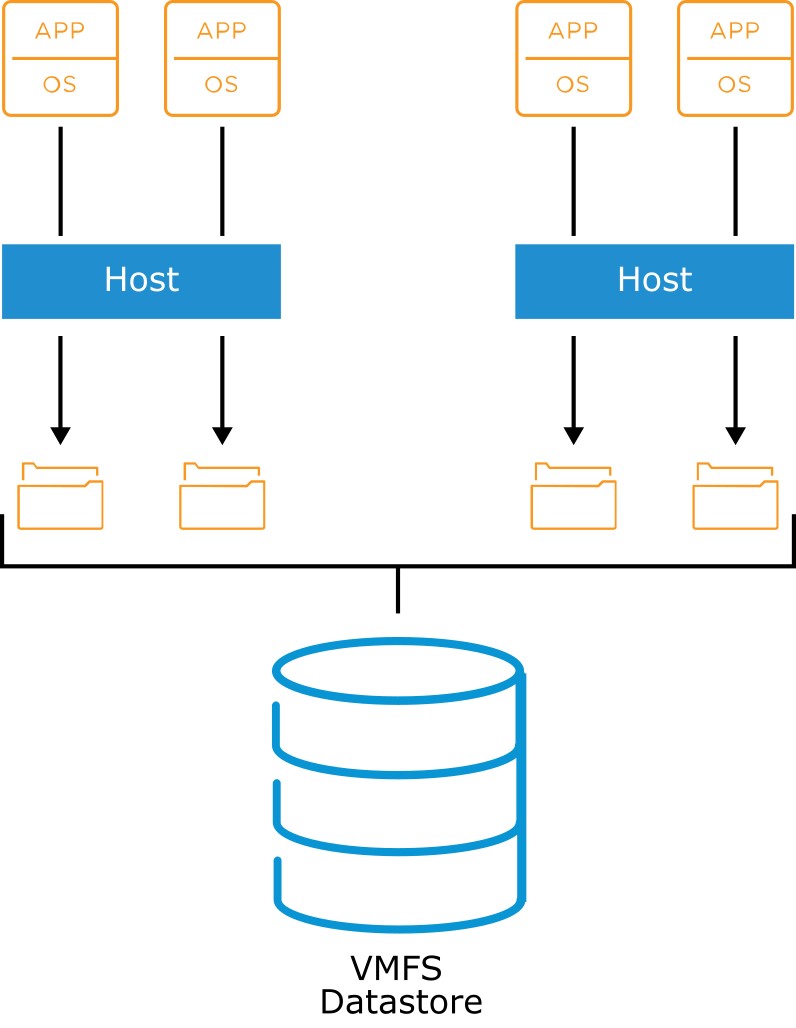
- ESXi hosts support VMFS5 and VMFS6:
- Features supported by both VMFS5 and VMFS6:
- Concurrent access to shared storage
- Dynamic expansion
- On-disk locking
- Features supported by VMFS6:
-
- 4K native storage devices
- Automatic space reclamation
About NFS
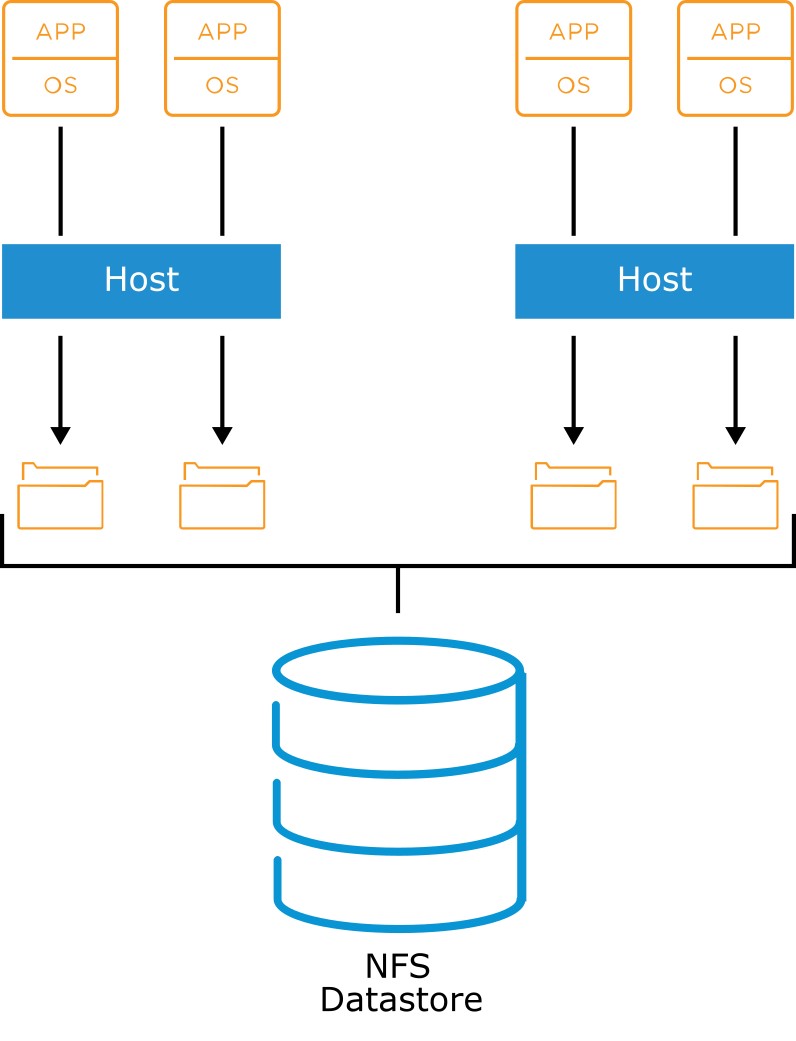
