About Lesson
Binary Number System
Calculate numbers between decimal and binary systems.
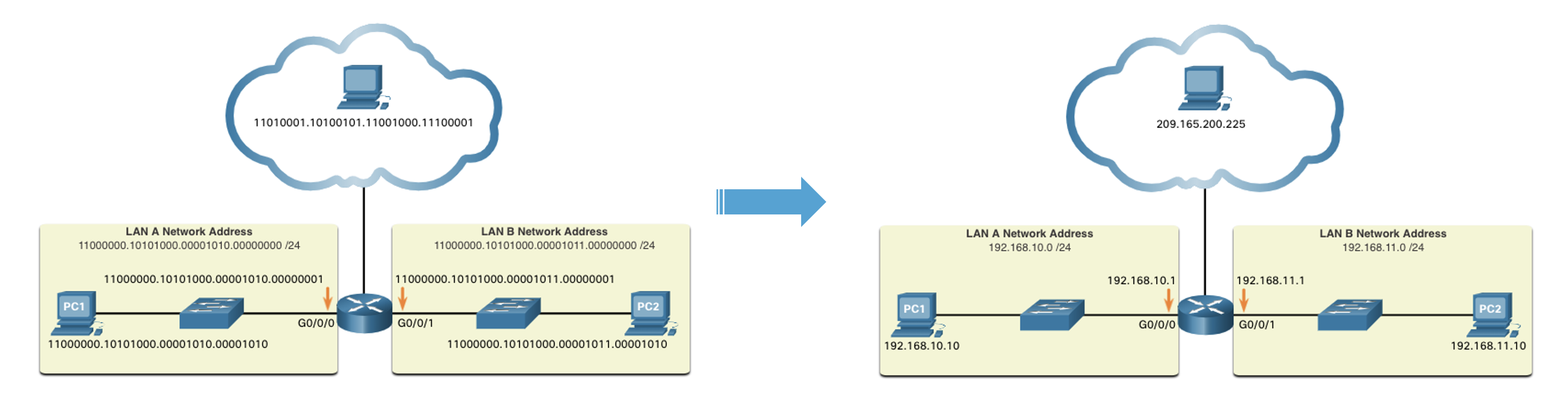
Binary and IPv4 Addresses
- Binary numbering system consists of 1s and 0s, called bits
- Decimal numbering system consists of digits 0 through 9
- Hosts, servers, and network equipment using binary addressing to identify each other.
- Each address is made up of a string of 32 bits, divided into four sections called octets.
- Each octet contains 8 bits (or 1 byte) separated by a dot.
- For ease of use by people, this dotted notation is converted to dotted decimal.
Binary Positional Notation
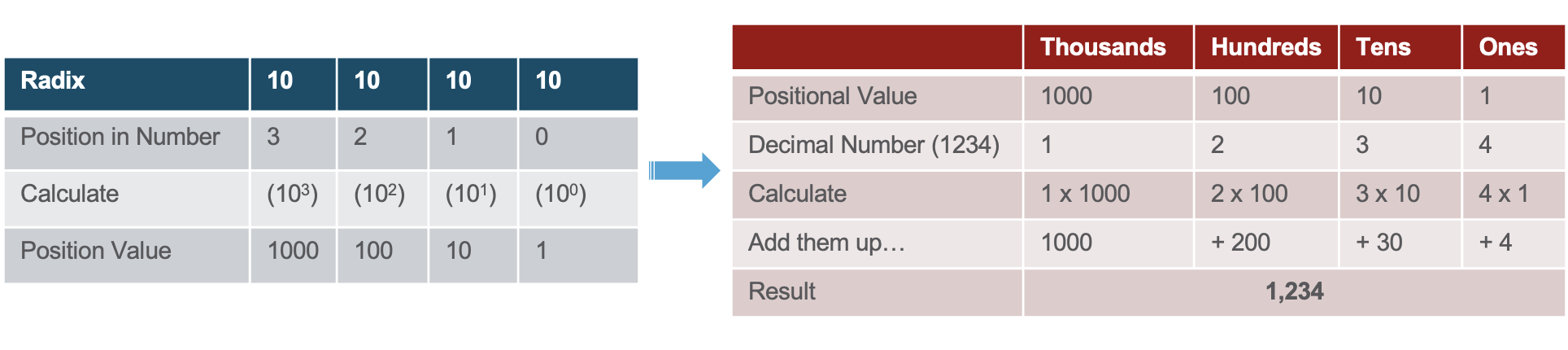
- Positional notation means that a digit represents different values depending on the “position” the digit occupies in the sequence of numbers.
