About Lesson
Spanning Tree Topology Tuning
some of the options for modifying the root bridge location or moving blocking ports to designated ports.
- In a properly designed network a switch is deliberately selected to become the root bridge and the designated and alternate ports are modified.
- Network design considerations factor in hardware platform, resiliency, and network topology.
Root Bridge Placement
To ensure root bridge placement set the system priority on:
- The root bridge to the lowest value
- The secondary root bridge to a value slightly higher than that of the root bridge
- All other switches to a value higher than the secondary root bridge
| Command | Description |
| spanning-tree vlan vlan-id priority priority | The priority is a value between 0 and 61,440, in increments of 4,096. |
| spanning-tree vlan vlan-id root {primary | secondary} [diameter diameter] | The primary keyword sets the priority to 24,576, and the secondary sets the priorityto 28,672. The optional diameter commandmakes it possible to tune STP convergenceand modifies the timers. |
Configuring the Root Bridge

- The initial priority for VLAN 1 on SW1 verified, 32,769.
- SW1 is configured to be the primary root for VLAN 1
- The priority is verified again to ensure the change took place.
Configuring the Backup Root Bridge
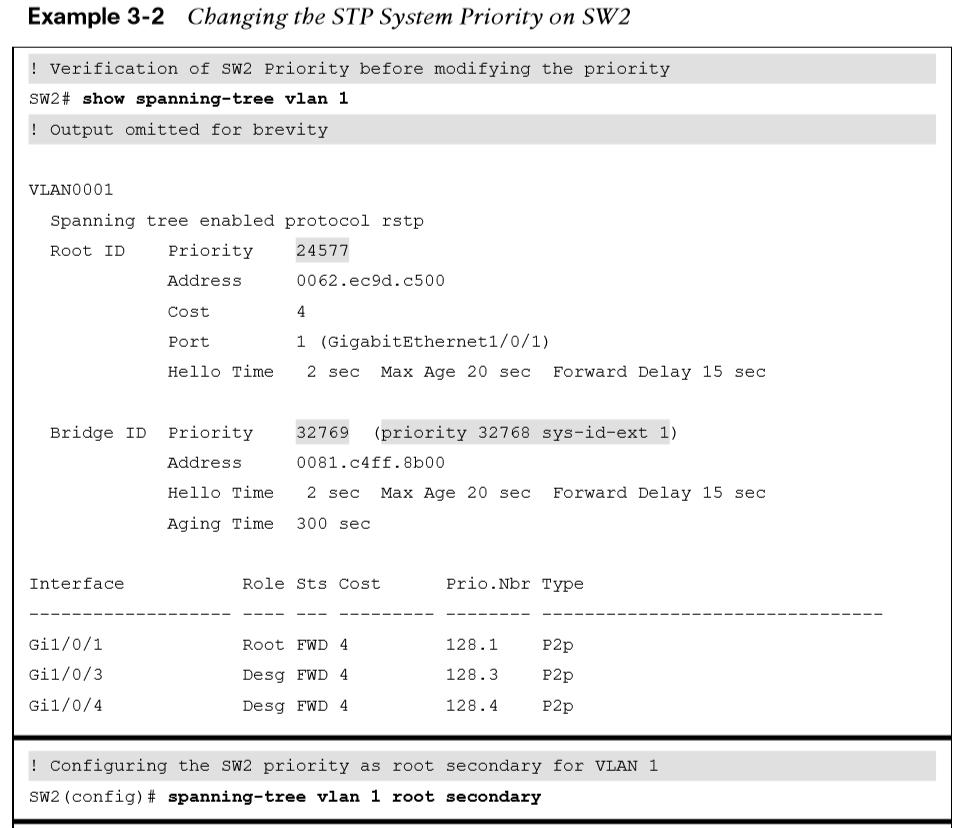
- The initial priority for VLAN 1 on SW2 is verified, 32,769.
- SW2 configured to be the secondary root
- The priority is verified again to ensure the change took place.