- NFS is a file-sharing protocol that ESXi hosts use to communicate with a networkattached storage (NAS) device. NFS supports NFS 3 and 4.1 over TCP/IP.
About vSAN
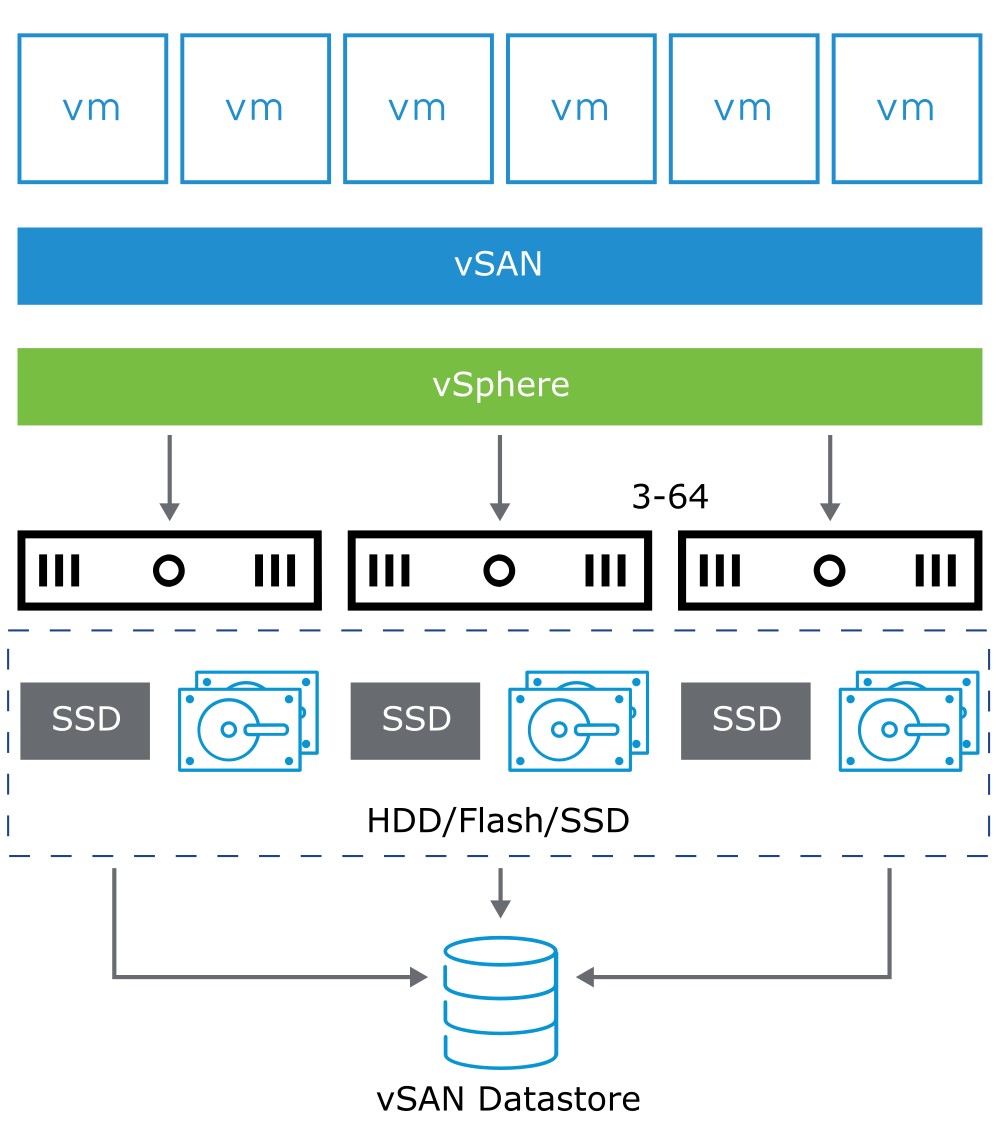
- vSAN is hypervisor-converged, softwaredefined storage for virtual environments that does not use traditional external storage.