- The decimal positional notation system operates as shown in the tables below.
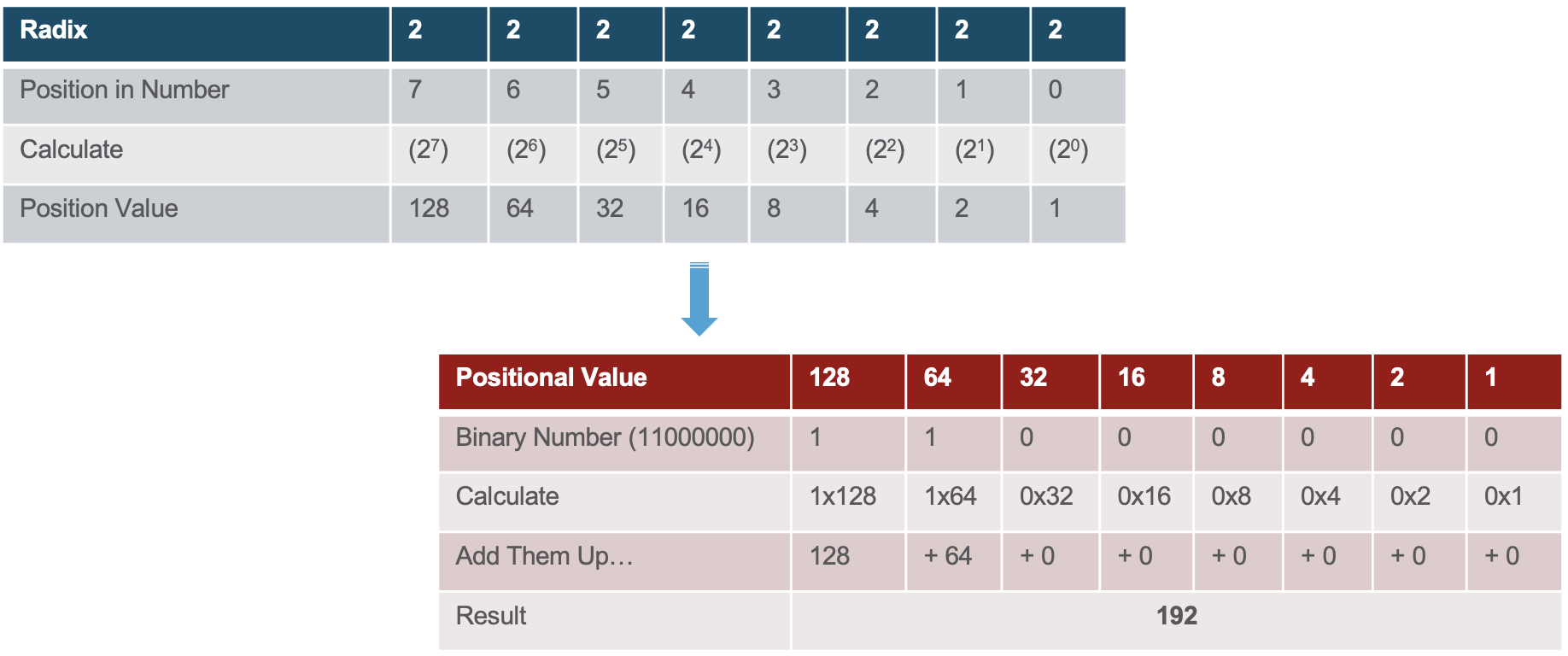
- The binary positional notation system operates as shown in the tables below.