Modifying STP Root Port & Blocked Switch Port Locations

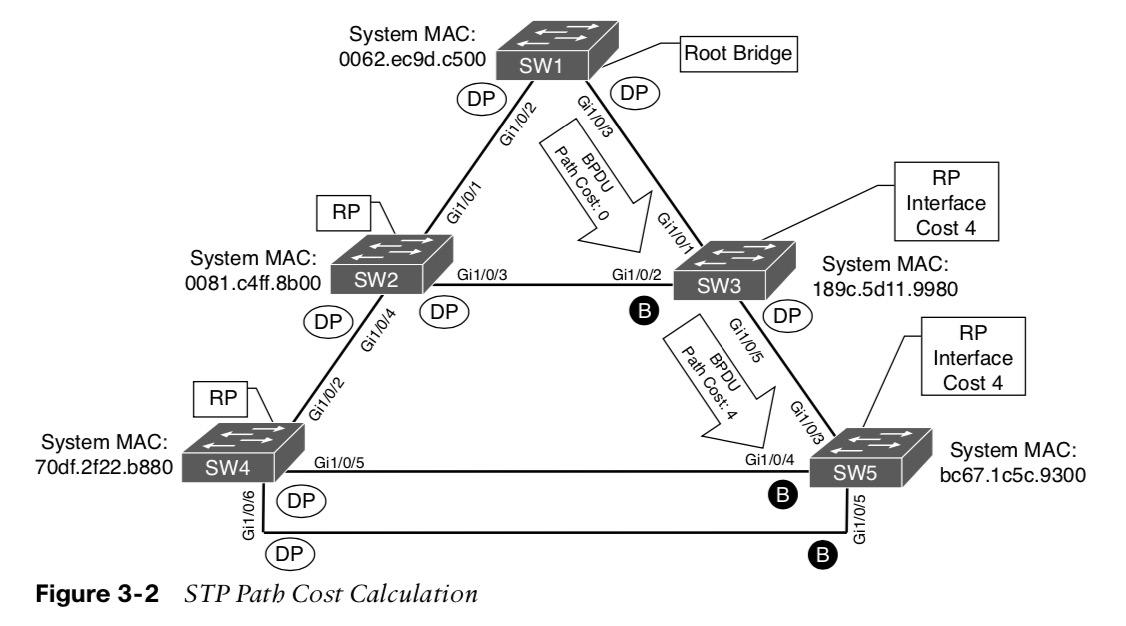
Calculating total path cost to the root bridge:
- SW1 sends a BPDU to SW3 with the path cost of 0.
- SW3 receives the BPDU and adds its root port cost (4) to cost from the BPDU (0), resulting in the cost of 4.
- SW3 sends a BPDU to SW5 with the path cost of 4.
- SW5 receives the BPDU and adds its root port cost (4) to the cost from the BPDU (4), resulting in the cost of 8 for SW5 to reach the root bridge.
Verifying the Total Path Cost
The example highlights the total path cost to the root bridge from SW3 and SW5. 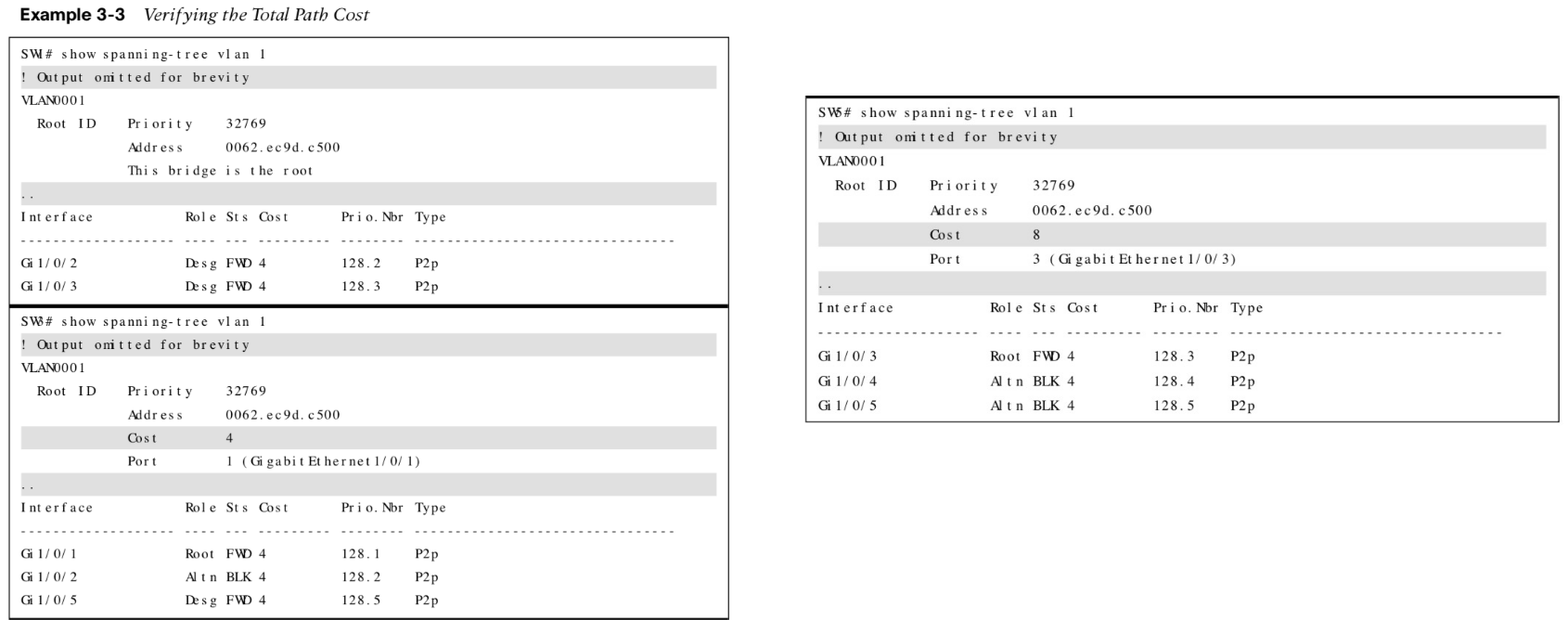 Note: There is not a total path cost in SW1’s output