- By clustering host-attached hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs), vSAN creates an aggregated datastore shared by VMs.
About vSphere Virtual Volumes
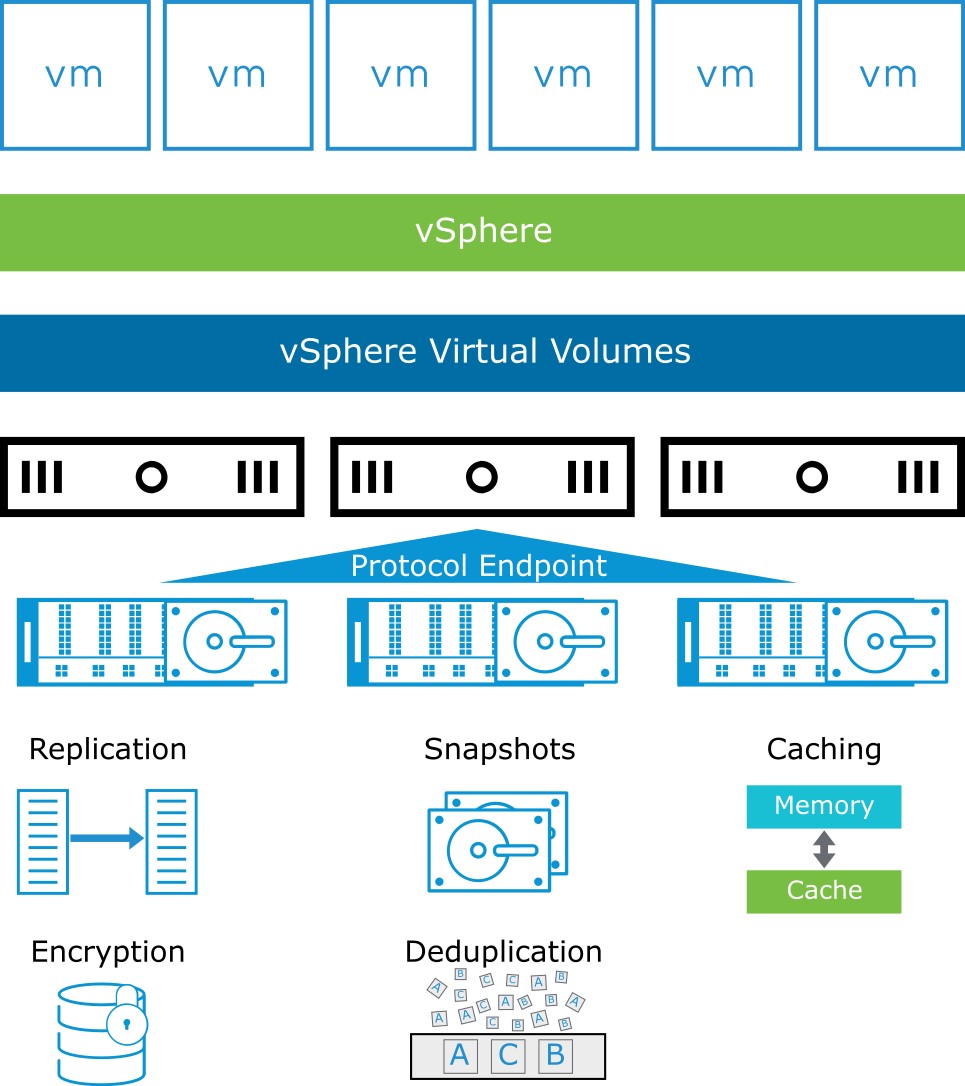
vSphere Virtual Volumes provides several functionalities:
- Native representation of VMDKs on SAN/NAS: No LUNs or volume management
- Works with existing SAN/NAS systems
- A new control path for data operations at the VM and VMDK level
- Snapshots, replications, and other operations at the VM level on external storage
- Automates control of per-VM service levels by using storage policies
- Standard access to storage with the vSphere API for Storage Awareness protocol endpoint
- Storage containers that span an entire array
About Raw Device Mapping
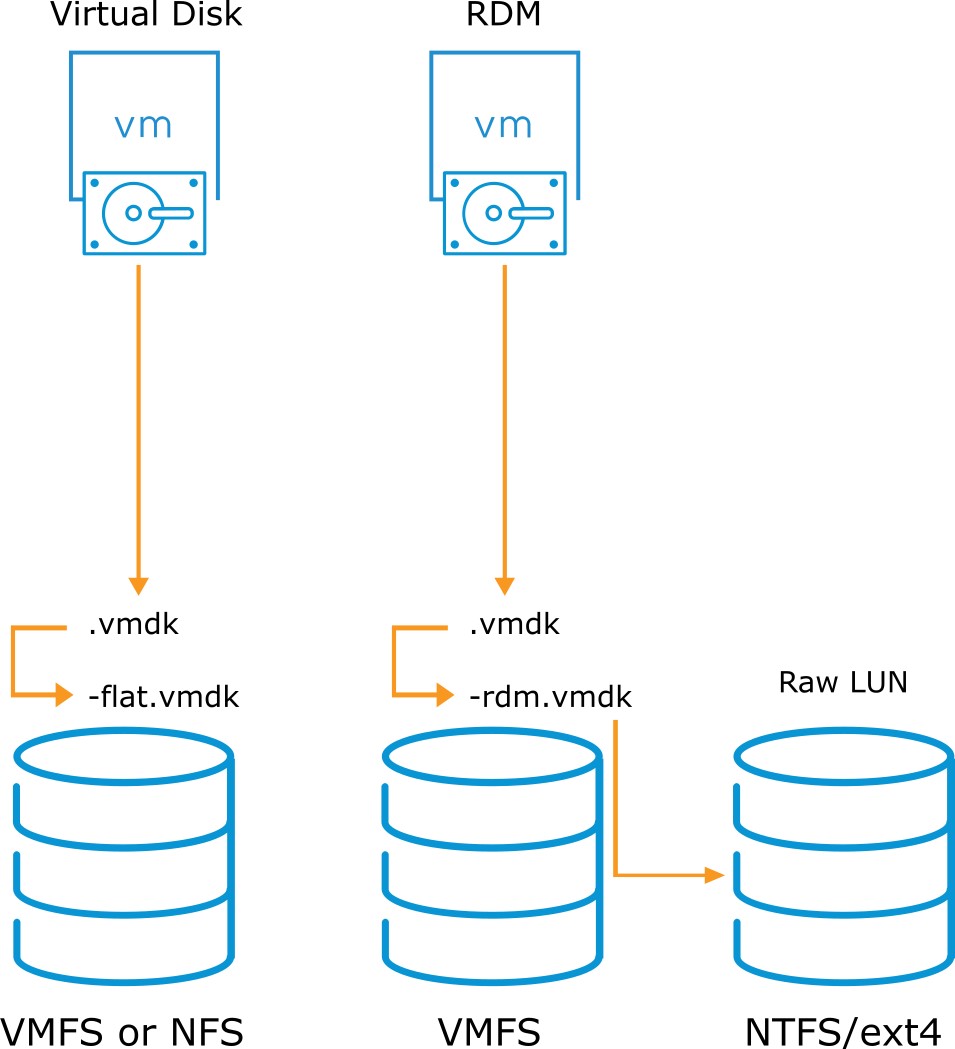
- Although not a datastore, raw device mapping (RDM) gives a VM direct access to a physical LUN.
- The mapping file (-rdm.vmdk) that points a VM to a LUN must be stored on a VMFS datastore.
Physical Storage Considerations
Before implementing your vSphere environment, discuss the storage needs with your storage administration team. Consider the following factors:
- LUN sizes
- I/O bandwidth required by your applications
- I/O requests per second that a LUN is capable of
- Disk cache parameters
- Zoning and masking
- Multipathing setting for your storage arrays (active-active or active-passive) • Export properties for NFS datastores
Review of Learner Objectives
After completing this vSphere Storage Concepts lesson, you should be able to meet the following objectives:
- Recognize vSphere storage technologies
- Identify types of datastores