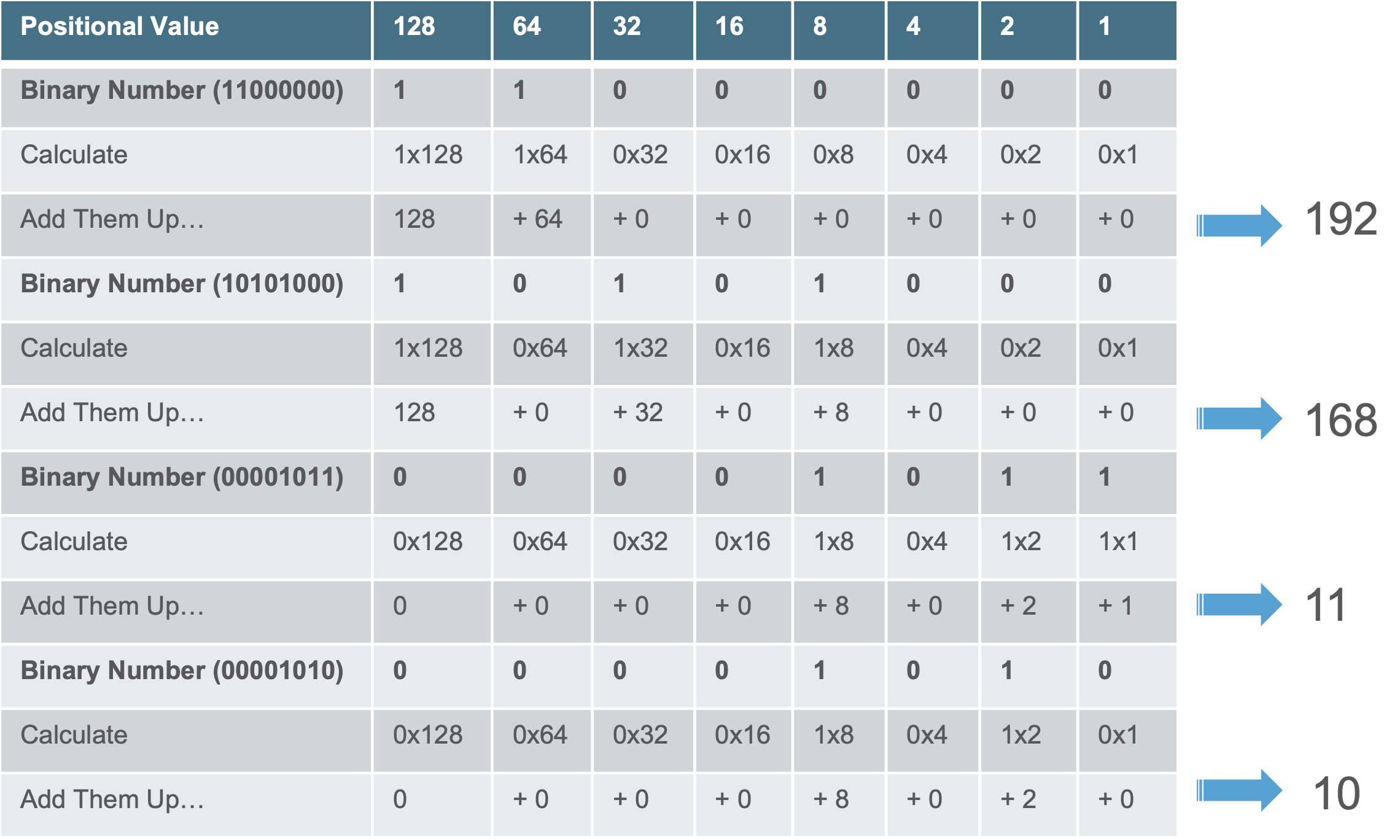
Convert Binary to Decimal
- Example: Convert 11000000.10101000.00001011.00001010 to decimal.