Note: There is not a total path cost in SW1’s output
Modifying STP Port Cost
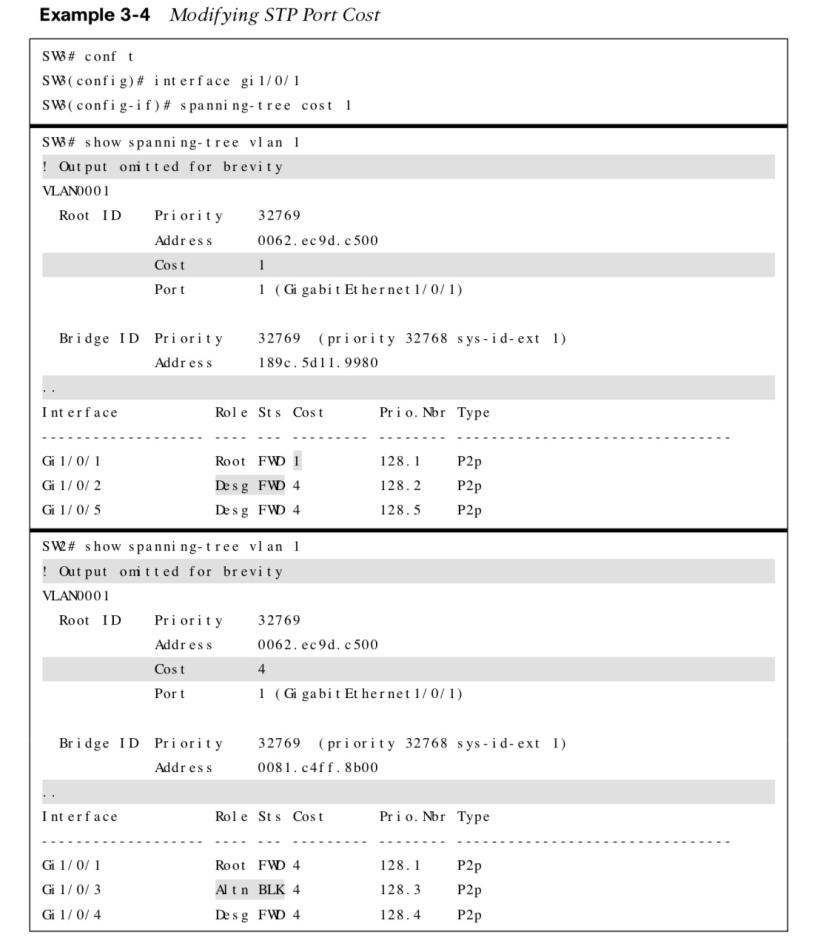
- The spanning tree [vlan vlan-id] cost cost command can be used to modify the STP forwarding path.
- Using the spanning tree command will modify the cost for all VLANs unless the optional vlan keyword is used.
Modifying STP Port Priority
STP port priority influences which port becomes the alternate port when multiple links are used between switches. Use the command spanning -tree [vlan vlan-id] port-priority priority to change the STP port priority on a switch’s interface. 
Other useful information:
Join the conversation