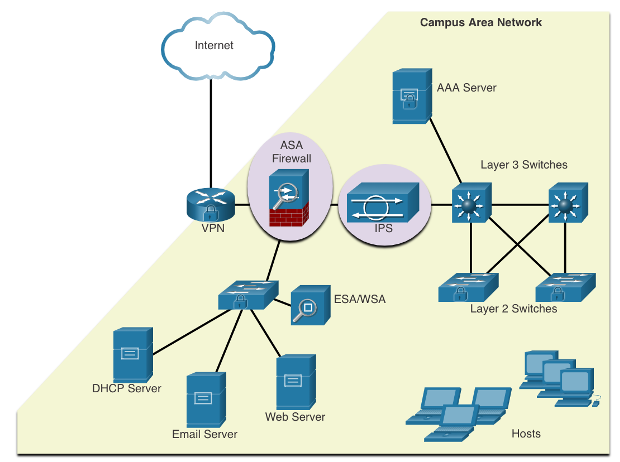
About Lesson
Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
Explain why basic security measures are necessary on network devices.
Types of Threats
- Attacks on a network can be devastating and can result in a loss of time and money due to damage, or theft of important information or assets. Intruders can gain access to a network through software vulnerabilities, hardware attacks, or through guessing someone’s username and password. Intruders who gain access by modifying software or exploiting software vulnerabilities are called threat actors.
- After the threat actor gains access to the network, four types of threats may arise:
-
- Information Theft
- Data Loss and manipulation
- Identity Theft
- Disruption of Service
Types of Vulnerabilities
- Vulnerability is the degree of weakness in a network or a device.
- Some degree of vulnerability is inherent in routers, switches, desktops, servers, and even security devices.
- Typically, the network devices under attack are the endpoints, such as servers and desktop computers.
- There are three primary vulnerabilities or weaknesses:
-
- Technological Vulnerabilities might include TCP/IP Protocol weaknesses, Operating System Weaknesses, and Network Equipment weaknesses.
- Configuration Vulnerabilities might include unsecured user accounts, system accounts with easily guessed passwords, misconfigured internet services, unsecure default settings, and misconfigured network equipment.
- Security Policy Vulnerabilities might include lack of a written security policy, politics, lack of authentication continuity, logical access controls not applied, software and hardware installation and changes not following policy, and a nonexistent disaster recovery plan.
- All three of these sources of vulnerabilities can leave a network or device open to various attacks, including malicious code attacks and network attacks.
Physical Security
- If network resources can be physically compromised, a threat actor can deny the use of network resources.
- The four classes of physical threats are as follows:
-
- Hardware threats – This includes physical damage to servers, routers, switches, cabling plant, and workstations.
- Environmental threats – This includes temperature extremes (too hot or too cold) or humidity extremes (too wet or too dry).
- Electrical threats – This includes voltage spikes, insufficient supply voltage (brownouts), unconditioned power (noise), and total power loss.
- Maintenance threats – This includes poor handling of key electrical components (electrostatic discharge), lack of critical spare parts, poor cabling, and poor labeling.
- A good plan for physical security must be created and implemented to address these issues.
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
|---|---|
| Security Threats and Vulnerabilities | Explain why basic security measures are necessary on network devices. |
| Network Attacks | Identify security vulnerabilities. |
| Network Attack Mitigation | Identify general mitigation techniques. |
| Device Security | Configure network devices with device hardening features to mitigate security threats. |
Other useful information
Join the conversation