 => 192.168.11.10
=> 192.168.11.10
Decimal to Binary Conversion
The binary positional value table is useful in converting a dotted decimal IPv4 address to binary. 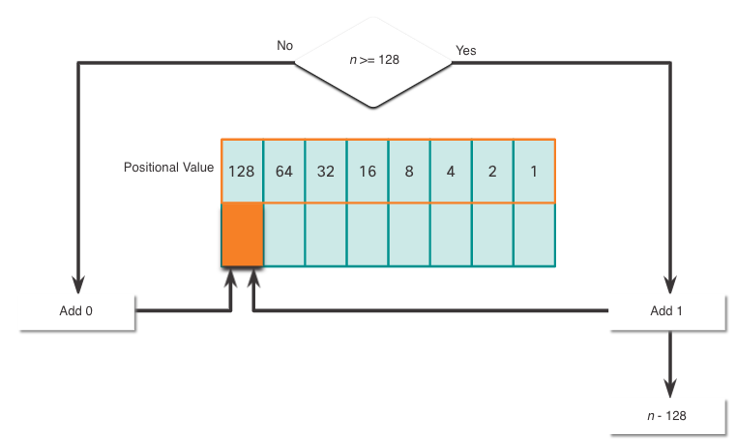
- Start in the 128 position (the most significant bit). Is the decimal number of the octet (n) equal to or greater than 128?
- If no, record a binary 0 in the 128 positional value and move to the 64 positional value.
- If yes, record a binary 1 in the 128 positional value, subtract 128 from the decimal number, and move to the 64 positional value.
- Repeat these steps through the 1 positional value.
Decimal to Binary Conversion Example
Example: Convert decimal 168 to binary
- Is 168 > 128? Yes, enter 1 in 128 position and subtract 128 (168-128=40)
- Is 40 > 64? No, enter 0 in 64 position and move on
- Is 40 > 32? Yes, enter 1 in 32 position and subtract 32 (40-32=8)
- Is 8 > 16? No, enter 0 in 16 position and move on Is 8 > 8? Equal.
- Enter 1 in 8 position and subtract 8 (8-8=0) No values left.
- Enter 0 in remaining binary positions
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Decimal 168 is written as 10101000 in binary
IPv4 Addresses
Routers and computers only understand binary, while humans work in decimal. It is important for you to gain a thorough understanding of these two numbering systems and how they are used in networking. 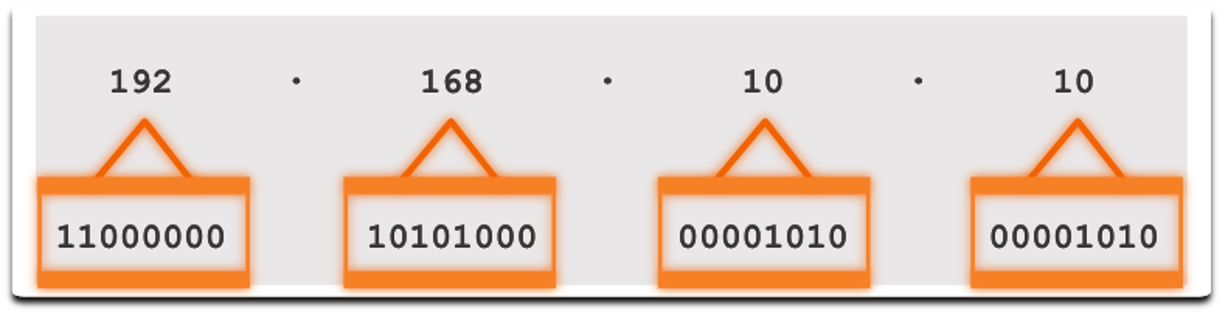
Other related topics
| Topic Title | Topic Objective |
|---|---|
| Binary Number System | Calculate numbers between decimal and binary systems. |
| Hexadecimal Number System | Calculate numbers between decimal and hexadecimal systems. |
Other useful information
- Full CCNA Course
- CCNA Certificate Information
- 200-301 CCNA Exam Questions and Solutions
- 200-301 CCNA Exam Topics
Join the conversation