VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
- Cisco created the proprietary protocol VTP to reduce the burden of provisioning VLANs on switches.
- Switches that participate in the same VTP domain can have a VLAN created once on a VTP server and propagated to other VTP client switches in the same VTP domain.
The Roles of VTP
| VTP Roles | Description |
| Server | responsible for the creation, modification, and deletion of VLANs within the VTP domain. |
| Client | receives VTP advertisements and modifies the VLANs on that switch.VLANs cannot be configured locally on a VTP client. |
| Transparent | receive and forward VTP advertisements but do not modify the local VLAN database. VLANs configured only locally. |
| Off | A switch does not participate in VTP advertisements and does not forward them out of any ports either. VLANs are configured only locally. |
The Versions of VTP
There are three versions of VTP:
- Version 1 is default.
- Versions 1 and 2 have limited propagation to VLANs numbered 1 to 1005.
- VTP Version 3 allows for the full range of VLANs 1 to 4094.
VTP supports having multiple VTP servers in a domain. These servers process updates from other VTP servers just as a client does. If a VTP domain is Version 3, the primary VTP server must be set with the executive command vtp primary.
VTP Communication
VTP advertises updates by using a multicast address across the trunk links for advertising updates to all the switches in the VTP domain. The three main types of VTP advertisements:
| Communication Types | Description |
| Summary | This advertisement occurs every 300 seconds or when a VLAN is added,removed, or changed. It includes the VTP version, domain, configurationrevision number, and time stamp. |
| Subset | This advertisement occurs after a VLAN configuration change occurs. Itcontains all the relevant information for the switches to make changes to theVLANs on them. |
| Client Requests | This advertisement is a request by a client to receive the more detailed subsetadvertisement. This occurs when a switch with a lower revision number joinsthe VTP domain and observes a summary advertisement with a higher revisionthan it has stored locally. |
VTP Configuration
| Terms | Description |
| Step 1 | Define the VTP version with the command vtp version {1 | 2 | 3}. |
| Step 2 | Define the VTP domain with the command vtp domain domain-name.Changing the VTP domain resets the local switch’s version to 0. |
| Step 3 | Define the VTP switch role with the commandvtp mode { server | client | transparent | none } |
| Step 4 | (Optional) Secure the VTP domain with the command vtp password password (This step is optional but recommended because it helps preventunauthorized switches from joining the VTP domain.) |
VTP Configuration Example

VTP Verification
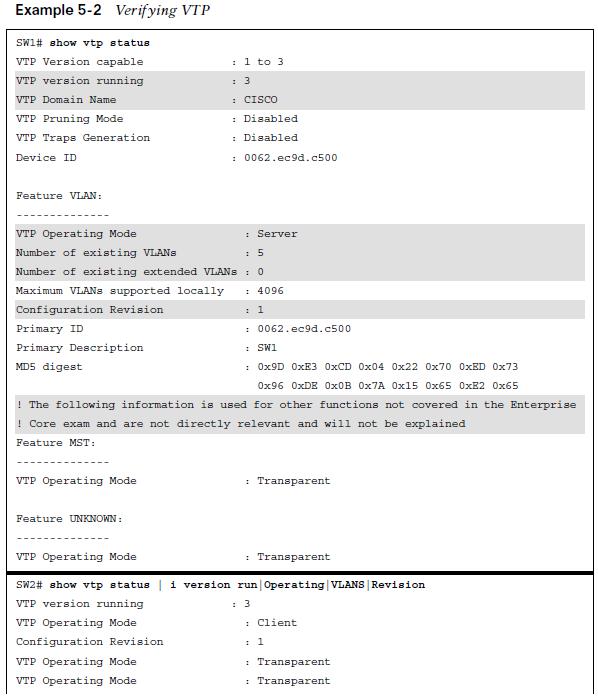
The most important information displayed is the VTP version, VTP domain name, VTP mode, the number of VLANs (standard and extended), configuration version.
VTP Verification
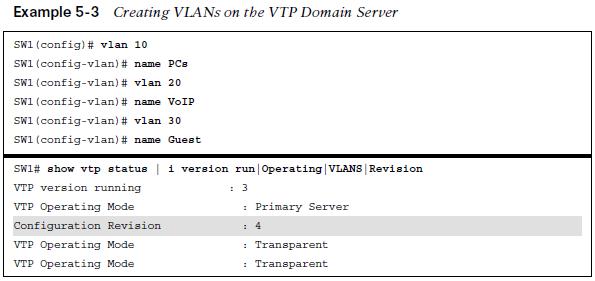
It is very important that every switch that connects to a VTP domain has the VTP revision number reset to 0. Failing to reset the revision number on a switch could result in theswitch providing an update to the VTP server. This is not an issue if VLANs are added but is catastrophic if VLANs are removed because those VLANs will be removed throughout the domain.
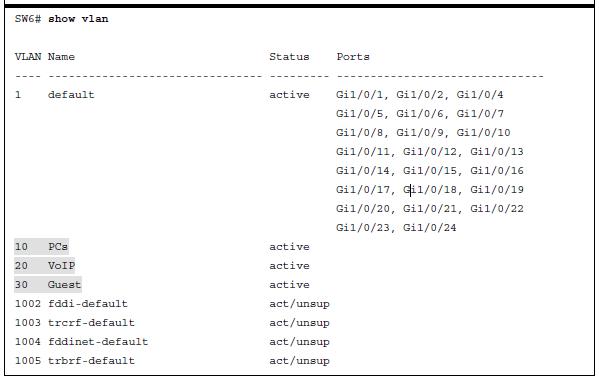
Other useful information: